What difference does wet planing honey have to go to flesh insolation? What's the way to treat coffee?
Yesterday we talked about sun treatment and water washing. Today we will take a look at the treatments between sun treatment and water washing: wet shaving, half-sun treatment, pulp sun treatment and honey treatment. What are these treatments? What's the difference between them?
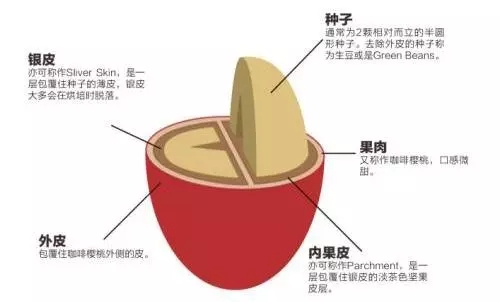
Let's first look at the structure of coffee cherries. A coffee fruit can be roughly divided into exocarp, pulp, pectin shell, hard shell / sheepskin, silver skin and innermost coffee bean seeds from the outside to the inside. In fact, these treatments are trying to remove these things from the skin and flesh, and take out the innermost coffee bean seeds.
Wet planing method
Wet ploughing is a common treatment in Sumatra.

When the bean body is moist and soft, and the moisture content is as high as 30-35%, remove the endocarp (parchment), let the surface of the raw bean be directly exposed, and then continue to dry, in order to solve the dilemma of drying for too long. In this way, because the drying time is shortened to two to four days, the fermentation period of coffee beans is shortened, and the acidity decreases a lot, but the relative thickness increases, and the aromas of caramel and fruit are obvious, even with aromas of herbs or herbs and wood. this is the unique "regional flavor" of Sumatra.

The reason for this treatment is mainly due to the humid climate of Sumatra, the method developed according to local conditions, in order to speed up drying.
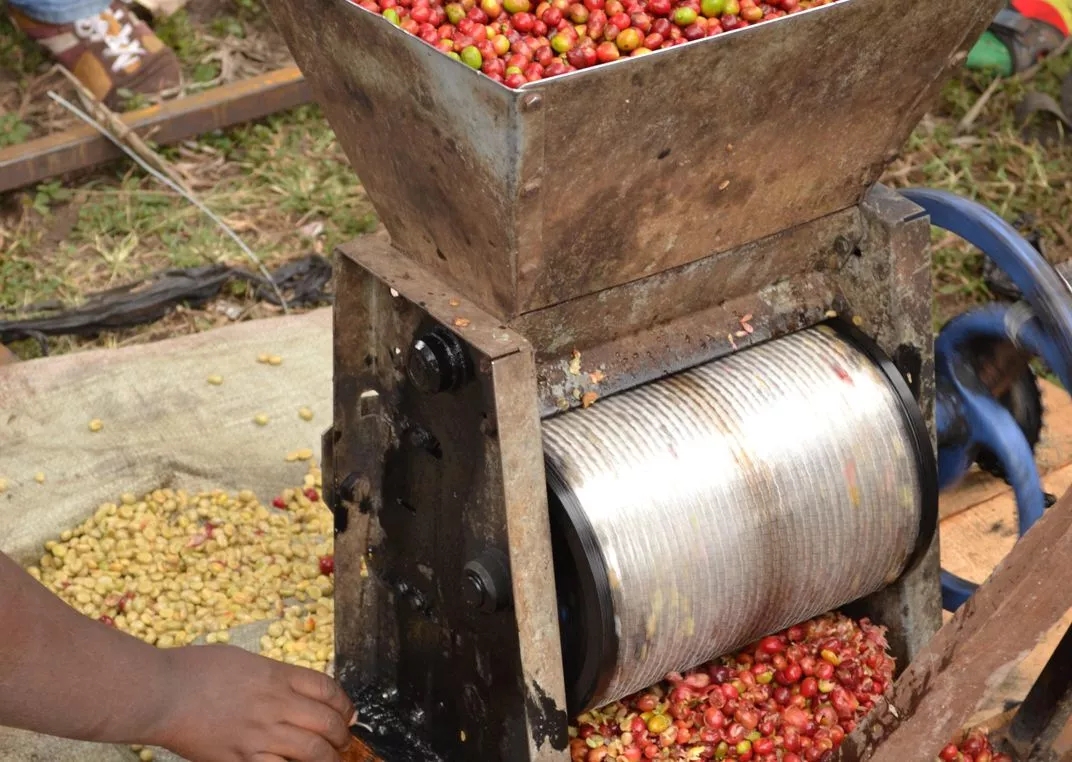
I. screening

Peel the coffee fruit, put the shell beans into a vat or sink filled with water, and remove the defective shell beans floating on the liquid surface.
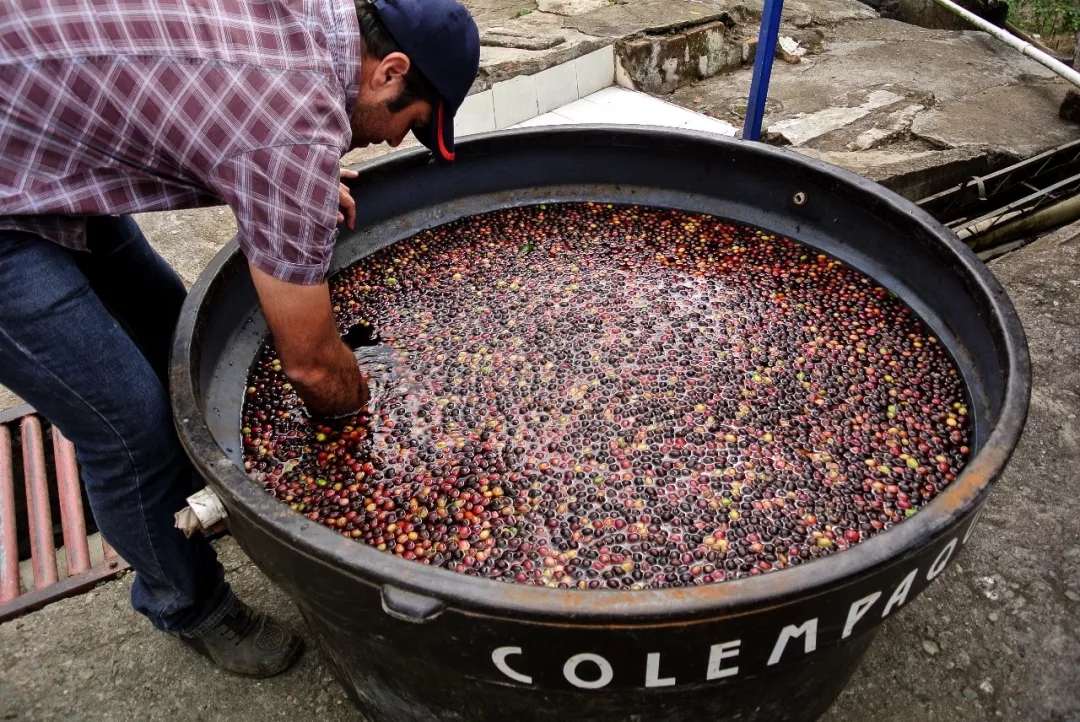
2. Fermentation

Wash the dense shell beans that have sunk to the bottom of the water, put them in a bucket or plastic bag, and do dry body fermentation, that is, to ferment and flavor the pectin sugar on the surface of the seed shell. Basically, the longer the fermentation time, the more sour. The fermentation time varies from person to person, generally only a few hours, but some manors omit the dry body fermentation stage and directly expose the shell beans, which can always be sour and improve the sticky taste, so that the pectin sugar can be fully fermented to increase the flavor, usually between 12-36 hours, depending on the specific situation.
Third, shelling and drying
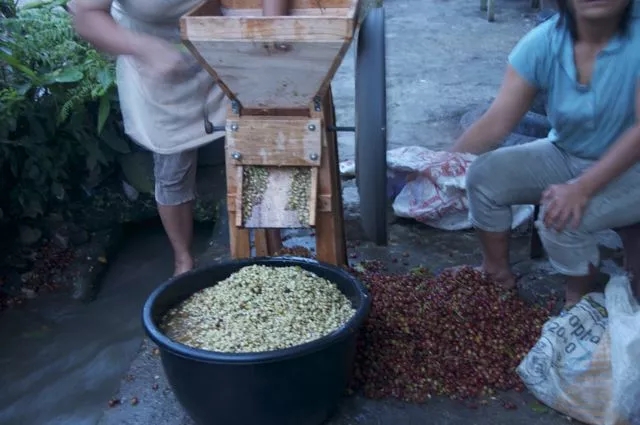
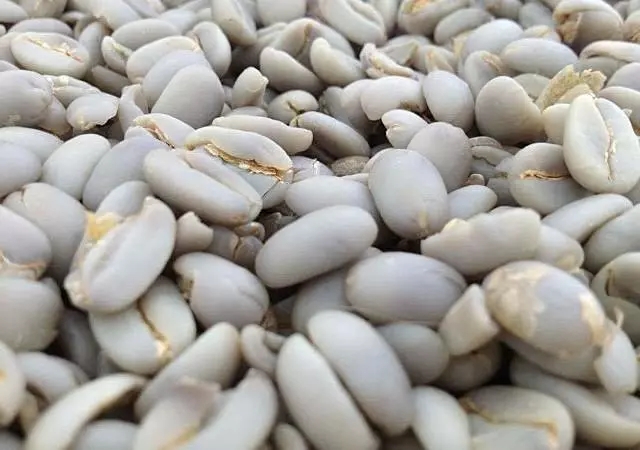


With shell beans exposed to the sun for one to two days, the moisture content of the bean body is up to 30% Mel 50%, and the bean body is still semi-hard and semi-soft. Wipe off the seed shell with a shell planer to speed up the drying process. After about two days, the moisture content of the beans reaches 12% Rue 13%. The coffee beans will be collected into woven bags, usually 40 kg and 80 kg each, and will be sent to the coffee processing plant for shelling, and the success will be completed in about four days.
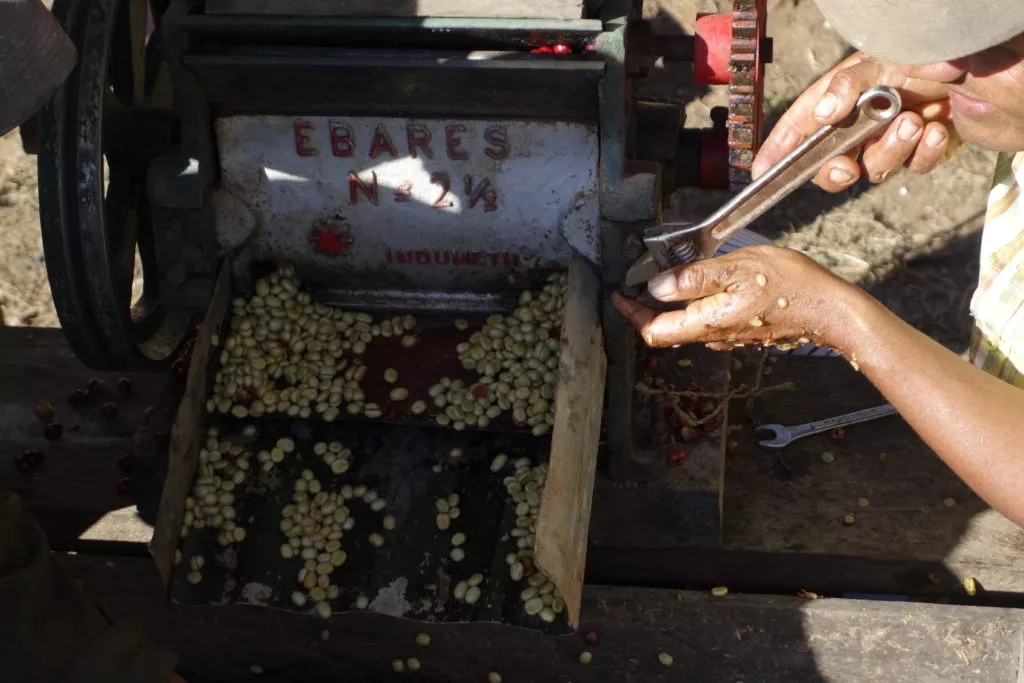

The shelling process is to grind off the bean shell with a shell planer and then bask it in the sun until the moisture content reaches about 12% Murray 15%. The coffee beans are then sent for machine selection to remove a variety of impurities and then sorted by particle size.
However, the wet ploughing method also has some disadvantages, in the shell planing process, the coffee bean temperature will rise to 30-60 degrees, and completely destroy the parchment, which is likely to trigger the bean sprouting. And it will also occur because the peel is shaved off in the production process, and let the beans come into direct contact with the air, so defective beans such as moldy beans are much higher than washing and tanning.
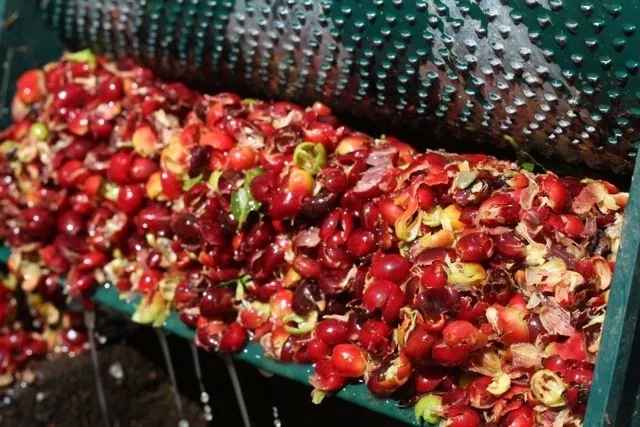

The effect of early removal of the seed shell is that the raw beans are half dry without the last two layers of protection (note: the four layers of coffee beans: pericarp, pectin, seed shell, silver skin), which is like taking off your clothes and basking in the sun. Although the wet planing method solves the problem of drying time, the relative probability of raw beans contaminated by molds, fungi and yeasts is also greatly increased. Paradoxically, however, these factors have become the key factors in creating Manning's special aroma.
Sheep's foot bean
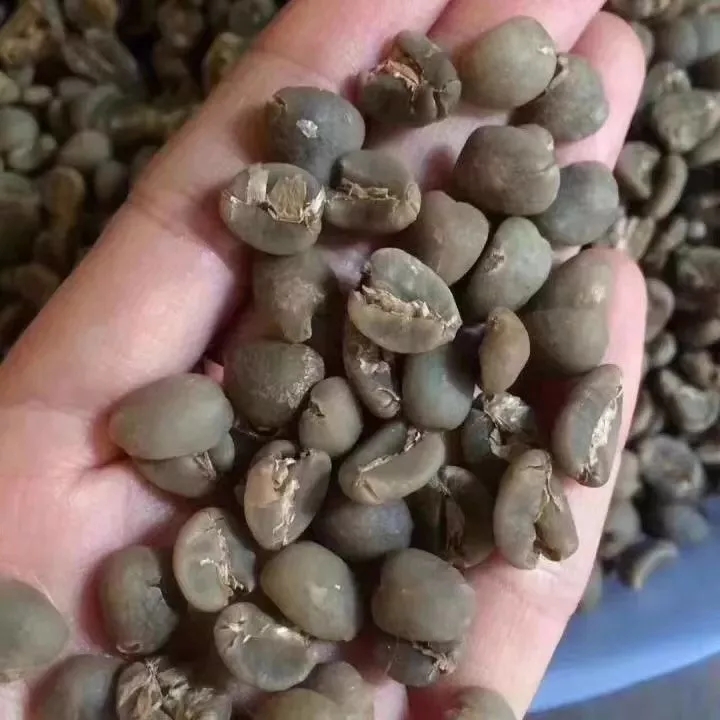

When it comes to wet ploughing, we have to mention sheep's hoof beans! If you look closely at Manning's raw beans, you will find that there are a lot of sheep's hoof beans. Because semi-hard and semi-soft wet raw beans are easily crushed by mechanical force when removing seed shells, beans are easy to crack like sheep's hoof, which is why there is a high ratio of sheep's hoof beans in Sumatra.
Half-sun treatment (semi-dry processing)
This is a method between the two treatments of tanning and washing, and can be divided into two categories: peeling and tanning and honey treatment. The two kinds of treatments are basically very similar, first, like washing treatment, removing the outer skin of coffee cherries, but skipping the process of "pool fermentation and rinsing with clean water" and directly drying in the sun. Although the methods seem to be similar, because of one of the important differences, there are two very different flavors, which are worth explaining separately.

This treatment uses much less water than the water washing method, and some of it is similar to the water washing treatment (removing the peel and pulp) and some is similar to the sun treatment (without fermentation in the pool), so it is also known as the semi-washing method (semi-washed method).
Flesh solarization method
Pulp solarization / peel solarization (Pulped Natural) this treatment was born in Brazil in 1990. Brazilians in order to give up the rotten sunburned coffee that has been criticized for a long time, and can not solve the problem of water use in coffee washing, so they finally found another way to combine washing with sunlight to create pulp solarization. The pulp solarization method not only reduces water consumption, but also reduces the effect of exocarp on coffee beans, which is a cost-effective coffee treatment method. The coffee produced by this pulp tanning method contains the characteristics of both washing treatment and sun treatment. The acidity, sweetness, seasoning, and flavor of this kind of coffee are quite good; the only drawback is that the taste of flesh tanning coffee is not as strong as that produced by pure tanning or water washing.
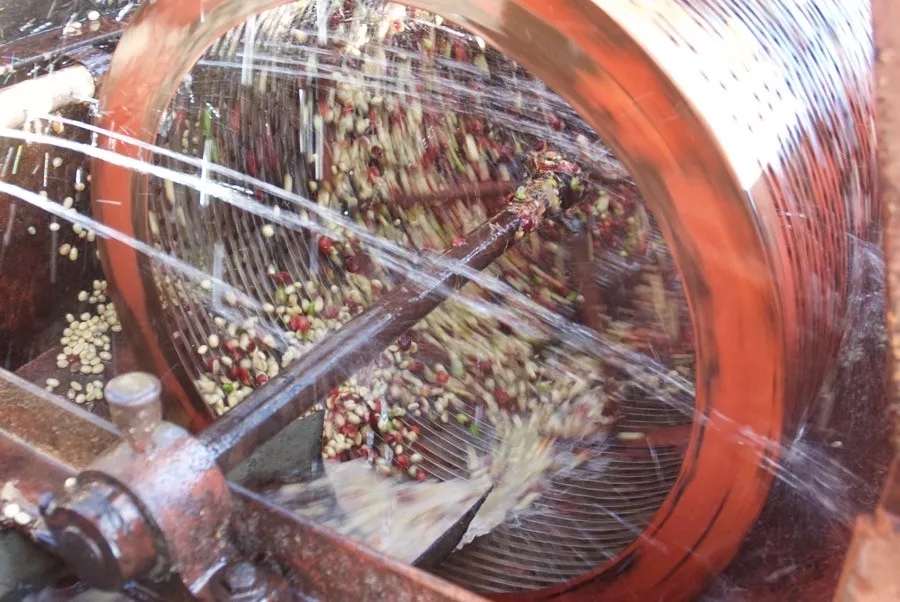

The process of removing the peel and the sun is as follows: the coffee fruit is first removed by the sink to remove the defective floating fruit, then the peel, pulp and part of the colloid layer are removed, and then washed in water for an hour. Because the immersion fermentation time is very short, the pectin is not easy to be washed away, and there is still pectin left on the bean shell. At this time, the sticky answer with shell beans are spread in the exposure field to dry, and it is best to use an African viaduct with good permeability.
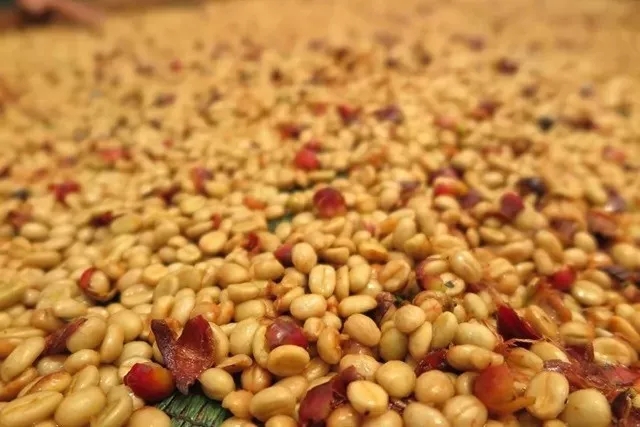

First, select beans
First put the coffee fruit into a large water tank, remove the floating fruit, and then put the sunken fruit into the pulp sieving machine to remove the pulp. To better remove the immature fruit, it is more important to let the coffee beans dry in the sun no longer with pulp, but only wrapped in a layer of pectin, which is more helpful to control the subsequent fermentation process.
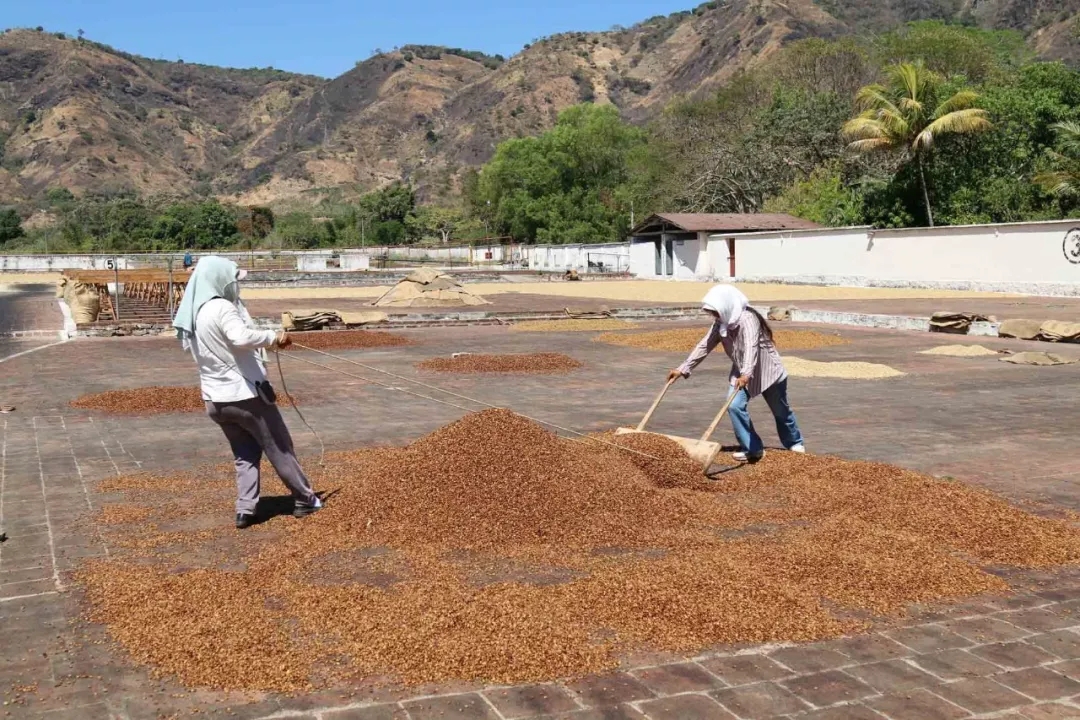

2. Drying
Move the beans to the bean drying farm to dry, and it will reach a certain degree of dryness in about 3 days.
Third, drying
Dry the beans further in a dryer until the water content of the beans reaches 10.5% Murray 12%.
Fourth, polish
Finally, polishing and polishing are carried out before the beans are bagged and exported.
Honey treatment method

Although it is called honey treatment, it doesn't mean that honey is added or tastes like honey. Today, honey treatment is used in almost all the producing areas of Costa Rica. This method is also widely spread throughout Central America. Because the surface mucosa of coffee beans is extremely slippery and the sugar content is extremely high, it is often called "honey". In the process of honey treatment, coffee will leave some or all of the "honey" when it is dried. After the coffee fruit is picked, graded and peeled, it is placed on a drying bed to dry.
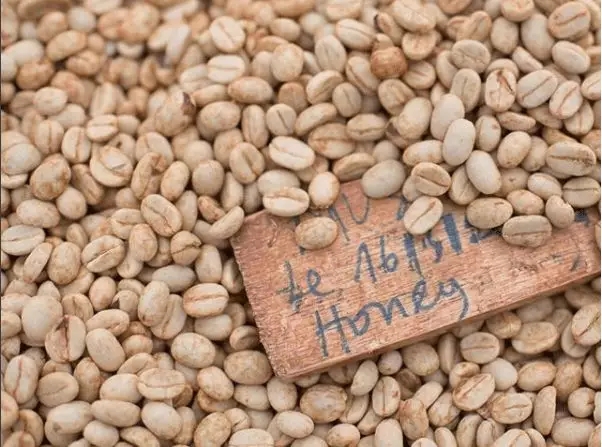

Because the drying time of the mucous membrane is very short, coffee beans hardly ferment during the drying process. The acidity of coffee beans processed by this method is slightly higher than that of natural washing, but much lower than that of natural washing and natural sun processing.
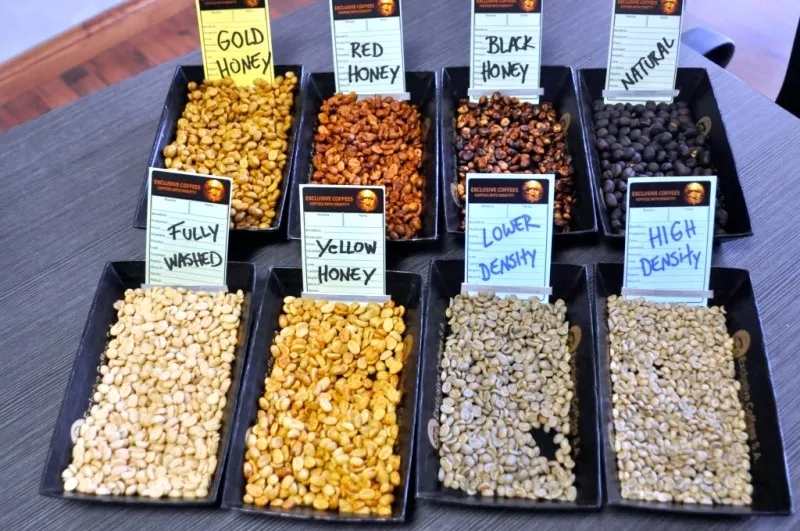

According to the proportion of pectin retained and the drying method, it can be divided into:
White Honey white honey 80% mae 90% pectin has been removed.
Yellow Honey yellow honey retains 50% pectin and has no fermentation.
Red Honey red honey basically retains all pectin and has no fermentation.
Black Honey black honey basically retains all pectin and dries at a slightly higher temperature at low altitude. It is covered with slight fermentation in the first 24 hours, and then the drying process is transferred to an African drying bed for drying.
Gold Honey Jinmi basically retains all pectin, drying at low temperature at high altitude and prolonging the drying time.
Treatment of flesh with sun-cured ≈ honey
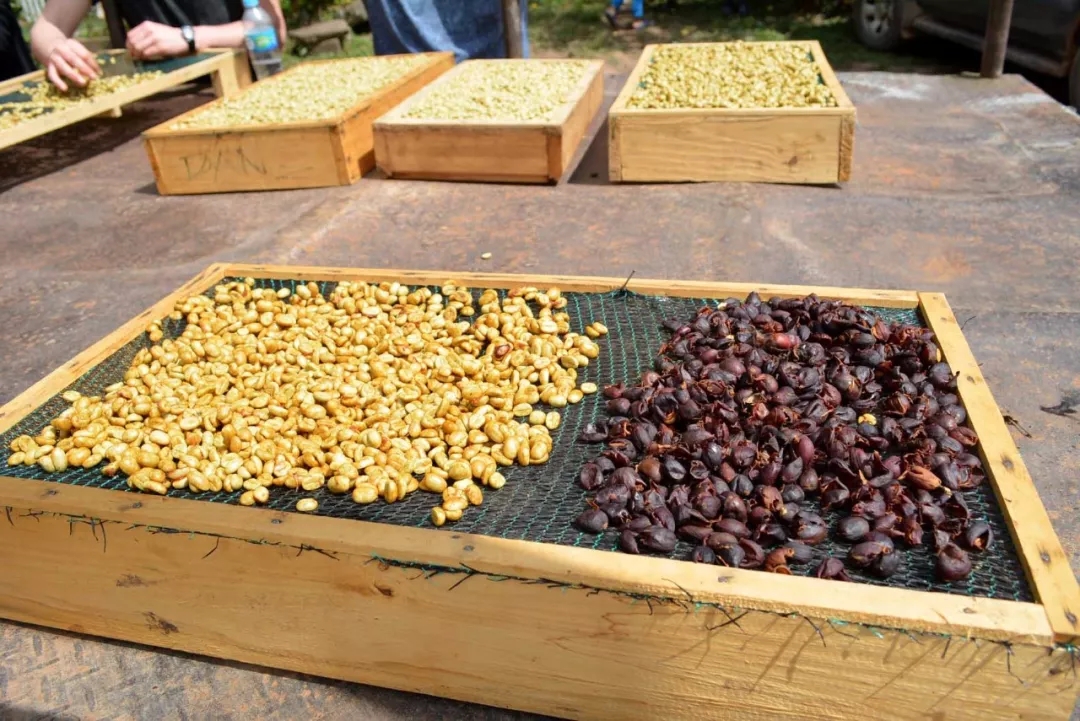

Pulp tanning method, while ensuring that the water consumption is much less than washing, at the same time, it reduces the mildew phenomenon that coffee fruits often appear in the sun method. Since the peel and part of the pulp were scraped off from the beginning, the pulp content of the outer layer of the coffee bean is much less than that of the sun method, and the "air permeability" of the coffee bean is much better. The fermentation process in the sun is not as violent as the sun method. The flavor of the coffee treated by flesh and sun is very similar to that of sun-cured coffee, with a thick taste and low acidity and high sweetness, which is the so-called "honey treatment".

In Brazil, flesh solarization is called Pulped Natural;, while in Costa Rica, the same principle of pulp solarization is called Honey/Miel Process, which is also known as honey treatment. Coffee farmers in Central America think that the pulp left on the bean shell is as thick as honey, so they call it honey-treated Miel Process.
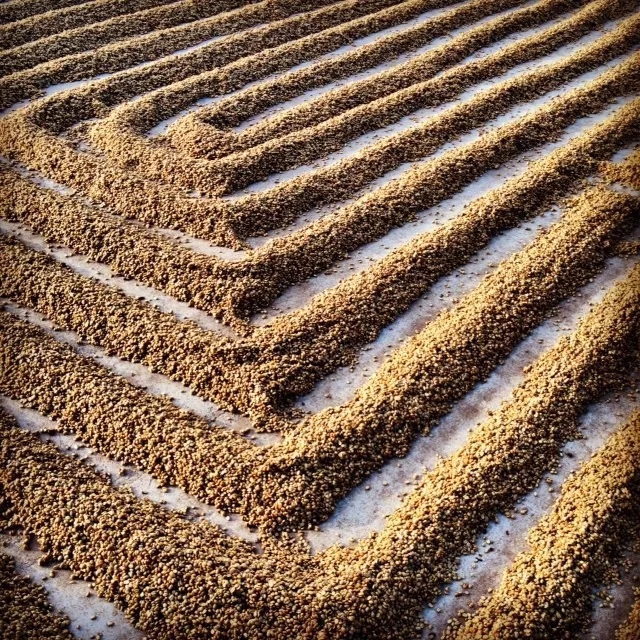

So, when it comes to pulp tanning, 99% of people are talking about Brazil and Costa Rica. Unlike washing and sunbathing all over the world, pulp solarization is a relatively "regional Regional" treatment. Of course, other producing countries also have experimental small farms, but they are not representative.
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev
Coffee bean treatment method what is the difference between sun treatment and washing treatment?
Usually when drinking coffee, it is always written on the labels of merchants such as sun exposure, water washing, honey treatment and so on. Sun exposure and water washing are relatively easy to understand, but what honey treatment and wet planing method really do not understand what the ghost is. So the editor would like to talk to you today. What are the common methods of coffee treatment? But it is small because there is a lot of content.
- Next

The principle and steps of Coffee Breaking how to make Coffee with Milk Bubble temperature
Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) a cup of coffee, what is the most impressive? In my spare time, take the book to the coffee shop and order a hot latte. The most enjoyable thing is the moment the hot coffee is served, the strong aroma of the coffee is accompanied by dense milk bubbles, and apart from that, it is amazing.
Related
- What is the meaning of lactic acid fermentation with coffee bean treatment?
- How to judge the state of foam by sound?
- How does the latte pull out the unicorn pattern? Come to get for a little trick to improve the flower pull!
- Will flower pulling affect the taste of the latte?
- Do you know the history of coffee?
- The difference between honey treatment and sun washing what is raisin honey treatment?
- What kind of milk can a novice use to make coffee foam to keep the foam longer? The correct method and skills of milking tutorial sharing
- Why do washed coffee beans taste sour? Flavor characteristics of washed Coffee
- Introduction to the skill of how to practice the size and height of water injection around the circle of hand-brewed coffee
- How do beginners practice coffee flower drawing from scratch?

