How to pass the Q-grader exam (3) there are 8 major items, a total of 20 subjects
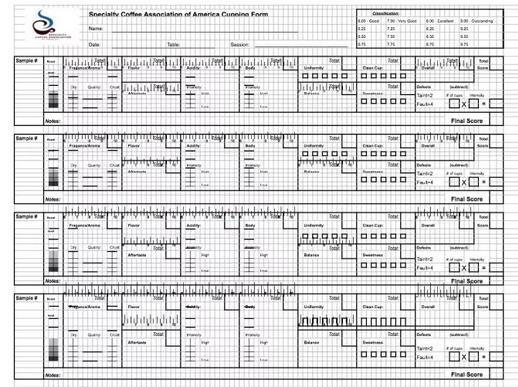
SCA cup test table
If you sign up for the Q grader test, you should already know how to use the SCA cup test form correctly. In order to practice this part of the test, it is recommended that you test a large number of cups of coffee from different places and different processing methods. You should understand the flavor of coffee in different regions and how these flavors are expressed in the cup test.
Matters needing attention
Find out the coffee you don't know and test them frequently so that through practice you can understand the flavor related to the origin or processing process. Note that most roasters have their own coffee baking curves, and coffee flavors vary slightly from roaster to roaster. Take a cup test with your friends to see what they think of coffee.
Raw bean
This part of the exam is to fill in the raw bean scoring form and make a physical analysis of the coffee. This is an important skill. You should carefully study the grading criteria of forms and raw beans to understand the difference between primary and secondary defects and their causes. During the exercises and exams you will have a manual on defects in Arabica coffee beans to help you read and identify defects. The grading score is mainly aimed at the raw bean quality of coffee, not the roasting quality of coffee.
Matters needing attention
Don't make too harsh an assessment of raw coffee beans. Just find out the defects of raw beans that you have the confidence to identify.
If any defect does not appear in the Arabica coffee raw bean defect manual, then it should not be regarded as a defect.
Coffee roasting recognition
The degree of roasting can affect people's perception of coffee quality and flavor. A Q-grader should be able to identify baking flavor defects such as underdeveloped, baked, etc. This part of the exam for coffee roasters should not be difficult. If you are not familiar with evaluating the degree of roasting, ask a baker to bake you some samples of coffee with different roasting degrees for practice
In the exam, you need to taste five roasting degrees of coffee: extremely shallow roasting too light, roasting just right correctly, roasting too deep too dark, underbaking underdeveloped, and roasting baked.
Extremely light roasted too light coffee has a strong citric acid and a low sugar content that is easy to identify. Coffee that is too deep-roasted too dark is also easy to recognize. The acidity is so low that most of the acid volatilizes during roasting and is replaced by the flavor of sugar browning.
Roasted underdeveloped coffee underdeveloped will have some special flavors, such as cereal and vegetable starch (peas). If you are not a baker, it is difficult to recognize the taste of baking baked. The roasting degree of roasted coffee baked can be very light (shallow), but the roasting time is too long (related to the low bean temperature) and the acidity is very low. Some cup testers associate the taste of baking with the taste of toast.
Conclusion
The Q-grader exam is not as simple as walking in the park. It is challenging even for experienced cup testers. You must pass 20 separate tests to become a qualified Q-grader. The most comprehensive guide I found came from Coffee Strategies. You can also sign up for preparatory courses before the exam, which can help you prepare for the exam in less time and at a lower cost.
Some people vowed to eat light food during the test. I agree that eating strong-smelling food will affect your body's perception of taste, but don't go too far. If you are a smoker, I do not recommend that you give up smoking during the Q exam. When I quit smoking, the taste of coffee became different for me, and I had to work hard for months to bring my taste back to sync with my colleagues. Similarly, spicy food is the same as smoking. If spicy food has been part of your sensory vocabulary for coffee in the past few years, (if you stop eating spicy food during the exam) you may find it hard to get back to your old taste / feeling habits. If you must choose to quit smoking or stop eating spicy food, I suggest starting the process weeks or months before the exam.
If you are a smoker, or choose to eat a plate of garlic the night before, and other students will smell these smells during the exam, you may interfere with their exams, so pay attention to and respect others.
The Q-grader exam is challenging both mentally and physically. If you are not used to cups of coffee many times a day, you will soon become overwhelmed. Don't plan any other social activities during the exam. Have a good rest, eat well, and be ready both physically and mentally.

The following content is from the Internet for reference only
The Q-Grader exam consists of 8 items and a total of 20 subjects.
The first major item (4 subjects) sniffing bottle is tested together for every 2 subjects, with a time limit of 1 hour;
The second major item (1 subject) has a grading time limit of 1 hour for raw beans;
The third major item (2 subjects) ripe bean classification;
The fourth major item (1 subject) organic acid time limit of 1 hour;
The fifth major item (3 subjects) sensory skills test is limited to 1 hour;
The sixth item (4 subjects) triangle cup test is limited to 45 minutes per subject;
The seventh item (4 subjects) cup test score is limited to 1 hour for each subject;
The eighth item (1 subject) theory question written test time limit 1 hour.
The first big smell bottle
There are 4 subjects in total, each 2 subjects are tested together, and the time limit is 1 hour.
1. Enzyme Reaction (9 bottles)
2. Caramelization (9 bottles)
3. Dry distillation reaction (9 bottles)
4. Flawed Flavor (9 bottles)
Test format: 9 bottles of this group were placed on one side as reference group, and 6 bottles were placed on the other side, covered with adhesive tape.
Test environment: red classroom.
9 smelling bottles cover the smell of 6 smelling bottles. First, it is necessary to judge the serial numbers of 6 smelling bottles by relying on the reference group (each smelling bottle has its own serial number, and the bottle body of the reference group has no cover and the smell is the same, so the serial numbers of 6 smelling bottles can be filled in), and secondly, what is the smell of 3 smelling bottles?
Experience:
When practicing, you need to remember what the number of the 36 smelling bottles corresponds to, and then you can fill in the name of the smell of 3 bottles in the 6 bottles of the test group through the number of the bottles in the 9 reference groups. For example, smell bottle A in the test group and bottle 7 in the reference group smell is the same, previously known by memory that number 7 is "clove", so you can get the answer-bottle A corresponds to number 7, bottle A smell is "clove".
Recommendations:
Before the exam, find a set of smelling bottles to practice. When practicing, divide them into 4 groups corresponding to the exam. To close your eyes and pick out a bottle at random, you can accurately say the serial number and smell of its bottle through smell.
The second largest category of raw bean classification
Time limit 1 hour.
Test format: 3 boxes of raw beans per person, 350g per box, select defective beans according to SCAA standards, and distinguish which are Class I defects and which are Class II defects, calculate scores, summarize scores, and finally determine what grade this box of raw beans is (fine grade or commercial grade).
Test environment: Regular environment.
Excellent grade: 0 grade 1 defects, less than or equal to 5 grade 2 defects.
A green bean has both grade 1 and grade 2 defects, which are calculated as grade 1 defects.
Exam Notes:
One hour needs to select 3 boxes of raw beans and complete 3 reports of raw beans. The time is relatively tight, which requires candidates to remember the appearance and corresponding scores of the above two types of defective beans.
One of the things that is most likely to be missed during an exam is a foreign object with a flaw, such as a fiber.
Third largest ripe bean classification
There are 2 subjects in total--ripe bean screening and ripe bean sample identification
15 minutes for ripe beans
Cooked bean sample identification time limit 45 minutes
1. ripe bean screening
Test format: 100g cooked beans per person, select white beans, count the number of white beans, and grade the box of cooked beans according to this number (fine grade or Q-Grader grade or commercial grade).
Test environment: Regular environment.
Number of white eye beans corresponding to the level:
(1)0 A: Fine coffee
(2)1-3 pieces: Q grade coffee
(3)3 More than one: commercial grade coffee
Experience:
Relatively speaking, this item is relatively simple. Spread 100g of cooked beans. The color of white beans is relatively light and basically clear at a glance.
2. identification of ripe bean sample
Test format: 5 cups of coffee, including 1 cup of slow roast coffee, 1 cup of dark roast coffee, 1 cup of light roast coffee, 1 cup of normal roast coffee and 1 cup of repeat coffee (this cup of coffee may be the same as any of the first 4 cups). Determine which type of coffee these 5 cups are by cup test.
Test environment: red light classroom.
Experience:
Slow roast coffee is relatively bland, with a light barley flavor.
Deep-roasted coffee is easier to identify and will be relatively bitter.
Light roast coffee is relatively sour, especially at low temperatures.
Normally roasted coffee is relatively saturated in flavor and acidity.
Personal feelings are easier to discern at low temperatures. This item has 45 minutes. Don't worry.
Organic acids in Division 4
1 hour
Test format: A total of 8 groups of coffee, each group of 4 cups, candidates need to first pick out 2 cups of acid in these 4 cups of coffee, and then identify which acid.
Organic acids in the test include malic acid, citric acid, acetic acid and phosphoric acid.
Test environment: red light classroom.
Experience:
Of malic acid, citric acid, phosphoric acid, and acetic acid, acetic acid is the most volatile, so when the acidity of two cups of sour coffee in a group is felt to be extremely weak, it must be acetic acid. Phosphoric acid gives the tongue a certain astringency, and the acid strength is weaker than malic acid and citric acid, and stronger than acetic acid. The difference between malic acid and citric acid depends on both sides of the tongue and the root of the tongue. Malic acid is relatively sweet, and citric acid is the other.
Sensory Skills Test
A total of 3 subjects are limited to 1 hour, i.e. sweet and sour salt water examination
Subject 1
Test format:
Each person has 9 cups of white water, which is added with sour, sweet and salty flavors. Each flavor is divided into 3 different concentrations: weak, medium and strong. The test is divided into three groups to provide candidates, acid 3 concentrations for a group, sweet 3 concentrations for a group, salty 3 concentrations for a group, candidates after drinking each taste concentration to fill in the cup number.
Test Environment: Regular Environment
subject 2
Test format:
There are 9 cups of white water for each person, and the above 3 flavors are also added, but instead of grouping them separately, the cups of 3 flavors and 3 concentrations are mixed together. After drinking, the examinee writes down the flavor and concentration corresponding to the cup number.
Test Environment: Regular Environment
Subject 2 Pass Criteria
11 points per cup-6 points for "taste" type, 5 points for "taste" intensity
Out of 99, 79 passes.
subject 3
Test format:
Each person has 8 cups of white water in total. Add at least 2 flavors to each cup of water (8 cups, 4 cups add 3 flavors, and the other 4 cups add 2 flavors). The taste and concentration of each cup of water are different. After drinking, the examinee should write down which flavors and concentrations correspond to the cup number.
Test Environment: Regular Environment
Subject 3 Pass Criteria
4 points for the type of taste and 2 points for the intensity of taste in each cup
Out of 96, 68 passes.
Experience:
1. Subject 1, because the three subjects are tested together, the time limit is 1 hour, and the last level is the most difficult, so the first level needs to be completed as soon as possible to make time for the later exams.
2. Subject 2, taste all 9 cups first, then classify the solutions of sour, sweet and salty flavors, i.e. weak acid, medium acid and strong acid together, weak sweet, medium sweet and strong sweet together, weak salty, medium salty and strong salty together, and then identify their concentration strength by comparison as in the first pass.
3. Subject 3, the last level is called "Devil's Water".
First emphasize: sour + sweet--increase sweetness; sour + salty--reduce sourness; salty + sweet--there will be no change in taste concentration. Secondly, the solution can be refilled after drinking, so if you really can't taste it, drink it down and the effect will be more obvious. Finally, when you taste it, you must be quiet and carefully feel the taste with your tongue. Most of them can be identified.
The sixth largest triangle cup test
There are 4 subjects in total. Each subject is limited to 45 minutes.
Test format:
There are 6 groups of 3 cups of coffee in each group, one of which has a different flavor than the other 2 cups. You need to write the different cup number on the answer sheet.
This exam requires starting from smelling the dry fragrance of coffee powder, filling water, smelling wet fragrance, breaking slag, fishing slag, cup test all rely on the examinee to complete, so the exam can be judged according to their own smell and taste.
Test environment: red light classroom
Experience:
Through the smell of dry incense link, preliminary judgment answer;
Smells the wet fragrant link, confirms or changes the answer;
High temperature cup time test to confirm the answer;
Cryogenic cup test time is the last to confirm the answer.
Each person distinguishes the flavor accuracy time period is different, some people smell dry incense when the identification accuracy will be high, then mainly rely on this link identification, some people low temperature cup test when the identification accuracy is high, then wait for cooling to determine the answer.
The seventh item cup test score
There are 4 subjects in total. Each subject is limited to 1 hour.
Test format:
There were 6 groups of 5 cups each, and coffee was scored by filling out the SCAA cup test.
This examination requires that the test starts from grinding beans, smelling the dry fragrance of coffee powder, injecting water, smelling wet fragrance, breaking residue, fishing residue, cup test are all completed by the examinee.
Test Environment: Regular Environment
The eighth theoretical question written test
100 multiple-choice questions, 1 point per question, 75 points pass. Time limit 1 hour.
The written examination covers a wide range of subjects, examining the accumulation and reserve of coffee knowledge, covering cup testing knowledge, extraction knowledge, cultivation, processing, storage, roasting, production area and trade, etc.
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev
There are many kinds of coffee beans roasted at home. How to quickly choose your favorite coffee beans?
Professional barista communication Please pay attention to coffee workshop (Weixin Official Accounts cafe_style) There are many kinds of coffee beans roasted by their own house. Common coffee beans named after producing countries or regions, such as Ethiopia, Mantenin, etc., as well as special beans with beautiful names. For beginners who taste coffee for the first time, they may be confused by exquisite items. What are single beans?
- Next

Start to distinguish the flavor from the degree of baking and try to choose a cup of coffee with your own style.
Communication of professional baristas Please follow the coffee workshop (official Wechat account cafe_style) We often forget that coffee beans are fruits, and different kinds of coffee from different places have their own local flavor. Roasting is more like the magic of coffee, turning coffee beans into mellow drinks with different characteristics. Light roasting, medium roasting, medium-deep roasting and deep roasting each have their own unique flavor, just like a human being.
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

