How to pass the Q-grader exam (2) Taste skills
Taste skills: sweet, sour, salty
This part of the test is related to the taste of your tongue, and the solution used for the test has no smell! There are three different concentrations of aqueous solution, which taste salty, sweet and sour. The first part of the test requires you to evaluate / confirm their taste.
The second part of the test requires you to rank the solution according to its strength from low to high.
Note that if you are in the wrong order, such as a low-intensity solution, next to a high-concentration solution, the low-intensity solution tastes almost tasteless. This situation will make it difficult for you to sort.
The third part of the test requires you to identify mixed solutions of different strengths (sour, sweet and salty). To be honest, this part of the test is very difficult. A mixture of low salty and highly sweet solutions is more difficult to identify. In the exercises before the exam, focus on the texture of the solution, not just the taste. Touch can help you identify the concentration of the solution, and sweetness is usually slippery or thicker than others.

Points for attention
1. You can use sugar, salt and citric acid to prepare a mixed solution for practice to understand the interaction between these flavors.
two。 Don't drink all the mixed solution, keep some for reference.
3. Don't overdo it when tasting the solution, which can lead to taste fatigue.
4. Trust your instincts and don't question them over and over again. Your first impressions are usually correct.
Triangular cup test
The triangle cup test is a simple concept; identify a different cup of coffee in a group of coffee (a group of three cups) according to different producing areas or processing methods, for example, two cups of coffee in three cups come from the same producing area, another cup of coffee comes from different producing areas, or two cups of three cups of coffee are treated in the same way, and the other cup is treated differently. There are four groups of this kind of triangle cup test.
During the pre-exam practice, you will have the opportunity to taste four of the six kinds of coffee used in the exam. You should taste these coffees carefully, understand them, and make a description of their characteristics. Please focus on the main flavor characteristics of coffee. What makes it different? Try to make these feature descriptions part of your sensory memory.
I like to use exclusion, that is, to find the two most similar coffees of the three cups, and the remaining cup of coffee should be the answer.
Points for attention
Excessive tasting will lead to taste fatigue, because small bites should be tasted.
Trust your instincts and don't question them over and over again. Your first impressions are usually correct.
Acid test
Acid testing is one of the most common tests for sensory professionals. As coffee cup testers, we often use different types of acids to describe coffee. Of course, not all acids are bad acids such as butyric acid butanoic acid (acid gas of vomit) and isovaleric acid Isovaleric ac (mildew / mildew acid). Fortunately, these two acids are not common in coffee. The most common acids associated with coffee are citric acid, malic acid, phosphoric acid, acetic acid, lactic acid and quinic acid. The last two, lactic acid and quinic acid, do not appear in the acid test, but may appear in the written test.
In the test, there were 4 cups of coffee (as a group), a total of 8 groups. Of the four cups, two cups of coffee remained unchanged, and the other two cups were added with acid. You have to find out which coffee is sour and say what kind of acid is added.
Here is a quick guide to help you identify the acid in coffee. My views on these acids are contrasted with each other.
Organic acid: carbon base
Lemon-A strong citrus fruit with a sour taste (lemon)
Malic acid-acid, ending with sweetness (green apple)
Acetic acid-the acid of vinegar that ends with bitterness (white vinegar).
Inorganic acids: minerals
Phosphoric acid-A complex citrus fruit acid that ends with a sense of convergence (dry), like a sprinkle of salt on melons or mangoes.
Points for attention
During practice, you should taste the acid in the coffee against the reference (different acid) samples provided in the exam, which is a common test method. As a roaster, you can use the "comparison method" to check the consistency of the product in the coffee production process.
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

How to pass the Q-grader exam (1) Taste skill smell bottle 36 Flavor Spectrum sensory training
Signing up for the Q-grader exam to evaluate raw coffee beans through people's senses is a very subjective thing. For example, coffee that you think is deeply roasted may be moderately roasted to me, or you think it is the flavor of berry jam, which is more like balsamic vinegar to me. Now there are more than 4000 Q grader,Q-grading systems around the world.
- Next
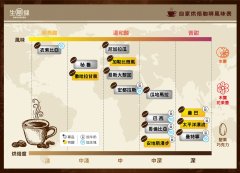
There are many kinds of coffee beans roasted at home. How to quickly choose your favorite coffee beans?
Professional barista communication Please pay attention to coffee workshop (Weixin Official Accounts cafe_style) There are many kinds of coffee beans roasted by their own house. Common coffee beans named after producing countries or regions, such as Ethiopia, Mantenin, etc., as well as special beans with beautiful names. For beginners who taste coffee for the first time, they may be confused by exquisite items. What are single beans?
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

