Peruvian coffee what are organic coffee beans? The difference between organic coffee beans and ordinary coffee beans
Professional coffee knowledge exchange More coffee bean information Please pay attention to coffee workshop (Weixin Official Accounts cafe_style)
Before this article talks about Peruvian coffee, let's take you to know about organic coffee first. Why Peruvian coffee has not been active in the boutique market, the front street will start with Peruvian organic coffee.
What is Organic Coffee?
Many coffee-producing countries use large amounts of chemical fertilizers and pesticides to control pests and leaf rust and increase yields, but these chemicals destroy natural nutrients in the soil and pollute groundwater and rivers deep underground. As yields increase, soil pollution becomes more serious. It is difficult to estimate the extent of ecological damage to nature caused by inorganic cultivation using chemical fertilizers and replanting Kadura and Kaduai, which do not need shade and can be exposed to sunlight.
Organic coffee can be said to be conscience coffee, emphasizing the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, using organic fertilizers, kitchen waste, compost and so on. Old shade cultivation is used, which happens to be a favorite way of growing old iron pickups and bourbon coffee trees. But organic farming costs more, so yields are relatively low.

Organic coffee needs to be certified by international agencies to have credibility. Basically, the more backward the country, the more natural the way coffee is grown, but because of poverty, it loses the opportunity for organic certification.
Why Peru is not active in the specialty coffee market because of organic coffee?
All right, back to business. Peruvian organic coffee has low production costs and the export price is also the lowest price among organic coffee, which has caused dissatisfaction among many producing countries and believed that Peru deliberately destroyed the market. Peru has good mountains and good water, it is easy to grow high-quality extremely hard beans, but the low-price market strategy affects the quality of coffee, coffee farmers in order to yield, will ignore the treatment and selection of defective beans. Just because organic coffee is sold at a low price doesn't mean Peru's boutique coffee is extinct. In the SCAA Cup 2010 test, the iron pickup of the Secovasa Cooperative in Puno, southeastern Peru, won the fifth place with a score of 89.2 points, narrowly beating the Emerald Manor Rose Summer Coffee with a score of 89.125 points. It also proved to the world that Peruvian coffee is a very affordable product.
Peruvian coffee-producing regions
Peru is located in the west of South America, with a coastline of 2254 kilometers. The Andes runs through the north and south, and the mountains account for one third of the country's area. They belong to the tropical desert area and have a dry and mild climate. Rich microclimate, large temperature difference between day and night, and Colombia belong to the coffee paradise with talent. Peru is mainly planted with tin card, cadura, katim, planting altitude: 1000-1800 meters.
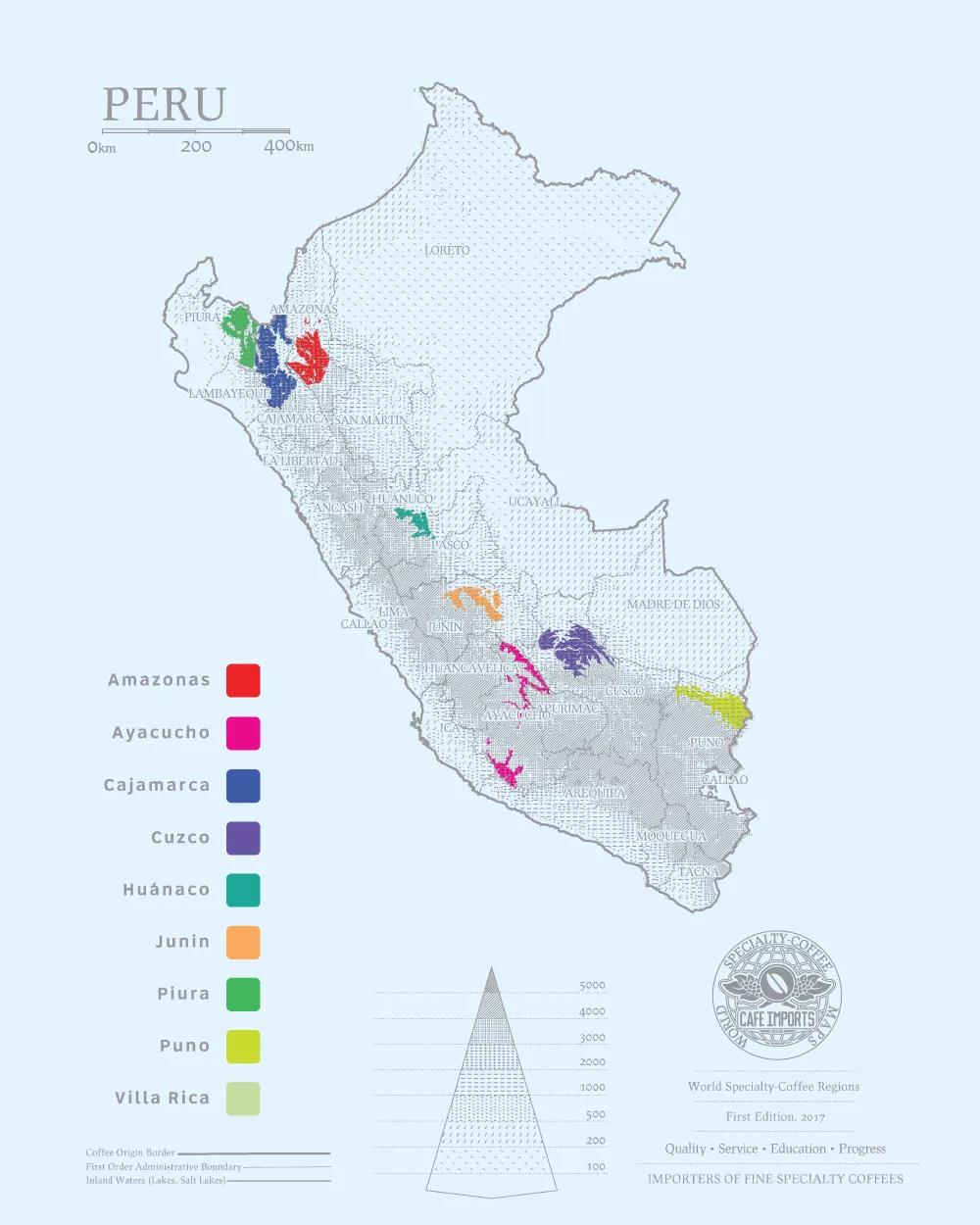
Specific to Peru's northern, central and southern coffee producing areas, 70% of the coffee varieties are iron pickups, 20% are kadura, and the rest are other varieties such as katim. Due to Peru's complex and diverse natural resources and rich culture, coffee produced in different regions has its own characteristics.
northern region
Coffee cultivation in the north accounts for 43% of Peru's total area, including Amazonas, Cajamarca, Piura, San Martin, elevation: 1250 - 1950m. Coffee produced in the north, with high acidity, rich flavor, aroma overflowing, alcohol and flavor moderate. Some people taste it as "more chocolate and nutty than southern coffee."

central region
Coffee cultivation in the central region accounts for 34% of Peru's total area, including Huánuco, Junin, Pasco and Ucayali, with an altitude of 800 - 1200m. The characteristics of coffee in the central region are appropriate acidity, light and mild aroma, smooth and not too heavy alcohol, quietly wake up your taste buds.

southern region
Coffee cultivation in the south accounts for 23% of Peru's total area, including Apurimac, Ayacucho, Cusco, Madre de Dios, Puno, elevation: 900 - 2050m. Through the Andes Mountains, accompanied by the old terraces of the Inca era, this is the plateau of southern Peru, and it is also the place where coffee is produced with excellent alcohol. Taste carefully, and the unique taste is slightly sweet.
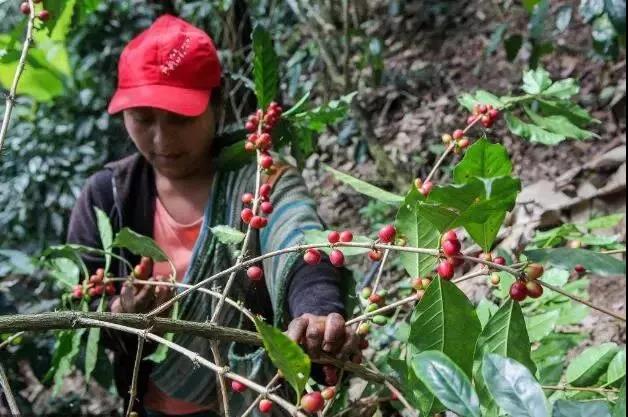

Peruvian coffee grading system
Grading in Peru is usually done by altitude classification for high mountain beans and green bean size classification for low and medium altitudes. The origin also uses "number of defects" as an auxiliary classification, while buyers use custom "cup test quality" as an auxiliary. Basically, the higher the elevation at which coffee trees grow, the harder the beans will be; this is because factors such as low temperature, short sunshine and high humidity will make coffee grow slower and produce higher density fruits. All aspects of coffee beans, such as acidity and sweetness, will be more saturated.
Strictly High Bean (SHB): Over 1350m
High Bean (HB): 1200-1350m
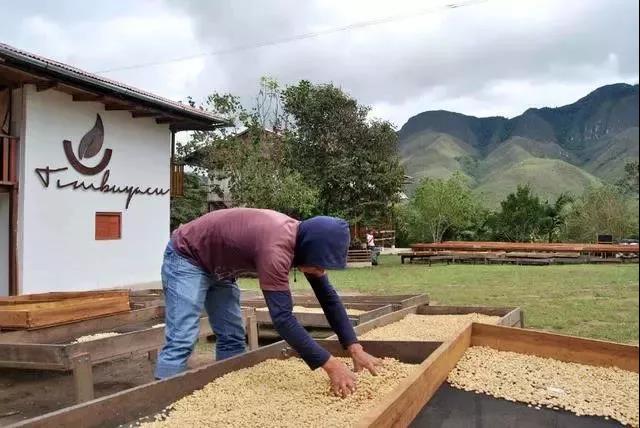

Basically, the higher the elevation at which the coffee tree grows, the harder the coffee beans will be; this is because factors such as low temperature, short sunshine and high humidity will cause coffee to grow slower and grow more dense fruits, and all aspects of coffee beans, such as acidity and sweetness, will be more saturated.
Peruvian coffee bean processing
Peru because of abundant water resources, traditional treatment method to wash mainly. Harvested berries are peeled to remove most of the pulp from the beans. The beans are then directed to a clean tank where they are soaked in water for fermentation to remove the remaining pulp layer. In the past (about five years ago), washing was often the preferred method of preparing good coffee beans.
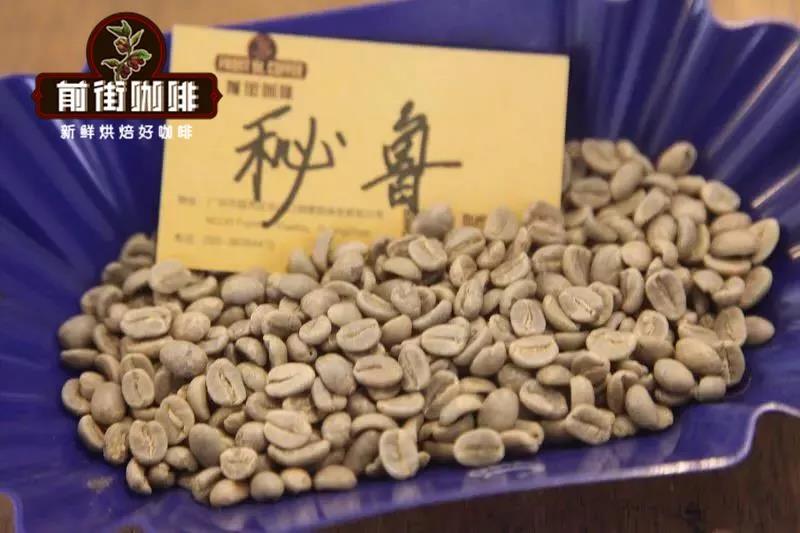

Through water treatment, immature beans and defective beans are selected due to buoyancy, and the fermentation process is better controlled, so the flavor is not as messy as sun-baked beans, but presents obvious acidity, slightly more complexity and cleaner cup characteristics (no negative flavor, such as astringency or sharpness). However, it is also because it is too "clean" and the richness of flavor is slightly weaker.
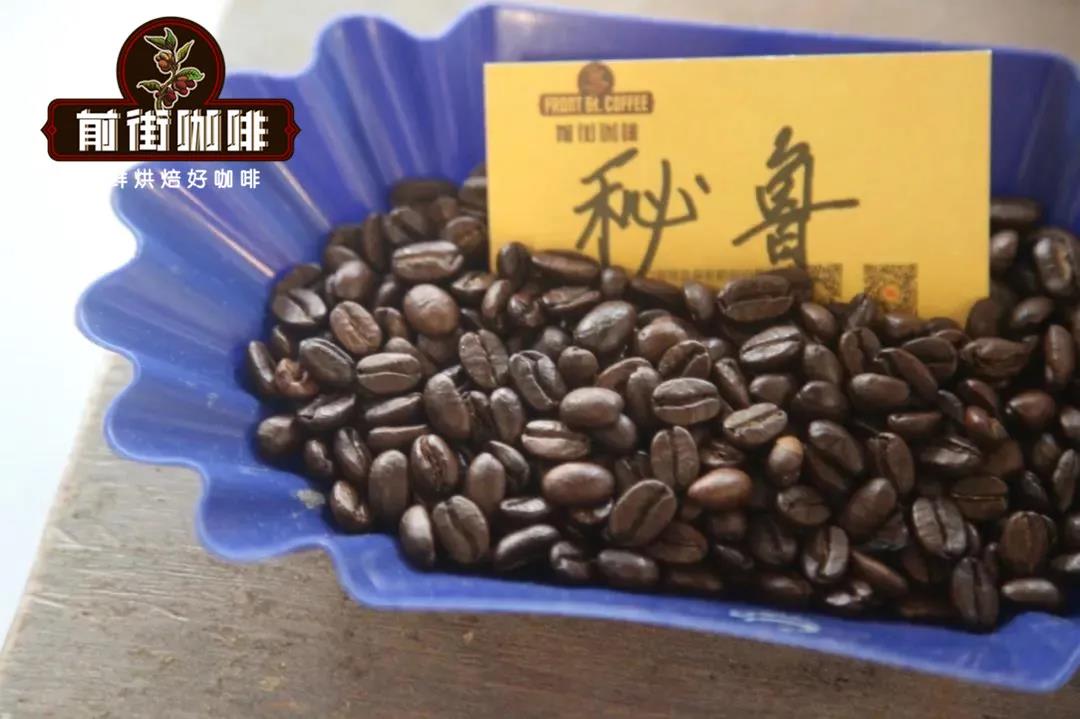
Front Street Baking Advice
Excellent quality Peruvian coffee with a rich aroma, smooth taste, structured, rich sweet, and elegant mild acidity. Therefore, the front street baker recommends a medium to dark roast to reveal its flavor characteristics.

Front Street Brewing Advice
Front Street brews Peruvian coffee using kono filter cups. Kono's ribs are less than half the height of the filter cup. This design is actually to ensure that the filter cup is wet and clings to the wall of the filter cup to limit the airflow. This will increase the water absorption time of the coffee powder particles, so that the extracted coffee is more uniform as a whole and enhances the mellow taste. And the groove skeleton at the bottom of the kono filter cup is a key design to create a siphon effect for later brewing.

Recommended water temperature: 87-88 degrees
Grindability: Small Fuji Ghost Tooth 4.5 (coarse sugar size)
Powder water ratio: 1:15
Powder: 15g
Brewing method of Qianjie coffee: steam with 30 grams of water for 30 seconds, inject water in a small circle to 125 grams for segmentation, continue to inject water to 225 grams when the water level is about to expose the powder bed, and remove the filter cup when the water level is about to expose the powder bed,(steam start timing) extraction time is 200 - 210.
More fine coffee beans, please add private WeChat Qianjie Coffee, WeChat: kaixinguoguo0925
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

The impact of the epidemic on the coffee industry in 2020 How to deal with the impact of the epidemic from producing areas to stores
As we all know, 2020 is an important year for the coffee industry. Due to Covid-19, logistical problems and the widespread closure of cafes have taken a huge toll. But, of all the difficulties facing the supply chain, stakeholders across the industry work together to innovate and address them. Industry-wide discussions highlight the importance of collaboration and explore
- Next

African Fine Coffee beans the Heart of Africa the flavor and taste of coffee beans in Burundi
Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information Please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) mentioned Burundian coffee, reminiscent of its distinct acidity and fruity aroma. When it comes to sour coffee, we have to mention coffee from Ethiopia and Kenya in Africa. In the front street, Burundian coffee is compared with two producing areas, Burundian coffee.
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

