The composition of coffee fruit and coffee beans what is the reason why coffee is bitter? Caffeine content of coffee beans
Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style)
Guide reading
After reading the title, some friends began to wonder: "Coffee fruit and coffee beans are not the same thing?" Yes, the relationship between the two is like a mother and a son. Coffee beans come from the core part of the coffee fruit.
The composition of a coffee fruit
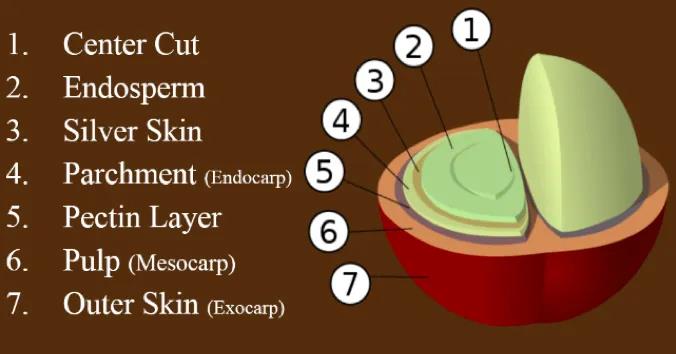
This is a picture of the structure of the coffee fruit, which is divided into seven parts from the outside to the inside:
⑦ exocarp
⑥ pulp
⑤ pectin layer
④ parchment
③ silver skin (the film between coffee beans and parchment)
② kernel (coffee bean)
① midline (germ)
Exocarp
The exocarp consists of 1-2 layers of cells, and its structural characteristics are similar to those of biological epidermis, with stratum corneum and stomata. When the coffee fruit is immature, the parenchyma cells of the exocarp mostly contain chloroplasts, which will turn into colored bodies when they mature. According to different maturity, the outer skin of coffee fruit will slowly change from green to red.

pulp
From a biological point of view, the pulp of coffee is part of the pericarp and develops from the ovary wall of plants. Coffee pulp contains sugar and acid, with melon-like sweetness and clear and pleasant acidity.

Pectin layer
Coffee pectin layer between the pulp and endocarp (parchment) polysaccharides, feel slippery and insoluble in water. Pectin is the part with the highest sugar content in coffee fruit, and it is an important part of coffee fermentation. For example, the more pectin retained during honey treatment, the more obvious the fermented feeling and sweetness of coffee beans will be.
Parchment paper
Parchment consists of parenchyma cells that protect coffee beans.

Silver skin
A thin film between parchment and coffee beans, belonging to the plasma membrane.

Fruit core (coffee bean)
The seeds of the coffee tree. Generally speaking, a coffee fruit contains two coffee beans, because the veneer is flat, so it is called flat beans / lentils. Some are in the growth process of one of the coffee beans stunted, so that the other has enough room for growth, showing an oval shape, so it will be called garden beans / beads.

Germ
The crack in the middle of the coffee bean belongs to the germ part, which will develop into leaves and stems after breaking through the skin of the coffee seed.
The ingredients of a raw coffee bean

After processing and drying, the moisture content of a raw coffee bean will be less than 13%. The moisture content of coffee beans does not greatly affect the aroma and taste of coffee, but the proportion of anhydrous compounds hidden in coffee beans affects the flavor of coffee. So what anhydrous compounds are contained in a raw coffee bean?
Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides account for the largest proportion of coffee beans, accounting for about 35%, 45%, is the basis of plant fiber and other substances, insoluble in water, no sweetness, will not directly affect the flavor of coffee. The coffee grounds left after the coffee is brewed is the fiber part made up of polysaccharides. There was no significant difference in the proportion of polysaccharides between Arabica and Robusta coffee beans.

Protein
Coffee beans contain 12% protein, which, like polysaccharides, does not directly affect the flavor of coffee. There was no significant difference in the proportion of protein between Arabica and Robusta coffee beans.
Lipids
The lipids of coffee beans are composed of linoleic acid, palmitic acid and other oils. Arabica coffee beans account for 20% of lipids, while robusta coffee beans account for 10% of lipids. Because many aromatic aliphatic carboxylic acids (including citric acid, malic acid, acetic acid, lactic acid, formic acid) can be dissolved in lipids, the amount of lipids in coffee determines the richness of coffee flavor.

Oligosaccharides (sucrose)
The amount of sucrose in coffee beans determines the flavor of coffee. The higher the sucrose content, the better the coffee. The sucrose content of Arabica coffee beans is 6% Mel 9%, while that of Robusta coffee beans is 3% Rue 5%.
Chlorogenic acid
Chlorogenic acid in coffee beans is a kind of bad acid that makes people feel sour and unpalatable. Chlorogenic acid can be degraded into quinic acid by roasting. Quinic acid is a phenolic acid, which is non-volatile, so it can not be smelled through the sense of smell, but its taste is bitter. It is one of the sources of the bitter taste of deep-roasted coffee. Arabica coffee beans account for 5% of chlorogenic acid at 8%, while robusta coffee beans account for 7% of chlorogenic acid at 11%.

Other organic acids & inorganic acids (phosphoric acid)
In addition to chlorogenic acid, citric acid, malic acid, acetic acid, lactic acid, formic acid and phosphoric acid account for up to 2% of Arabica and Robusta coffee beans.
Amino acid
The amino acids in raw coffee beans include aspartic acid and chitosan, accounting for up to 2% of Arabica and Robusta coffee beans.

Caffeine
The caffeine content of coffee beans is closely related to coffee variety and growth altitude. The caffeine content of Arabica is about 0.9-1.4%, while the caffeine content of Robusta is generally 2% and 3%. The caffeine content of different Arabica varieties planted in different regions will be slightly different.
For more boutique coffee beans, please add private Qianjie coffee on Wechat. WeChat account: kaixinguoguo0925
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

What is the coffee flavor? the aroma of ground coffee beans? how to describe the taste of coffee
Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information Please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) recently when the barista chatted with his guests on the front street, he was asked: is the coffee flavor equal to the coffee aroma? Why can't you smell the smell in the flavor description? The previous article on Qianjie talked about how to improve your judgment on the taste of coffee. This article is connected to the last time.
- Next

What is the flavor of coffee producing areas? what are the factors that affect the flavor of Arabica coffee beans?
Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) recently saw a Qianjie fan message asked: is it the variety or the planting place that affects the coffee flavor? On this issue, Dr. Francesco Illy, founder of illy Coffee, once explained that 70% of the characteristics and alcohol thickness of coffee beans are determined by genes.
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

