Professional coffee roasting knowledge Coffee roasting process and stage characteristics
Baking process Most people think that baking is nothing, just frying raw beans with fire. In fact, roasting is the most difficult step in the coffee processing process. It is a science and an art, so experienced roasters enjoy a highly respected position in Europe and America. The baking process can be divided into the following three stages
1. Drying
At the beginning of baking, green beans begin to absorb heat, and the water inside gradually evaporates. At this time, the color gradually changed from green to yellow or light brown, and the silver film began to fall off, you can smell the faint smell of grass. The main function of this stage is to remove water, which accounts for about half of the roasting time. Since water is a good heat conductor, it helps to roast the internal substances of coffee beans. So, although the goal is to remove water, bakers use the temperature of the water and control it so that it does not evaporate too quickly; usually, it is best to control the water to reach the boiling point in 10 minutes and turn into steam. At this point, the internal substances are fully cooked, and the water begins to evaporate, washing out the outside of the coffee bean.
2, high temperature decomposition
Roast to about 160 degrees Celsius, the moisture inside the beans evaporates into gas, which begins to rush out of the beans. At this time, the inside of the raw beans changed from endothermic to exothermic, and the first cracking sound appeared. After the crack, it will turn to heat absorption, when the pressure inside the coffee bean is extremely high, up to 25 atmospheres. The heat and pressure begin to break down the original tissue, forming new compounds that create the taste and flavor of coffee; at about 190 degrees Celsius, the conversion between endothermic and exothermic occurs again. Of course, pyrolysis continues to occur, and coffee beans turn from brown to dark brown and gradually enter the stage of heavy roasting.
3. Cooling
Coffee must be cooled immediately after roasting to quickly stop pyrolysis and lock in flavor. Otherwise, the high temperature inside the beans, if it continues to act, will burn off the aromatic substances. There are two cooling methods: one is air-cooled; the other is water-cooled. Air-cooled coffee requires a lot of cool air to cool the beans quickly in 3-5 minutes. In the field of professional roasting, large roasters are equipped with a tray with a rotatable push arm; when roasting is completed, the beans are automatically fed into the tray, and the fan at the bottom of the tray is immediately activated to blow cold air, and the coffee beans are stirred by the push arm to cool them. Water-cooled coffee is slow, but clean and pollution-free, and retains the aroma of coffee. It is used by specialty coffee makers. Water-cooled coffee beans are sprayed with a mist on the surface, allowing the temperature to drop rapidly. Because the amount of water sprayed is important, it requires precise calculation and control, and it increases the weight of baked beans, which is generally used for large commercial roasting.
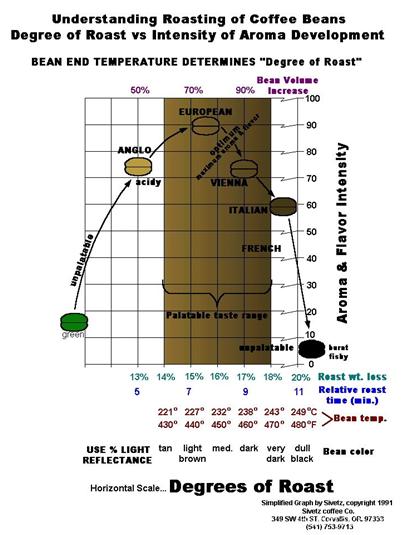
Roasting degree and characteristics From the perspective of roasting degree, the deeper the roasting degree, the more bitter the bitterness; the lighter the roasting degree, the more sour the sourness. The degree of roasting depends on the characteristics of the coffee beans themselves. For coffee beans with strong bitterness and light acidity, moderate and light roasting degree is generally selected.
1. Light baking
The mildest fried culture, no flavor and concentration at all, beans are not ripe, green taste of raw beans, not suitable for grinding drinking. Generally used for testing.
2. Deep shallow baking (Cinnamon)
Also known as cinnamon baking, for the general popular frying degree, leaving a strong sour taste. Bean color is quite close to cinnamon, so it is also called cinnamon baking, sour emphasis. It is popular with western Americans.
3, lighter medium baking (Media)
Deepen the color, easy to extract the original flavor of coffee beans, mellow, sour and delicious. It is mainly used to mix coffee.
4. Medium baking (High)
Coffee tastes stronger and less sour, which is how coffee beans are generally roasted. Acid neutral and bitter, suitable for coffee such as Blue Mountain and Gili Mazaro. It is loved by Japanese and Nordic people.
5. Deep medium baking (City)
Also known as city baking, bitter acid is thick, almost no sour, unique flavor. Coffee suitable for Colombia and Brazil, loved by New Yorkers.
6. Normal baking (Full City)
Also known as all-city roast, it is suitable for brewing iced coffee. No sour, mainly bitter, bitter will be aggravated, but high-quality beans will have sweet taste. It is used for iced coffee and is preferred by Central and South Americans.
7, French baking (French)
French baking method, slightly black color, bitter strong, but also exudes oil, bitterness and concentration are deepened. Coffee brewed in a steam press.
8. Deep baking (Italian)
Also known as Italian baking, the deepest degree of baking, beans black and translucent, surface oil oozing, bitter very strong. At this stage, the coffee beans have been severely carbonized, and the taste of one coffee bean and another coffee bean has been difficult to distinguish. For Italian steam coffee.

Baking characteristics around the world Every city in every country has its preferred baking tendency.
In Tokyo, slightly deeper medium roasts are more popular, but slowly there is a trend towards deeper roasts as well. In the West, deep baking has been popular since ancient times.
New York, as its name suggests, tends to prefer urban roasting, but because of the variety of people living in the city, coffee beans of different roasting degrees are sold, and the variety is quite rich.
Vienna prefers deep baking. French people prefer French baking; Italians often use Italian baking.
However, in recent years, Europeans and Americans have widely used Italian roasts (Brazil and Italy most commonly used deep roast), and the variety is also colorful, and steam pressure machine coffee is still loved by people.
Deep roasting Ethiopian coffee beans would be wasteful. Because that would lose the distinctive character of the coffee. It's also not good to roast Yauco Specialty and Kona beans black, because then you lose the classic flavor you were looking for when you bought it.
Some coffee beans will develop new and interesting qualities when roasted black. Mexican coffee beans produce an interesting sweet taste when roasted black.
Guatemala Antigua coffee beans tend to retain their acidity and fruity flavor when deeply roasted, which is difficult for other coffees.
Sumatra coffee beans are usually full, but less acidic than medium, and when roasted deeply, they lose their acidity and tend to turn into a sugary paste.
In general, the darker the roast, the lower the quality. A deeper roast means that most of the flavor of the coffee beans will be lost. Roast coffee beans at home

The hardest coffee-related activity is roasting coffee beans at home. When brewing high-quality coffee, the freshness of the beans is crucial.
The easiest way is to roast coffee beans in an oven. The biggest benefit of doing this is that you can adjust the temperature and not let your home smell of roast coffee. Heat the oven to 230 degrees beforehand. Remember to keep air flowing between coffee beans and not spread them too thick. After baking for about 10 minutes, observe the color change. Listen for the crackle of coffee beans and check the color at all times. When the beans are only slightly lighter than you want, remove them from the oven and cool them. The residual heat will keep the coffee beans warm for 2-4 minutes.
Home baking ovens can also be used, but the best are traditional pan or popcorn models. A handle operates two vertical metal blades inside the machine that rotate the beans as they roast. This can be bought at secondhand stores or good kitchen appliance stores, where you can also buy inexpensive oven thermometers.
When the coffee is done, remove it from the roaster and place it in a heatproof bowl. Set the bowl by a window or outdoors.
The grinding of roasted coffee beans into powder is called grinding. The props for grinding coffee beans are called grinders.
The best time to grind coffee is before cooking. Because ground coffee is easy to oxidize and lose flavor, especially in the absence of proper storage, coffee powder is easy to change flavor, naturally unable to cook a fragrant coffee.
Some people are afraid of trouble or do not want to buy a grinder, usually at home to buy coffee has been ground ready-made coffee powder, then pay special attention to the storage problem. If the climate is humid, it is best not to place the coffee powder at room temperature after opening. The more appropriate way is to put it in a sealed jar and put it in the refrigerator, and do not place it with garlic, fish and shrimp and other foods with heavy taste. Because coffee powder is easy to absorb flavor, a careless coffee becomes a strange taste, so even the best quality coffee is ruined. Some people put ground coffee in the refrigerator as deodorant, which is a good way to make the best use of it.
When grinding the beans, the thickness of the powder depends on how it is cooked. Generally speaking, the shorter the cooking time, the finer the ground powder; the longer the cooking time, the coarser the ground powder. In terms of actual cooking, ESPRESSO machines take a very short time to make coffee, so the grinding is the finest, and the coffee powder is as fine as flour; it takes more than a minute to cook coffee in the air, and the coffee powder is medium; American filtered coffee takes a long time to make coffee, so the grinding of coffee powder is the coarsest.
Ground coffee powder with appropriate thickness is very important for making a good cup of coffee, because the extraction of water-soluble substances in coffee powder has its ideal time, if the powder is very fine, and cooked for a long time, resulting in excessive extraction, coffee may be very bitter and lose aroma; on the other hand, if the powder is very coarse and cooked too fast, resulting in insufficient extraction, then coffee will be tasteless, because there is no time to dissolve the water-soluble substances in the powder.
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

Professional coffee roasting knowledge Coffee roasting concepts and principles
Roasting, as the name suggests, provides heat to coffee beans, causing a series of chemical changes to occur within them. Green coffee beans through roasting, showing coffee unique color, flavor and taste. Each coffee bean contains flavor, sourness, sweetness and bitterness. How to release it depends on the roasting temperature. From the tasteless raw beans to the lingering fragrance in the cup
- Next

Professional coffee roasting knowledge coffee grinding process
(1) the principle of grinding, generally speaking, a good grinding method should include the following four basic principles: 1, the degree of grinding suitable for cooking method should be selected; 2, the temperature of cattle produced during grinding should be low; 3, the powder should be uniform after grinding; 4, it should be ground before cooking. No matter what kind of grinder is used, it is bound to generate heat by friction in operation. Most of the excellent substances are highly volatile.
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

