Popular science | does milk tea contain caffeine? How long will caffeine be metabolized in the body?
"Let's go for coffee at three o'clock in the afternoon." No, I'm afraid I can't sleep at night after drinking coffee. Let's go and have a cup of milk tea. In the afternoon, I wanted to have coffee and tea with my friends, but I was unexpectedly declined? The reason is that the caffeine in coffee interferes with sleep. But the behavior of girlfriends who can't sleep without coffee and milk tea is also confusing.
Caffeine is a naturally occurring stimulant found in more than 60 plants, including coffee beans, tea, cola nuts, (a plant used to flavor cola) and cocoa pods (used to make chocolate products). Of course, there is synthetic (artificial) caffeine, which is added to drugs, food and drinks. For example, some painkillers, cold medicines and over-the-counter drugs used to increase alertness all contain synthetic caffeine. Small snacks such as energy drinks and some chewing gum that are common on the market also add extra caffeine. The amount of caffeine in various foods and drinks varies, according to the National Institutes of Health:
A cup of coffee about 225 grams contains 95-200 milligrams of caffeine
A can of about 340 grams of cola contains 35-45 milligrams of caffeine
A can of about 225 grams of energy drink contains 70-100 milligrams of caffeine
A cup of about 225 grams of tea: 14-60 milligrams of caffeine

So milk tea actually contains caffeine, but it contains less caffeine than coffee drinks. It is well known that caffeine has many effects on the body: stimulating the central nervous system keeps people awake. Increase the release of gastric acid, excessive drinking will lead to stomach discomfort and so on. Worried about caffeine intake affecting sleep? Then we need to understand how caffeine works in the human body. According to BBC focus Science, the effects of caffeine are usually evident in about 10 minutes, but caffeine is not absorbed by the small intestine and distributed in all body tissues until about 45 minutes after intake. Peak blood concentration is reached within 1-2 hours. If you take the same dose of caffeine in the form of a tablet, the time to reach the blood peak often needs to be lengthened. For most people, the amount of caffeine in the body is halved about every 3-7 hours (depending on the person). This is what we often call the half-life of caffeine. 50% of the caffeine drunk at 3 p. M. is still circulating in the body before going to bed.
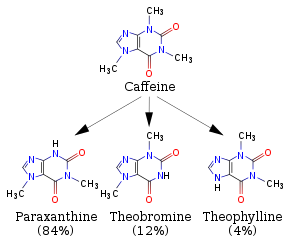
So how long will it take for caffeine to be fully metabolized? In fact, there is no standard answer. In 2019, Ananya Mandal, M.D., published an article pointing out that the duration of caffeine varies from person to person, depending on the amount of caffeine consumed and a number of personal factors, including age, weight, pregnancy, kidney health and individual sensitivity to caffeine. Caffeine is processed or metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P450 oxidase system and decomposed into three metabolites dimethylxanthine: paraxanthine (84%), theophylline (12%) and theophylline (4%). These metabolites are then further broken down and excreted into the urine and finally metabolized. I believe that after reading this article, you will have a new understanding of your "coffee power". As for the best time to drink coffee (caffeinated drinks), you still need to explore for yourself. Photo Source: Internet
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

What is the harm of drinking milk tea for a long time? How can I quit milk tea? Will fat-planting powder make people fat?
How fast does milk tea make people fat? it was one of the hot topics on Weibo last night. The top Weibo was a complaint from a netizen. The netizen and now many workers have the same habit of drinking milk tea, usually 4 or 5 cups a month. There was a lot of pressure in September, so the frequency of drinking milk tea increased a lot, on average.
- Next

Ceylon manor fine tea where can I buy? Sri Lanka Colombo Tea Auction House History Story
Colombo is a veritable tea trading centre of Sri Lanka. Sri Lanka sells about 320,000 tons of tea to the world every year from Colombo port. Sri Lanka's highest tea management agency-Sri Lanka Tea Board, the largest international tea auction house-Colombo Tea Auction House, tea brokerage company, several
Related
- How to choose a semi-automatic espresso machine correctly? What is the difference between a hundred yuan/thousand yuan/ten thousand yuan coffee maker?
- The sales look strange! Lucky's new cream top encountered a problem!
- Unexpectedly! Is the last store in Guming Xi'an closed?!
- Flavor characteristics of alo Hamathiu coffee in Sidamobansa, Ethiopia! Flavor characteristics of coffee beans in Ethiopia 74158, the world's top ten coffee producing areas!
- What is the reason why the coffee brewed in the mocha pot is bitter and sprayed with double ponytails? Should I use light or medium to deep roast coffee beans to make mocha pot coffee?
- Is the extracted flavor of hand-brewed coffee metaphysics? Hand-brewed single-item boutique coffee grinding ratio, water temperature time, which parameter is the most important?
- What ratio of milk and coffee should I use to make-86°Cdirty? Should I use a frozen cup or a refrigerated cup to make dirty coffee?
- What is the difference between decaf coffee and regular coffee? Can caffeine intolerance be combined with decaffeinated coffee? What are the methods to treat decaf coffee?
- Do I need to pick defective beans for Italian hand-brewed single-piece coffee? What is the difference between the mouldy beans, black beans, insect eaten beans, Quake beans in coffee?
- What does the flow distance and flow rate of Italian latte pull flowers mean? Share tips on making coffee flowers, love leaves, tulip patterns!

