Why do roasted coffee beans smell so good? Did you add flavors and spices?
Professional barista communication, please pay attention to coffee workshop (Weixin Official Accounts cafe_style )
baking
Roasting

Coffee beans must be roasted to have the aroma of coffee, because when roasting green beans, the volatile substances and other components will decompose or interact with each other to form coffee's unique aroma and flavor. Therefore, good coffee beans do not need to add any substances at all, and are themselves a "spice" library.
1
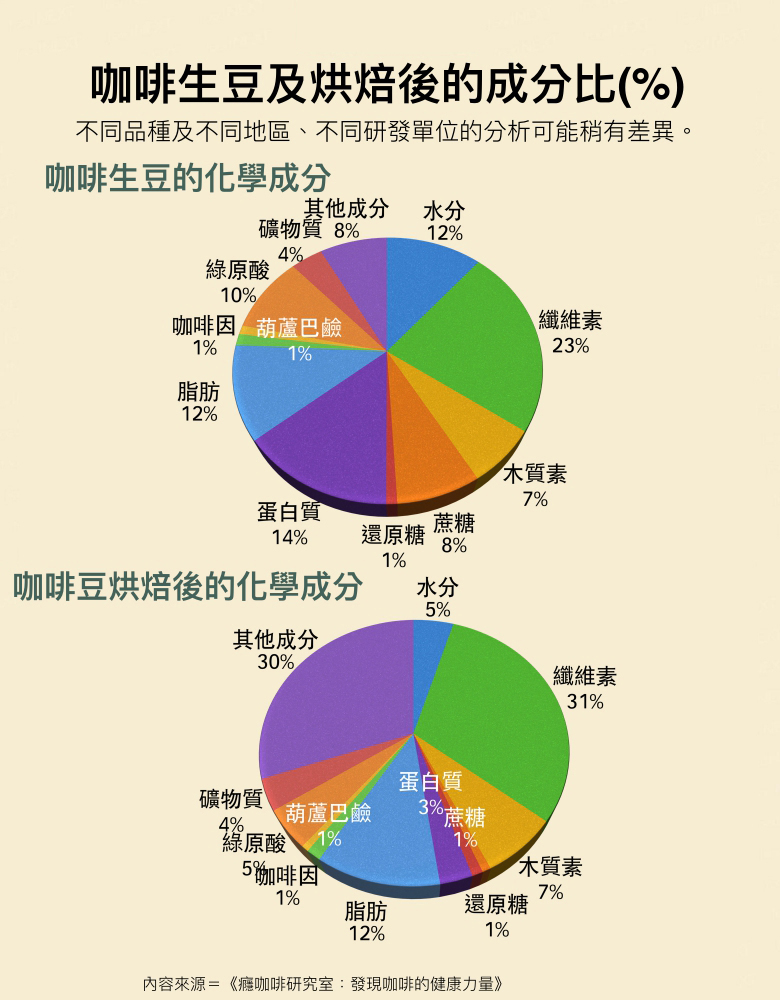
Green coffee beans are warehouses full of chemicals
Nutritionist Jonny Bowden lists coffee as one of the 150 healthiest foods on earth and the No. 1 antioxidant food source in the American diet. Of all the ingredients and drinks, coffee is the most artistic, skillful and varied, but also controversial. Coffee's complex composition, complex manufacturing process, and chemical changes during processing are important basic knowledge carefully studied by coffee researchers and enthusiasts.
Green coffee beans are a warehouse full of chemicals, such as certain types of Arabica coffee, more than a thousand ingredients have been identified, hundreds of which are aromatic, the most aromatic of human drinks.
There are at most 150 vanilla aromas commonly used in the catering industry, and even wine and tea are far less mellow than coffee. Coffee contains many high-quality acids, such as chlorogenic acid, citric acid, malic acid, acetic acid, phosphoric acid and quinic acid, as well as other organic acids, which will be produced with the decomposition of carbohydrates in the baking process. At present, there are as many as 30 kinds of organic acids measured, 15 of which are volatile. In general, organic acid concentrations are highest during medium baking and decrease with heavy baking.
a carbohydrate
The carbohydrates contained in coffee beans can be divided into polysaccharides and low molecular weight sugars, which include mono-, di-and tri-sugars, and can be divided into reducing sugars and non-reducing sugars. In addition, they also contain some sugar derivatives, such as gelatin. Carbohydrates contribute to coffee in terms of aroma and color. In terms of aroma, after roasting, carbohydrates not only emit aroma themselves, but also absorb other volatile aromas, making coffee present different special flavors.
The carbohydrate content of coffee beans is about 38.5%, of which about 8.7% belongs to low molecular weight sugars, which will produce caramelization reaction during the roasting process and be converted into caramel pigments; polysaccharides and pectin are mainly cellulose (23.1%) or lignin (6.7%).
Low molecular weight carbohydrates
Sucrose is the main free carbohydrate in green coffee beans, and its content varies with varieties, sources and maturity. Other simple sugars, such as reducing sugar, can also be detected in the extract of green coffee beans, as well as glucose and fructose.
After roasting coffee beans, low molecular sugar will change, and its changes vary according to the degree of roasting. Sucrose loss is the fastest, with a loss rate of 97% for light roasting, 99% for moderate roasting, and 100% for heavy roasting. As for glucose, fructose, and arabinose, there are also considerable losses.
polysaccharides
This is a very important component of coffee green beans, accounting for about 40 to 50% of the dry matter. According to the classification of types, polysaccharides include polygalactose, polymannose, polyarabinose and cellulose, which are the substances that constitute coffee bean plastids.
Even after baking, polysaccharides will still retain a certain amount, previous studies have found that the degree of baking has little effect, the retention rate is about 70~75%, cellulose retention rate is the highest, polymeric arabinose is the lowest.

Protein and Amino Acid
The protein content of green coffee beans is about 14.4%. After deducting caffeine and trigonelline and other nitrogen compounds, the protein content is about 11.9%. In addition to crude protein, coffee beans also contain a variety of enzymes, such as lipase, proteolytic enzyme, carbohydrase, galactohydrolase and peroxidase. Green coffee beans contain about 0.15~0.25% free amino acids, which have a greater impact on coffee flavor, but have a lower impact on taste. Once green beans are roasted, their protein content will drop to 3.0%.
lipid
Coffee oil, which is present in the endosperm of green beans, and the waxy outer layer of coffee beans together constitute the lipids of green coffee beans. Coffee oil contains triglycerides and a considerable amount of other lipids, but its content and composition will vary according to different varieties, in general, the average content of raw beans is about 11.5%, even if baked, there are still about 97% preserved in the form of lipids.
volatile material
Volatile compounds are the main source of coffee flavor and affect coffee quality greatly. There are many kinds of volatile substances, and their existence conditions will affect the aroma and quality of coffee. When roasting green beans, especially volatile substances are cut off or derived after reaction. Any thermal decomposition or interaction between components, such as sugars, amino acids, organic acids and phenolic compounds, will form coffee's unique aroma and flavor.

In addition, factors affecting the volatile composition of coffee include bean variety, climate, soil conditions, storage of raw beans, roasting temperature and time, and roasting equipment.
Green coffee beans must be roasted to produce the coffee aroma we usually smell. Before roasting, there is no special aroma of coffee. At present, it has been determined that the volatile aroma in raw beans can produce at least 650 kinds of aroma after roasting, such as hazelnut flavor, cream flavor, caramel flavor, grass flavor, smoky flavor, burnt flavor, spicy flavor and bitter flavor, etc., which are the most volatile aroma components in all foods and beverages. In addition, the degree of roasting will also affect the flavor of coffee.
moisture
With different processing stages and products, the moisture content of coffee beans varies greatly, including wet coffee beans with film, its moisture content is about 50%, dried green coffee beans are about 11.5%, and roasted coffee beans have only about 4.8% moisture content. Because coffee beans contain a considerable amount of water colloidal macromolecular substances, such as proteins and polysaccharides, can combine water in a variety of different physical and chemical ways, and exist in beans.

Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev
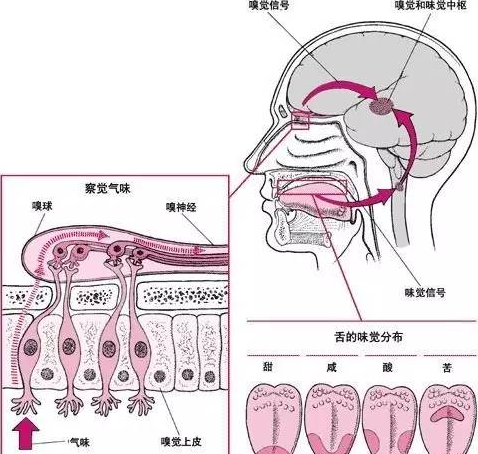
What are the senses and coffee flavor?
Following Cafe (Wechat official account vdailycom) found that Beautiful Cafe opened a small shop of its own. What is the sense of sense organ? the magical human body has organs that sense the stimulation of external things: eyes, ears, nose, tongue, body, etc., corresponding to vision, hearing, smell, taste and touch. If you want to have a good cup of coffee, you need at least three senses: smell and taste.
- Next

Coffee beans World ── Coffee defective beans World
Communication of professional baristas Please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) to introduce you to the world coffee growing environment of defective beans. The difference in appearance of coffee beans comes from different growth environments. The growth belt of coffee usually consists of the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Cancer and tropical areas near the equator. Unique coffee varieties are grown in special growth areas, categories of coffee beans and
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

