The taste of Starbucks decaf coffee introduces the difference between Starbucks decaf coffee and ordinary coffee

Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style)
Guide reading
One of the benefits of coffee is that it contains refreshing caffeine, and caffeine supplementation is also one of the reasons for many people's daily coffee, but everyone has different levels of sensitivity to caffeine. Some people are very sensitive to caffeine but want to drink coffee. Is there any coffee with less caffeine? Maybe decaf is the best choice for people who don't want to eat too much caffeine.
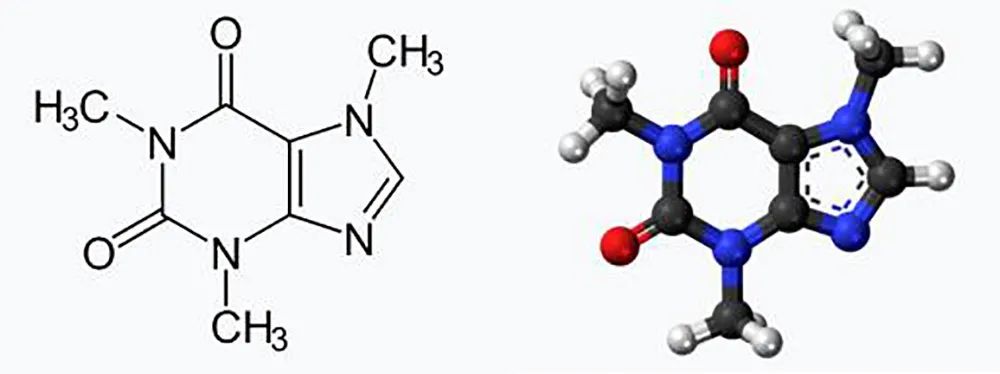
What is decaf?
In general, the weight ratio is used to measure the caffeine content of coffee beans. Arabica coffee beans have a caffeine content of 0.9% Mel 1.4% (an average of 1.2%), while Robsta has a caffeine content of 1.8% Rue 4% (average 2.2%). Decaf can be divided into natural decaf and artificially treated decaf (decaf).
The more common natural decaf coffee is Coffea Laurina, which has half the caffeine (0.6%) of regular Arabica. Unlike other artificially treated decaf coffees, pointed bourbon is genetically degraded, resulting in lower caffeine content and better flavor than the average Arabica coffee tree.

For artificially decaffeinated low-caffeine coffee, the EU standard for this type of decaf coffee is that the caffeine content after treatment does not exceed 0.1% of raw beans, while the FDA standard of the US Food and Drug Administration is less than 3% of the original caffeine content.
What are the ways to handle decaf?
Nowadays, there are many ways to remove caffeine, which can be divided into direct / indirect solvent treatment, supercritical carbon dioxide treatment, Swiss water treatment and mountain spring water treatment.
Direct solvent treatment
Direct solvent treatment is the use of dichloromethane, ethyl acetate and other chemical solutions to dissolve caffeine. First of all, steam is used to open the stomata of the raw coffee beans, and the dichloromethane solvent is directly added to the coffee beans. After the solvent and caffeine are fused, the caffeine-filled solvents are washed out, and the coffee beans are boiled again to remove all residual solvents.

There are concerns about using dichloromethane as a solvent because it is suspected that long-term exposure increases the risk of cancer. But in fact, FDA limits the dichloromethane content of decaf to 0.001%, which is actually lower than that, with little side effect.
The process of using ethyl acetate as a solvent is the same, ethyl acetate usually comes from sugar cane, so when used, the direct solvent method is sometimes referred to as sugarcane decontamination. This method is usually used in de-causation in Colombia. But ethyl acetate is a highly flammable substance, so it is more dangerous.
Supercritical carbon dioxide treatment
This treatment is to first let the coffee beans absorb water and expand, and the caffeine molecules are loose in the coffee beans. Add liquefied carbon dioxide and create more than 100 atmospheric pressure in water. Carbon dioxide is highly selective and does not "damage" the carbohydrates and proteins in coffee beans while dissolving caffeine, ensuring that the flavor of coffee beans is not destroyed. Liquid carbon dioxide that takes away caffeine can also be removed and recycled.

Coffee made from decaffeinated carbon dioxide has a lower burden on the human body, and according to the study, this method extracts more coffee than the direct solvent method, and the cost of this method is much higher than that of the direct solvent method.
Swiss water treatment method
The Swiss water treatment method was developed by the Swiss company Coffex in the late 1970s, and SWISS WATER ®is currently patented. This treatment will soak the raw coffee beans in hot water, and the soaking stage has actually partially removed caffeine. The soaked solution is then filtered with activated carbon and finally poured back into the coffee beans. This series of steps will be more effective in removing caffeine. In addition to not requiring the use of chemical solvents, the soaked solution can be reused in different batches of treatment procedures, but the coffee will still lose flavor during the filtration process.
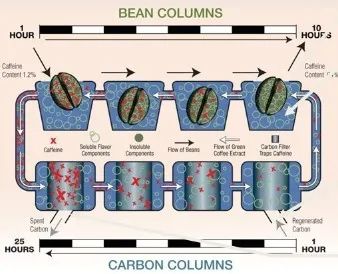
The caffeine removal rate of this method can reach 99.9%, which is also the highest method of caffeine removal. Qianjie coffee was tested in several low-caffeine beans, and last year a Colombian Swiss washing method was selected for shelves. The coffee beans come from Colombia's Huilan region, and the varieties include iron pickup, Kaddura and Castillo. Coupled with Swiss washing, this low-caffeine coffee bean shows obvious black cocoa, caramel, nuts and a full-bodied taste.
Mountain spring water treatment
Similar to Swiss water treatment, another special kind of water is used to extract caffeine from glaciers. The company Descamex says it uses a special filter to remove caffeine. After treatment, you will get a caffeine-free aqueous solution, which also dissolves the solid substance of coffee and can be reused in the decaffeinated process.

For more boutique coffee beans, please add private Qianjie coffee on Wechat. WeChat account: kaixinguoguo0925
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

What is the selling point of decaf coffee at the expense of taste and flavor? Is decaf good?
Professional coffee knowledge exchange more information about coffee beans Please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) caffeine is found in coffee and tea, two common and ancient refreshing drinks. In addition to keeping people awake, they also make people feel slightly happy, which may be related to the fact that caffeine affects the metabolism of dopamine, a substance that activates reward centers in the brain. In addition
- Next

Balzac, a French writer who drank 50,000 cups of coffee, taught you how to drink coffee!
Professional coffee knowledge exchange more information about coffee beans Please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) everyone drinks coffee in a different way. Some people must drink in the morning, have another drink in the afternoon, and do not refuse to come in the evening; some people who drink after noon may not be able to sleep at night. Some people are cool and black, the stronger the bitter, the better; others like a hot latte, thick
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

