Want to drink coffee but too bitter, add sugar and afraid of high calories? Try adding a pinch of salt.
Follow the caf é (Wechat official account vdailycom) and found that Beautiful Cafe opened a small shop of its own.
Want to drink coffee but too bitter, add sugar and afraid of high calories? Maybe you can try to add a pinch of salt to not only reduce the bitterness, but also make the coffee more mellow.
This "secret recipe" comes from a study published in the British journal Nature, which says that sodium ions in salt can suppress bitterness and increase aroma.
In fact, nothing can sweeten the coffee. A study from the University of Oxford shows that mugs of different shapes affect the taste of coffee, higher mugs make coffee sweeter, and coffee in "thin" cups tastes more bitter than "fat" cups. The reason why people feel that coffee in short cups is more bitter is that they subconsciously think that tall cups will be filled with more milk or water, and the difference between "fat" and "thin" cups is the same, the researchers reported in Food quality and preference.

[related reading]
It is said that the Japanese should sprinkle some salt first when eating watermelons. Is this true?
It's true.
The Japanese really like to sprinkle some salt before eating watermelons.
Why? It is not easy so sweet watermelon, but to sprinkle with salty salt, is not against their own sense of taste?
Before I explain this, let me explain two concepts: the contrast effect of taste and the inhibitory effect.
Use a taste additive with the opposite taste to produce a contrast effect, called the taste contrast effect. Use an additive with a similar taste to weaken the inhibitory effect of another sense of taste called taste. Through this effect, simply adding salt can enhance or suppress the irritating taste. Among them, salt is the most commonly used, so salt is also called taste enhancer.
[comparative effect of taste]
Sweet or spicy, this kind of food with strong taste, if it exists at the same time, one of them may enhance the subjective feeling of the other kind of taste, which is called the contrast effect of taste. Sprinkle some salt before eating watermelon, let the mouth and tongue first come into contact with the salty taste, and then touch the sweet taste, the sweetness will be magnified and feel sweeter, which is a typical taste contrast effect.
By the same token, in Japan, some salt is sometimes added to the sugar to enhance the sweetness. For example, putting some salt in fruit juice or rice wine can also enhance the sweetness. Japan's famous juice is a seasoning made from a mixture of various ingredients, which is necessary for almost every family, and it is usually used with a little salt in order to make it more delicious. The shrimp and crab that the Japanese like to eat are simply difficult to swallow without a little salt, and the same is true. In Japanese cuisine, there is a noun called "salt", which literally means hidden salt, which means that you can add a little salt to Japanese cuisine, so that you can't taste salt when you eat it, but salt can make it taste stronger.
[inhibitory effect of taste]
When two different flavors, such as sour and spicy, exist at the same time, one taste suppresses the other, making it less strong, which is called the inhibitory effect of taste. It is also a technology often used in Japanese food. Sushi rice is cooked after soaking in vinegar, with the smell of vinegar and, of course, the sour taste of vinegar. So sushi rice is often mixed with a little salt in order to suppress and weaken the sour taste. This is a typical use of the inhibitory effect of taste. Everyone knows that the Japanese like to eat plums. There is always a red plum on the bento white rice. There is a kind of plum called Yanmei in Japan. It's a plum mixed with salt. Use the salty taste of salt to reduce the sour taste of plum, while using the sour taste of plum to suppress the salty taste, to achieve an excellent balance, just the right taste can become salty plum. For example, adding a little salt to sauerkraut can also restrain the sour taste, and it is easier to eat dried plum with a little salt, which are examples of taste inhibition.
Give me another example. Pickles made from cabbage that the Japanese like to eat. If the pickling time is too short, it will feel very salty and taste bad because of the salt. The pickling is longer, and after full fermentation, the organic acid increases and the sour taste begins to appear. Just the right mix of sour and salty taste will become very delicious. But if it is pickled for too long, it will be too sour and become very bad. Friends who have eaten Japanese bran may be able to feel the taste of salt-acid balance strongly.
The same is true of soy sauce, which is inseparable from the Japanese diet. Recently, due to increased health awareness, there are a lot of reduced salt soy sauce on the market. But the salt content of reduced salt soy sauce is about 80.9%. The usual soy sauce is 17-18%. It doesn't feel particularly salty when eating. But the salt content of the sea is only 3%, but it feels very salty. In other words, if you give 10% or 18% salt water alone, you will feel too salty to swallow. However, if you dip the soy sauce with much higher salt content into sushi or sashimi, you will feel that the soy sauce is delicious, but the desalted soy sauce has no taste. This is because the various delicious amino acids produced by fermentation in soy sauce inhibit the salty taste of salt, resulting in a delicious taste. Miso soup, which the Japanese drink almost every day, has a salt content as high as 12%, but it doesn't feel that salty when eating it.
Among the foods that we human beings often eat, there is very little bitterness. Because animal instincts reject bitterness. But bitter gourd and coffee, which are supposed to be bitter, are very popular. If a little salt is added to balsam pear and coffee, the bitterness can also be suppressed. Of course, adding sugar can restrain the bitterness. But there are few people who add salt to their coffee. Would you like to try it next time?
And the famous Ganxia orange that the Japanese like to eat in summer. Friends who have eaten know that it is sour and bitter. When I say it, my mouth is full of saliva and it's very sour. If you eat with a little salt, it is amazing that the sour and bitter taste will weaken a lot and become sweet immediately. Remember to try it next time you eat.
Many examples are given to illustrate the contrast and inhibitory effect of taste. These are all physical phenomena. But from my experience living in Japan for many years, I think there is another social reason why Japanese people like to sprinkle salt when eating watermelons: expensive.
People who buy watermelons for the first time in Japan may be surprised, which is ridiculously expensive. Of course, we have to cherish such expensive food, and we have to do everything we can to enhance the sweetness of watermelons, but all kinds of means, including salt, have been come up with and used. In China and the United States, where watermelons are so cheap that it costs less than a few yuan to eat two watermelons a day, just throw away the unsweet watermelons and buy another one. I don't bother to sprinkle salt to enhance the sweetness.
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev
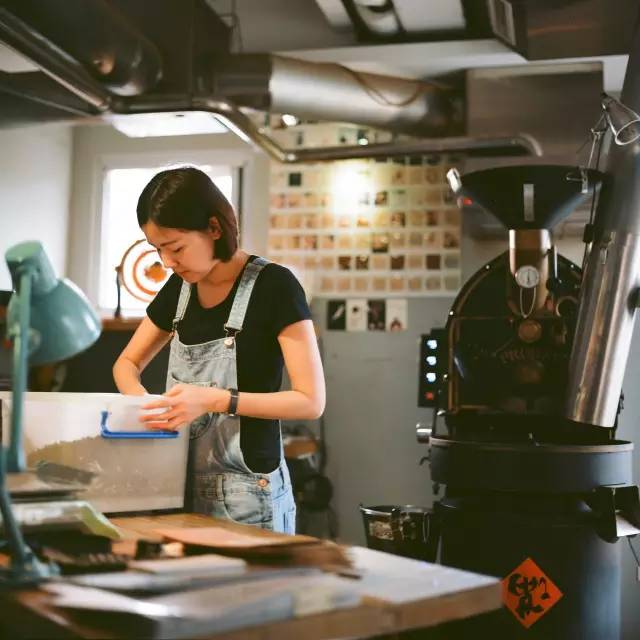

Chen Yujia, a teacher from Taiwan, talked about "how well this bean should be baked."
"how should this bean be baked?" as a baker, this is a question that is often asked. We often hear the owner of a small independent self-baking shop (usually also a bean baker) point out that my coffee beans are different from the deep roasting of ordinary chain stores when they talk about their own baking ideas. However, usually this also means dislike
- Next
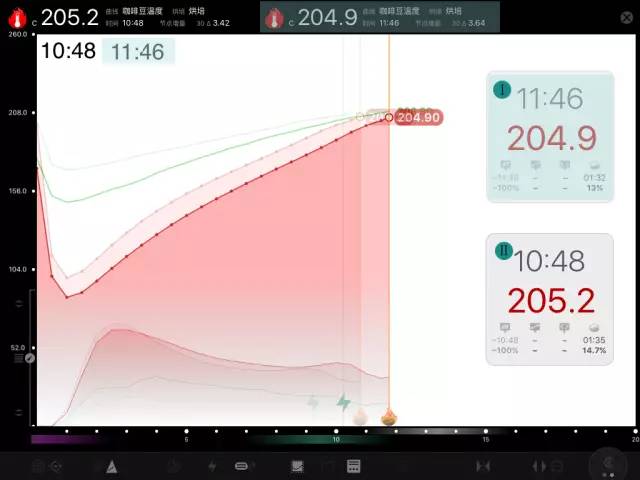
One cup of coffee and two curves
This time we were in a playful state of mind and did a test across time and space, and the results were not bad from the feedback results, the friend joked. You are going to open up a new world of cup testing (network cup testing). It's funny. A total of 37 copies of this event have been sent out, plus I am now drinking some friends to test, I believe that there should be more than 60-70 people playing this game. Straight
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

