Guatemala| Introduction to the coffee producing area selection series of coffee beans
Guatemala Guatemala
In the Americas, there is a country that is one of the centers of ancient Indian Mayan culture: the La Rep ú blica de Guatemala, which covers a total area of 108900 square kilometers and is divided into 22 provinces.
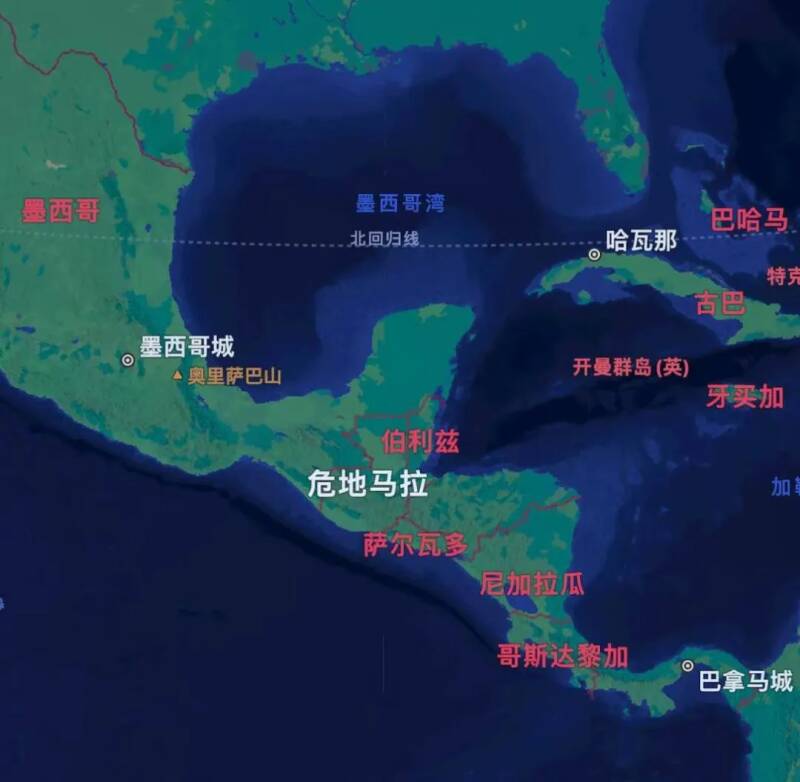
Located in the southern part of the North American continent, Guatemala is a land and sea country, bordering Mexico in the west and north, Belize in the northeast, Honduras and El Salvador in the southeast, the Gulf of Honduras in the Caribbean Sea to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the south. It has a coastline of about 500 kilometers and 38% of the country's forest area.
The face of the national flag consists of three parallel and equal vertical rectangles, with white in the middle, symbolizing the pursuit of peace and blue on both sides, symbolizing the Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean. In the center of the white rectangle is the national emblem, which is round, with an unfolded scroll in the middle that says "Freedom, September 15, 1821" in Spanish to commemorate Guatemala's independence from Spanish colonial rule. In addition, on the scroll stands the Guatemalan national bird, a green Gechar bird, also known as the "bird of freedom", symbolizing freedom, patriotism and friendship, while behind the scroll is a cross of rifles and swords, symbolizing that the people are always ready to defend the freedom of the motherland.

2/3 of Guatemala is mountainous and plateau, with the Kuchu Matanes Mountains in the west and Madre Mountains in the south, all of which belong to volcanic belts. There are 37 volcanoes in the country, of which Tahumurco volcano is 4211 meters above sea level, which is the highest peak in Central America. The north is mainly the Peten lowland, which is a tropical rain forest, and the main cities are released in the intermountain basins in the south.
Guatemala is located in the tropics, the northern and eastern coastal areas have a tropical rain forest climate, the southern mountains have a subtropical climate, with a wet season from May to October and a dry season from November to April of the following year. Coffee beans are generally grown in alpine areas, with annual temperatures ranging from 1300 to 1800 meters above sea level, with temperatures ranging from 18 ℃ to 28 ℃, usually colder from January to February, and annual rainfall of 2000 to 3000 millimeters in the northeast. High altitude, volcanic soil, large temperature difference between day and night, sufficient Rain Water and changeable microclimate bring elegant and lively acidity, clean taste and layered coffee flavor to Guatemalan coffee beans.
Coffee producing area
Coffee is grown in 20 of Guatemala's 22 provinces. Eight of them are well-known, divided into five volcanic producing areas and three non-volcanic producing areas, and coffee is planted at an average elevation of more than 1500 meters. Non-volcanic areas include Vivette Nanguo (Huehuetenango), Coban (Coban) and New Oriental (Nuevo Oriente). Volcanic areas include Atitlan, Antigua, Acatenango, Fraijanes and San Marcos.
Vivette Nanguo (Huehuetenango): Vivetta Nanguo is a non-volcanic producing area in Guatemala and is also one of the highest altitude producing areas, growing at an altitude of 1800-2100 meters. The name comes from Nahuatl, which means the land of the ancients (or ancestors). Vivette Nanguo is located in the western part of the country at the foot of Cuchumatanes in the Kuchu Matanes Mountains, the highest non-volcanic mountain range in Central America. Due to the large amount of hot air blowing towards the mountains from the tropical plains of Tehuantepec in Tavasco, Mexico, the coffee producing area is protected from frost and allows coffee to be planted higher, and the region has many river waters, making it an ideal growing area to cultivate quality coffee.
Coban: located in the middle of the country, Koban is an important coffee growing center in Guatemala. The producing area belongs to the rainforest region, and the climate is also tropical rainforest. It is cloudy and foggy all the year round, with abundant Rain Water and cool climate, while the local soil is rich in calcareous and clay. Most coffee is grown on hilly land at an altitude of 1300-1500 meters. Due to the weather, there are few sun-dried beans in this area, which is mainly treated with water washing.
New Oriental (Nuevo Oriente): located in eastern Guatemala, near Honduras, New Oriental is the youngest coffee producing area. It only began to grow coffee in this area in the 1950s. Rain Water is abundant in this area all the year round, with an altitude of 1500-2050 meters above sea level, so the area is always shrouded in mist, the sunshine time is relatively short, and it will be wetter than other producing areas. New Oriental was once one of the poorest and most isolated regions in Guatemala, because it was a volcanic area in ancient times, but it also led to the soil rich in minerals, coupled with the rich Rain Water and high altitude. The coffee beans produced here are quite complex and changeable in flavor. In front of the street, there is a honey-treated rose summer coffee bean from the New Oriental producing area, which will smell white flowers, sweet orange and bergamot flavor in the entrance, taffy-like sweetness and taste as soft as honey.
Atitlan: Attilan is located in Guatemala City in central Guatemala. The region is named after the country's largest volcanic lake, Lake Attilan, which is surrounded by three volcanoes. The volcanic soil is rich in minerals, and most of the coffee trees are planted on volcanic slopes at an altitude of 1500-1700 meters.
Antigua: Antigua is surrounded by three volcanoes: Agua, Fuego, and Acatenango. Most coffee is grown in the hinterland of the valley, which is 1500-1700 meters above sea level. Due to the active Fuego volcano, the humidity can be maintained at 65% all the year round. And mainly use shade planting, which can protect coffee trees from frost in cold weather. Dense shade and extremely shallow aquifers create a unique microclimate, coupled with fertile volcanic soil and suitable humidity, Antigua coffee has bright acidity and fruity aromas.
Introduction to Qianjie Coffee selected dangerous Mavite South Fruit Water washed Coffee Bean producing area: Vivette South Fruit area altitude: 1500-2000 m varieties: bourbon Kaddura Kaduai treatment: washing flavor: citrus lemon berry nut tea feeling
The Guatemalan Vivette South Fruit Coffee beans in Front Street Coffee are washed and moderately roasted. Qianjie will be boiled at the water temperature of V60 Personl 1591 ℃. The entrance will be slightly sour, with citrus, berry and nutty flavors, a soft taste and a tea finish.
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

The drought is serious! The water level of reservoirs across the country in Colombia is less than 30%
It is understood that because Colombia is located in the tropics of the equatorial region, December to February of the following year is the country's dry season. However, due to the impact of El Niño, the drought is exacerbated. As early as January this year, local media in Colombia reported that Colombia was affected by the El Niño phenomenon, causing serious drought problems.
- Next

What negative smells do you have in hand-brewed coffee? How to improve coffee tasting capabilities? What is the dryness caused by baking?
For coffee tasting, understanding its negative taste is also a very important thing. Although everyone's perception of positive flavor is already at your fingertips, when drinking an uncomfortable cup of coffee, they can only be described as negative flavors such as miscellaneous, bitter, and astringent. Of course we can just use these general terms
Related
- What grade does Jamaica Blue Mountain No. 1 coffee belong to and how to drink it better? What is the highest grade of Blue Mountain coffee for coffee aristocrats?
- What are the flavor characteristics of the world-famous coffee Blue Mountain No. 1 Golden Mantelin? What are the characteristics of deep-roasted bitter coffee?
- Can I make coffee a second time in an Italian hand-brewed mocha pot? Why can't coffee be brewed several times like tea leaves?
- Hand-brewed coffee flows with a knife and a tornado. How to brew it? What is the proportion of grinding water and water temperature divided into?
- What is the difference between Indonesian Sumatra Mantinin coffee and gold Mantinin? How to distinguish between real and fake golden Mantelin coffee?
- What does bypass mean in coffee? Why can hand-brewed coffee and water make it better?
- Unexpected! Ruixing Telunsu lattes use a smoothie machine to foam milk?!
- % Arabia's first store in Henan opens into the village?! Netizen: Thought it was P's
- Does an authentic standard mocha coffee recipe use chocolate sauce or powder? Mocha Latte/Dirty Coffee/Salty Mocha Coffee Recipe Share!
- What is the difference between Vietnam egg coffee and Norway egg coffee? Hand-brewed single product coffee filter paper filter cloth filter flat solution!

