Popular science | Nutrition and composition analysis of coffee beans
For professional baristas, please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style)
Many people like to have a full-bodied cup of coffee for breakfast in the morning, and enjoy a snack cake and mellow coffee at tea time, but those who like coffee also need to understand the ingredients in coffee beans. in order to understand their own nutrition, but also know the effect of coffee on the body and changes in the flavor of coffee.
The nutrients and ingredients of coffee beans can be roughly divided into 8 different nutrients and ingredients. Here are the ingredients of coffee beans one by one, and their effects on the body and coffee flavor:
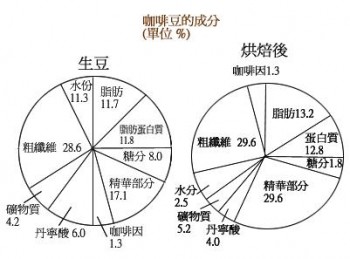
Caffeine: source of bitterness. An appropriate amount of caffeine increases the rate of cell metabolism and stimulates the central nervous system, cardiovascular system, respiratory system, gastrointestinal tract, muscles and kidneys. Wait.
Tannin: the source of sour taste. Boiling will decompose to produce pyrosylic acid, and too much tannic acid will cause the coffee to taste astringent.
Fat: the fat contained in coffee beans can be roughly divided into acidic fat and volatile fat, which are described as follows:
Sour fat: that is, fat contains acid, its strength will vary according to the type of coffee.
Volatile fat: the source of coffee aroma, will emit 40 aromatic substances, but also will evaporate due to exposure to air.
Protein: the source of calories. But the protein in coffee is not easy to dissolve, so the calorie intake is limited.
Sugar: the source of sweetness and color of coffee. After roasting, the sugar in the coffee beans is converted into caramel. The combination of caramel and tannic acid will make the coffee astringent and sweet.
Crude fiber: the source of coffee color. The fiber of raw beans will be carbonized after baking. When carbon fiber is combined with caramel, the color of coffee is formed.
Minerals: slightly astringent source. There are a small amount of lime, iron, phosphorus, sodium carbonate and so on.
Water: raw beans contain about 11% moisture, leaving about 2.5% after baking.

Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

The 11 Most Expensive Coffee in the World, You Must Not Have Drank All of It
Coffee is a beautiful enjoyment. In the past, coffee seemed to be a luxury enjoyment, but now it can be close to the people and luxurious. Consumers who like luxury enjoyment can try the most expensive coffee in the world by Forbes in 2006 and experience the luxurious aroma and flavor. Name: Musk
- Next

Correlation between coffee beans and grinding degree and cooking machines and tools
Professional barista communication Please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) Coffee is a science, the deeper the knowledge, the more difficult it is to read. In addition to making a perfect cup of coffee, there are many specialties. It seems like a simple grinding, but there are many details to pay attention to. If the grinding fails, the flavor of the coffee extraction will be consumed. one
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

