Detailed explanation of coffee producing areas in Honduras
Honduras is located in the north of Central America, facing the Caribbean Sea to the north, the Gulf of Fonseca in the Pacific Ocean to the south, Nicaragua and El Salvador to the east and south, and Guatemala to the west, mostly mountains and plateaus. It covers an area of 112492 square kilometers and the coastline is about 1033 kilometers long. The whole territory, except the coastal plain, is mountainous, with the highest elevation of 3000 meters in the northwest and more than 2400 meters in the south.
The main rivers in the territory are the Koko River, the Patuca River and the Wulu River. Rivers from inland mountains crisscross and flow into the two oceans. Many basins and river valleys are formed between the various mountain ranges. The larger basins are the Siria and Rapagu Alai basins, and the main river valleys are the Komayagua and Hamastland River valleys.
Coastal islands are dotted with the main islands being the Baya Islands and the Tigris Islands in the Gulf of Fonseca. The terrain of Honduras is complex and the climate is diversified. Located in the coastal plain of Central America, it has a tropical rain forest climate, with an average annual temperature of 31 ℃. The mountain belongs to subtropical forest climate, the annual average temperature is 23 ℃, the rainy season is from June to November, the temperature is mild and the rainfall is abundant, so it is an ideal place for coffee growth.
Honduras produces two kinds of coffee of very good quality, which are highly respected by coffee lovers. One is the "Highland Coffee", which is grown at an altitude of 1000 Mueller 1500 Michael, and the other is the "selected Highland Coffee", which represents the highest level of Honduran coffee, which is grown at an altitude of 1500 Murray 200 meters. Most of the Honduran coffee is exported to the United States and Germany.
The timeline of coffee cultivation
Although there is no exact information on when coffee was first grown in Honduras, most people believe that Honduran coffee was first introduced to Honduras by Spanish businessmen in the late 18th century.
1804
Colonial records show that Don Ramon de Anguiano, the then governor, declared that "Honduran coffee is of the same quality as Moka." It means that Honduras had already planted it on a small scale.
1894
Because investment takes several years to harvest, many small farmers can not wait that long, so the scale of coffee production in Honduras is not very large. However, coffee cultivation has also begun to grow, laying the foundation for coffee to become a major industry in Honduras.
1900
Honduras exports only raw coffee beans worth about 54410 pesos.
1949
The new leader took office to invest in coffee-related road infrastructure. Roads help to transport coffee at the exit. In the second half of the 20th century, the number of small farmers engaged in coffee cultivation began to increase.
1970
The Coffee Institute (IHCAFE) was established in Honduras.
1975
Coffee production fell sharply, while Honduras took advantage of the opportunity, with coffee production surging from 500000 bags to 1.8 million bags and being looted. It was only after that that coffee production in Honduras really developed.
1990
With the rise of fine coffee in Central America, other countries have won by quality, while Honduras has lagged behind in boutique coffee production. The country's high-quality buyers have a bad reputation due to the lack of infrastructure for processing and quality control.
1993
The National Coffee Fund was established to provide support from coffee producers' organizations of the National Coffee Fund.
1998
Hurricane Mitch destroyed 80% of crops in Honduras.
2004
For the first time in Honduras, the Zhuoyue Cup Raw Bean Competition was held. 21 coffees from all over the country were recognized and participated in online auctions.
2011
Duras has become the highest coffee producer in Central America and the second largest Arabica coffee producer in the world.
Today
Honduras has become one of the top ten coffee producers in the world and the second Arabica coffee producer in the world. Coffee has played an important role in its economy and national development.

On the development of Honduran coffee in fact, Honduran coffee is not so smooth at the beginning, compared with other Central American countries: Costa Rica, Guatemala, Nicaragua and so on, coffee development can be said to be very late. The main reason for this is the lack of transportation between the origin and the port in Honduras, which has delayed the start of the coffee industry in Honduras, but after 1970, the government created an official agency for coffee: Instituto Hondure o del Cafe (IHCAFE), which is dedicated to improving the quality of coffee, and coffee trees can be planted all over Honduras, which allowed Honduras to produce more coffee than Costa Rica and Guatemala in 2011.
Coffee condition
It is understood that there are 280000 hectares of coffee gardens in Honduras, mainly small coffee merchants, most of which are less than 3.5 hectares. In the coffee garden, people collect coffee beans by hand, then handle them carefully and process them to meet the needs of the market and consumers' different tastes. Honduras collects 3 million bags of coffee every year, provides a lot of coffee and unique coffee aroma, and has become the second largest coffee exporter in Central America and the tenth largest coffee exporter in the world.
Coffee producing area distribution
Honduras has six major coffee producing areas, mainly located in the western and southern regions of Copan, Opalaca, Montecillos, Comayagua, Agalta Tropical and El Paraiso. The average altitude of high-quality products is more than 1100 meters. 69% of the coffee grown in these areas is HG, and 12% is SHG,19% and CS.
Section District (Copan):
Located between Copan, Ocotepeque and Lempira regions, showing a strong chocolate flavor, characterized by the sweetness of honey and caramel, the fruit flavor is relatively light, planted at 1000-1500 meters above sea level, from November to March.
Obalaca District (Opalaca):
Located between Santa B á rbara, Intibuca and Lempira regions, with very fine acidity, overall balance, taste of tropical fruits such as grapes, mulberries, etc., with a sour and sweet finish, showing a strong lemon flavor, neutralized with honey and caramel sweetness, with obvious fruit flavor, 1100-1400 meters above sea level, from November to March
Mondesius (Montecillos):
Located between the La Paz, Comayagua, Santa B á rbara and Intibuca regions, it is full of fruity and sweet aromas with lemon and floral aromas. Lemon and fruit aromas are important features, especially peaches and oranges, with lively and bright acidity, velvety texture and a lingering finish. 1200-1600 meters above sea level, from December to April
Gongma Agua (Comayagua):
Located between Comayagua and Francisco Moraz á n region, mainly lemon flavor, obviously sweet fruit aroma, taste more creamy mellow, but also with citrus sweetness, and exudes sweetness and chocolate flavor, 1000-1500 meters above sea level, from December to March
Akata (Agalta Tropical):
This region, which straddles parts of the provinces of Olancho, El Paraiso and Francisco Moraz á n, is mainly the eastern province and is the most scattered region. It consists of 14 protected areas to increase their plant diversity to balance the ecosystem, and is of high ecotourism value. The aroma and aroma of honey, it has a strong citrus flavor and subtle and obvious acidity, and a pleasant finish. 1200-1500 m above sea level
Paraso (El Paraiso):
1100-1400 meters above sea level, with gentle fruit acidity, caramel aroma and balanced taste.
Coffee grading
Honduran coffee is graded mainly by altitude, supplemented by defect rate.
[classification]: mainly based on altitude
Standard grade, planting height less than 1000 meters
High Grown grade, planting height is 100-1500 meters
Strictily High Grown grade, planting height is more than 1500 meters
Graded by defect rate:
American standard USP,US preparation; European standard EP Euro preparation
The meaning and rules of the name of coffee raw bean in Honduras:
Honduras SHG EP
Country + altitude level + defect standard

Flavor characteristics
The granules of coffee beans in Honduras are large in shape, uniform in size and glossy in color. In order to facilitate harvesting, farmers will prune the coffee trees to no more than 150 centimeters, because if they grow too high, they have to set up ladders to pick, which is not only time-consuming, but also may damage the trees by bending branches. As the ripening period of each fruit of coffee beans is different, in order to maintain the good quality of coffee beans, it is necessary to pick them manually, and then select the ripe fruits. For coffee fruits of the same branch, it often takes several weeks to pick them all.
The granules of coffee beans in Honduras are large in shape, uniform in size and glossy in color. Honduran coffee has a rich and mellow taste, taste is not astringent, not sour, mellow and aroma are very high, quite personality.

Marcala SHG SCAA scores range from 82 to 83, with excellent acidity, texture and sweetness.
SHG,SCAA score between 79 and 81, with solid acidity, body and sweetness, potential flavors are citrus, bitter chocolate, caramel, sugar cane and silky
HG, low acidity, good health, medium sweetness.
Although Duras coffee does not have very distinct characteristics, its biggest feature is its rich and balanced taste as a whole. In detail, it has a medium or shallow acidity, which is obvious but not strong. Sometimes with a slight floral or fruity aroma (generally speaking, different producing areas, different elevations of beans have different flavor performance) slightly bitter and obvious sweet. The overall taste of Honduras is balanced, sour and bitter are not strong, and the balance between the two is better. Therefore, the extremely balanced nature of Honduran coffee makes it widely used. Can be used to mix coffee, can also be used as a single product to brew, with Honduran coffee mixed with Italian concentration will have a more admirable flavor display.
Coffee variety
Most of the coffee varieties grown in Honduras are Arabica, mainly derived from Bourbon Bourbon, Kaddura Caturra, Kaduai Catuai, Iron pickup Typica and Pacas Pacas.
Coffee treatment

High-quality coffee in Honduras uses water washing to deal with coffee beans, usually after soaking, when the defective fruit will surface, it can be discarded first. Then put the good fruit into the fruit peeling machine and peel off the peel with the rotating force of the machine. Peeled fruits are screened by machines to select fruits of high quality. Usually the bigger the fruit, the better the maturity. Coffee in Honduras is dried in the sun, so there is always a hint of fruit in the taste.
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

The three schools of Japanese style with a full sense of ritual: volcanic rush, loose grip and drip method (with visual
Japan is really ceremonial about coffee. The coffee powder will bulge like a volcano and the spoon will dig a big hole in the coffee powder or drip like an hourglass. Wow! For the first time, the editor saw that Japanese hand flushing was really deeply infatuated. The coffee hasn't been drunk yet, but the technique is leveraged. It gives the highest respect to a cup of coffee. Today, the editor will talk about Japanese coffee.
- Next
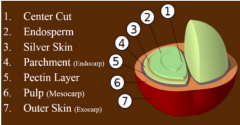
Coffee knowledge | grading of defective beans in SCAA boutique coffee
According to the SCAA (American Fine Coffee Association), raw beans are divided into category I and II defects. Before we understand the defective beans, let's take a look at the structure of the coffee fruit. The structure of coffee fruit after picking, the coffee fruit needs to go through a series of processes before it can become what we call coffee raw beans. This series of processes are often referred to as the handling of raw coffee beans or in the industry.
Related
- The sales look strange! Lucky's new cream top encountered a problem!
- Unexpectedly! Is the last store in Guming Xi'an closed?!
- Flavor characteristics of alo Hamathiu coffee in Sidamobansa, Ethiopia! Flavor characteristics of coffee beans in Ethiopia 74158, the world's top ten coffee producing areas!
- What is the reason why the coffee brewed in the mocha pot is bitter and sprayed with double ponytails? Should I use light or medium to deep roast coffee beans to make mocha pot coffee?
- Is the extracted flavor of hand-brewed coffee metaphysics? Hand-brewed single-item boutique coffee grinding ratio, water temperature time, which parameter is the most important?
- What ratio of milk and coffee should I use to make-86°Cdirty? Should I use a frozen cup or a refrigerated cup to make dirty coffee?
- What is the difference between decaf coffee and regular coffee? Can caffeine intolerance be combined with decaffeinated coffee? What are the methods to treat decaf coffee?
- Do I need to pick defective beans for Italian hand-brewed single-piece coffee? What is the difference between the mouldy beans, black beans, insect eaten beans, Quake beans in coffee?
- What does the flow distance and flow rate of Italian latte pull flowers mean? Share tips on making coffee flowers, love leaves, tulip patterns!
- How to control the concentration and extraction rate of hand-brewed coffee? What does the powder and water ratio, concentration and extraction rate of hand-brewed coffee mean?

