Drinking coffee before going to bed will delay the body clock?

Washington, September 16 (Reporter Lin Xiaochun) Coffee drinkers should be careful: if you drink two espressos three hours before going to bed, the body clock will be delayed for about an hour. This shows that most people really should not drink coffee at night, otherwise they will easily become "night owls" who do not sleep at night and do not wake up in the morning. The report was published in the American Journal of Scientific Translational Medicine on the 16th.
Researchers at the University of Colorado recruited two men and three women to participate in the trial. During the 49-day study, five people took a placebo or a caffeine pill three hours before bed, which contained the same amount of caffeine as two espresso servings.
The researchers regularly tested participants' saliva levels of melatonin, an important regulator of the body's biological clock. The results showed that compared with taking a placebo in low light, taking a caffeine pill in low light delayed the body clock by 40 minutes, while being exposed to sleep-disrupting bright light for 3 hours delayed the body clock by 85 minutes. If the strong light plus caffeine tablets, then the body clock will be delayed by 105 minutes.
Kenneth Wright, a professor at the university who led the study, said in a statement: "this is the first study to show that caffeine-the world's most widely used psychoactive drug-has an effect on the body's biological clock." it provides new insights into the effects of caffeine on human physiology. "
Wright said the result is a further illustration of not drinking coffee before going to bed, but it can also benefit some travelers, and drinking coffee at the right time can help people with jet lag adjust their biological clocks. This result is also of great significance for the development of treatments for circadian rhythm disorders.
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev
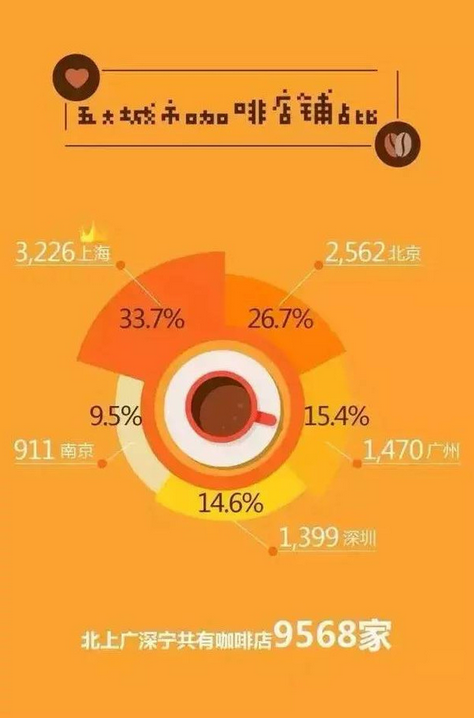
Ten pictures give you an instant understanding of the digital world of coffee brands.
At present, there are about 200 to 250 million potential coffee consumers in China, which is on a par with the market of the United States, the world's largest coffee consumer. The huge consumer market brings more opportunities. If you want to get a piece of the coffee market, the first thing to do is to understand the market.
- Next

Coffee video: at what time of day is it better to drink coffee? This is fastidious.
It is an indisputable fact that drinking coffee can cheer you up. However, the refreshing coffee also needs to pay attention to the time period, which must be unknown to many people. Sometimes, after we drink coffee, the refreshing effect is not obvious, why? Next, let's take a look. Http://v.qq.com/boke/page/k/0/n/k0162q172un.html needs to know if he wants to be refreshed.
Related
- Can I make coffee a second time in an Italian hand-brewed mocha pot? Why can't coffee be brewed several times like tea leaves?
- Hand-brewed coffee flows with a knife and a tornado. How to brew it? What is the proportion of grinding water and water temperature divided into?
- What is the difference between Indonesian Sumatra Mantinin coffee and gold Mantinin? How to distinguish between real and fake golden Mantelin coffee?
- What does bypass mean in coffee? Why can hand-brewed coffee and water make it better?
- Unexpected! Ruixing Telunsu lattes use a smoothie machine to foam milk?!
- % Arabia's first store in Henan opens into the village?! Netizen: Thought it was P's
- Does an authentic standard mocha coffee recipe use chocolate sauce or powder? Mocha Latte/Dirty Coffee/Salty Mocha Coffee Recipe Share!
- What is the difference between Vietnam egg coffee and Norway egg coffee? Hand-brewed single product coffee filter paper filter cloth filter flat solution!
- What is the difference between sun-cured and honey-treated coffee? What are the differences in the flavor characteristics of sun-honey coffee?
- How to make Italian latte! How much milk does a standard latte use/what should the ratio of coffee to milk be?

