Africa Kenya AA hand-made coffee beans are so sour how to do Kenya AA coffee introduction

Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style)
When it comes to African coffee beans, you will certainly think of Ethiopian and Kenyan boutique coffee beans represented by acid. Today, Qianjie Coffee is going to talk about Kenyan coffee. Although Kenya borders Ethiopia and is also famous for its acidity, they are quite different in their sour flavor. Qianjie Coffee believes that the present success of Kenyan coffee is inseparable from the history of the first British colonial rule in Kenya, which created a very harsh living environment for local farmers at that time. However, it has brought a fine management model of the coffee industry, but it has provided a direction for the future development of coffee in Kenya.

Kenyan coffee
Kenya is located in eastern Africa and borders Ethiopia, the birthplace of coffee. It was not until near the 20th century that Kenya introduced coffee, during which coffee almost circled the world before returning to Africa. But Qianjie Coffee believes that although Kenyan coffee started late, it developed rapidly. Under British colonial rule, whether it was the establishment of the cultivation mechanism or the establishment of a grading system, Kenyan coffee beans all led to the boutique coffee market. Kenyan boutique coffee is now famous all over the world, and Qianjie Coffee summarizes the following reasons:
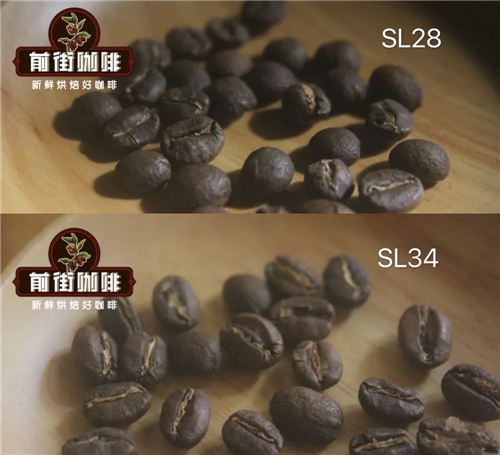
1. The establishment of cultivation mechanism. In 1883, Britain brought coffee to Kenya from Reunion Island. In 1922, Kenya established the Scott Agricultural Laboratory (hence the name Scott Labs,SL28 SL34) to engage in coffee cultivation research. In more than 10 years after its establishment, the laboratory selected SL28 and SL34 from 42 kinds of coffee, which provided a good start for the development of coffee industry.

2. The attention of the government. In 1931, the Kenyan growers' Cooperation Union and the Kenyan National Coffee Council were established to guide the development of the coffee industry at the private and national levels. In 1937, the Nairobi Coffee Exchange was established and the auction system of Kenyan coffee began. Good coffee has a good price, which sets the tone for the price of coffee. In particular, this year the Kenyan Ministry of Agriculture launched a coffee revitalization program of 1.5 billion shillings.
3. The determination of grading system. Kenya is graded according to the particle size and cup test results of coffee beans. According to the size, shape and hardness of coffee beans, from high to low is AA or AA+, AB, PB, C, E, TT, T. For the raw coffee beans of AA grade and AB grade, the special classification of cup test results (not officially recognized by Kenyan countries, made by exporters) is added, and the order from high to low is TOP, PLUS (+) and FAQ.
AA grade with excellent quality (flavor, taste) in AA Plus (AA+) cup.
AA particles: size (Screen Size) 17-18 mesh.
AB particles: size (Screen Size) 15-16 mesh, accounting for the majority of output.
C particles: those whose size (Screen Size) is smaller than AB.
TT from AA and AB beans: lighter beans blown out with an airflow filter.
T from Class C beans: lighter beans blown out with an airflow filter.
E Elephant Bean: two beans into one of the large mutant beans, also known as elephant ear bean Elephant ear.
PB Peaberry: classified by appearance, independent of flavor weight.
For the raw coffee beans of AA grade and AB grade, the special classification of cup test results (not officially recognized by Kenyan countries, made by exporters) is added, and the order from high to low is TOP, PLUS (+) and FAQ. The Kenyan Asalia flavor level on the front street coffee bean list has reached the TOP level, but as mentioned earlier, this is not an official grading system, and not every coffee bean collected in front street coffee from several Kenyan producing areas has a flavor grade, so there is no need to worry too much about this piece, generally reaching the AA level and AB level, the flavor is actually very high quality by default.

4. K72 treatment. The unique acidity of Kenyan boutique coffee has a lot to do with its excellent treatment. General washing method, screening of mature coffee fruit, peel pulp, soak in the tank fermentation to remove pectin, this process is rarely more than 36 hours, but the fermentation time in Kenya is as long as 72 hours. Then dry it until the moisture content reaches 12%. Qianjie believes that Kenya's unique water washing treatment can make Kenyan coffee beans reflect bright acidity and full juicy taste.
Kenyan coffee producing area
Kenya's coffee producing areas are mainly distributed in the central and western parts of the country. The main coffee producing areas in central Kenya are Kiambu, Nyeri, Kirinyaga, Muranga, Embu, Machakos, Ruiri, Thika, Kisii and Mt in the west. Bungoma district of Elgon).
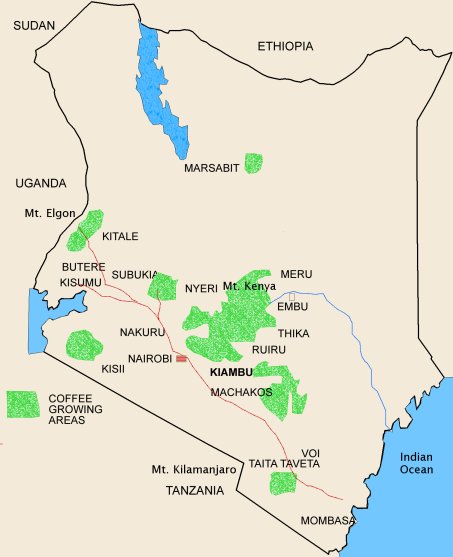
Qianjie Coffee updates the coffee producing areas on the bean list every once in a while, and Kenya is no exception. Last month, Qianjie Coffee collected a batch of Kenyan coffee beans from different coffee producing areas. Through roasting, cup testing, hand brewing and other links, it can be found that each producing area has its own different characteristics. Boutique coffee producing areas are mainly from the following areas: Nyeri, Kirinyaga, Murang'a.
Nyeri (Nieli)
Nyeri, a Nyeri producing area in central Kenya, is home to the extinct volcano Mount Kenya. The red soil in this area breeds the best coffee in Kenya. Agriculture is extremely important in this area, and coffee is the most important crop. The common cooperatives composed of small farmers in Nyeri producing areas are more common than large manors.
Altitude: 1200 to 2300 m
Harvest period: October to December (main production season), June to August (by-product season)
Varieties: SL-28, SL-34, Ruriu11, Batian.

Muranga (Mulanga)
The Muranga producing area belongs to the Central Province, where there are about 100000 coffee farmers. This inland producing area was the place of settlement chosen by the first missionaries because Portugal banned them from living in coastal areas. It is also another producing area that benefits from volcanic soil, with more small coffee farmers than manors.
Altitude: 1350 to 1950 m
Harvest period: October to December (main production season), June to August (by-product season)
Varieties: SL-28, SL-34, Ruiru11, Batian
Kirinyaga (Kirin Yajia)
Kirinyaga is located on the hillside of Mount Kenya, close to Nyeri. It is famous for its strong flavor, rich layers and solid taste of coffee. Together with Nyeri, it is recognized as the two best producing areas in Kenya. Most of the producers in this area are small coffee farmers who join the cooperatives, while the cooperatives play an integrated role, providing washing plants, and coffee farmers send the coffee fruits to the cooperative processing plants for processing.

"Kirinyaga" originally refers to Mount Kenya, but when the British colonized the mountain, they found it difficult to remember, so they changed the name of the mountain to "Mt Kenya" instead of "Kirinyaga". Mount Kenya is the second highest peak in Africa. Although it is located in the tropics, the mountain is often covered with snow. Kirin Yajia originally means "white peak". Mount Kenya is not only a United Nations protected area, but also the surrounding foothills and grasslands, where wild animals gather and forage, and is a favorite attraction for tourists. "Kirinyaga" comes from the Kikuyu, which means "white mountains" and is thought to be the place of the gods. The Kikuyu are the most populous people in Kenya, accounting for 1/5 of the total population.
Altitude: 1300 to 1900 m
Harvest period: October to December (main production season), June to August (by-product season)
Varieties: SL-28, SL-34, Ruiru11, Batian.
Kenyan auction system
Qianjie Coffee mentioned earlier that in the history of colonial rule in Kenya, local farmers did not benefit much from coffee. This is also a dark moment in the history of coffee cultivation in Kenya. In 1931, in order to enable farmers to win better prices and incomes and no longer be subject to distant excessive traders, the government set up the Kenyan growers' Cooperation Alliance and the Kenyan National Coffee Council to set up an auction mechanism. The Nairobi Coffee Exchange was established in 1937, when the auction trading system became more popular and widely supported.
Most of the coffee beans are graded and then sold at the auction site by the Kenya Coffee Bureau. The system of public auction can be traced back to 1934, and the auction method adopts the agent system. There are 50 licensed agents in Kenya who send sample beans to their customers for cup testing. Customers can bid for their favorite coffee by agents at auction. But this approach seems to encourage intermediaries to erode farmers' incomes, so in 2006 Kenya opened 32 more independent sales agents to approach foreign coffee buyers directly without going through auctions. However, all these must meet the standards such as the guarantee of the quality storage bank by the Kenyan Coffee Agency. The two systems operate in parallel at the same time. After several years of development, the most transparent auction distribution system is. The better the quality of coffee, the better the price can be measured through the cup. More cooperatives and farms are willing to join. Qianjie Coffee also pays close attention to the coffee auction market, which can not only understand the changes in the local coffee market, but also benefit not only farmers but also buyers from all over the world.
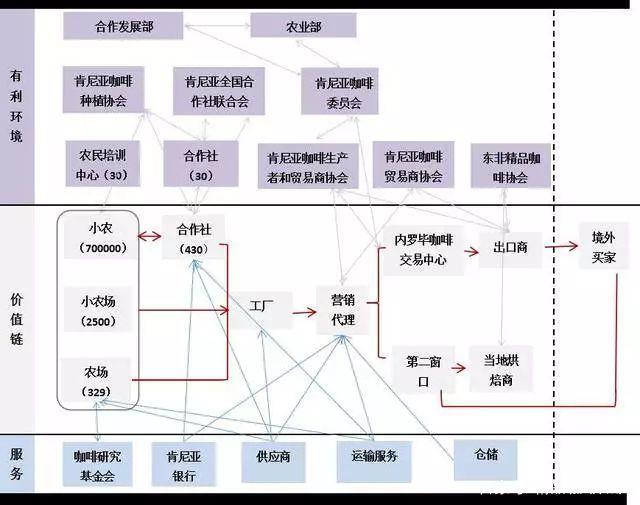
There are two main modes of trading coffee beans in Kenya:
① Nairobi Coffee Exchange auction (central auction system), 85% of coffee beans are traded through the auction system. Since the establishment of the auction system in the 1930s, most Kenyan coffee has been traded in this way. Coffee auctions are held every Tuesday during the harvest season. It is an auction system developed from a "public outcry" auction system, in which each trader bids by pressing an electric trigger. Through this system, the price of high-quality, highly popular coffee will soar as agents compete with each other.
② direct trade (often referred to as the "second window"), only 15 per cent of coffee beans are traded through direct trade. After 2006, the Kenyan government allowed farmers to trade directly with foreign buyers (such as bakers or importers) and to discuss and determine a price different from that of auctions before or during harvest. Some exporters also buy coffee directly from relevant marketing agents or factories, using the previous week's specific grade auction price as a negotiated reference price. Direct trade can lead to more income for farmers who produce high-quality coffee. When direct trade is not feasible, go back to the exchange and sell it by auction.
Coffee planting model in Kenya
Kenyan coffee consists of two main growing areas: large plantations and more than 3000 large farms, which account for about 25 per cent of Kenya's coffee-growing land. The other 75 per cent are agricultural cooperatives, consisting of a total of 700000 small-scale farmers.

In the 1960s, small farmers' cooperatives began to develop and build common processing plants to enable them to harvest and process coffee like large plantations. Qianjie Coffee believes that this model can make curry farmers focus on coffee cultivation and production. For example, the main coffee planting model in Ethiopia is also small farmers' cooperatives, a batch of Yejasefeckonga cooperative coffee beans collected in Qianjie coffee some time ago. There is an excellent flavor.
After several rounds of tasting, Qianjie coffee has been screened out from more than a dozen different producing areas, and only two or three coffee beans will eventually be put on the shelves. It is not that the rest of the coffee beans are not good. The original intention of Qianjie coffee is not to sell, but in this process, the purpose of Qianjie coffee is to understand each coffee producing area, different coffee varieties in the same producing area, and different treatments of the same coffee variety. And set up the corresponding database, as well as the comparison between different coffee producing areas, Qianjie Coffee hopes to let more coffee lovers know about the world of coffee.

Front Street Coffee-Asalia Coffee beans in Kenya
Producing area: Sika Thika, Kenya
Processing plant: Asali honey processing plant
Altitude: 1550-1750 m
Rating: AA TOP
Variety: SL28,SL34
Treatment: 72-hour washing in Kenya
Qianjie Coffee Baking record
This bean is full and round, and Qianjie coffee is roasted lightly in order to fully show its bright and mellow acidity. Yangjia 800N semi-direct fire, bean dosage 480g: furnace temperature to 160 degrees Celsius into the pot, throttle open 3, firepower 120. Temperature recovery point: 1 temperature rising to 130 degrees, throttle opening 4. Baking to 6: 00 ", temperature 154.6 degrees, bean surface turns yellow, grass smell disappears completely, dehydration is complete.
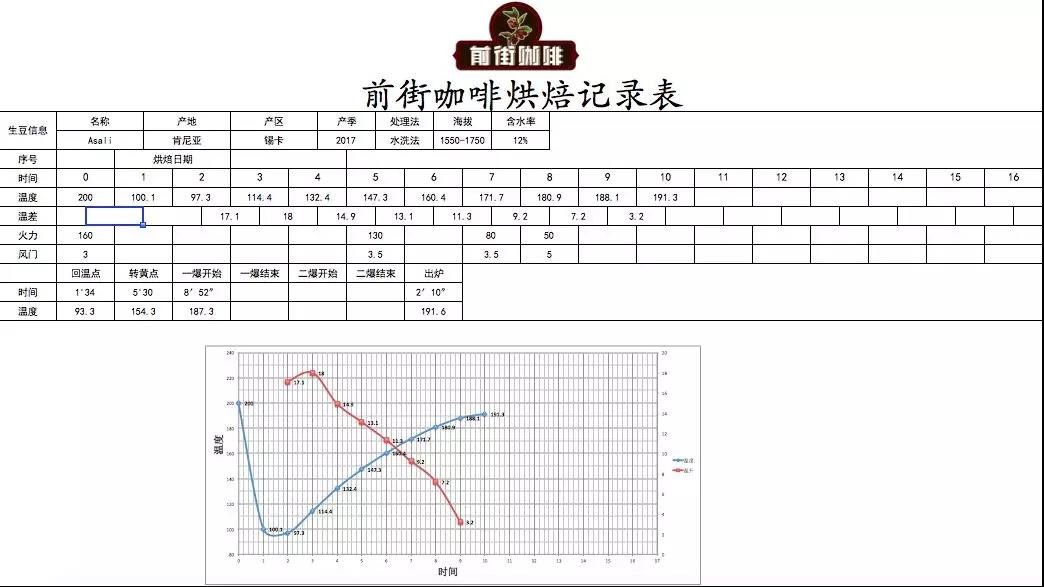
When the bean surface appears ugly Hu wrinkles and black markings, the smell of toast obviously changes to the smell of coffee, which can be defined as a prelude to an explosion. At this time, it is necessary to listen carefully to the sound of the explosion point, to 9: 28 ", the throttle remains the same, and the development time of the explosion is 2: 20". Put the pot at 193.8 degrees.
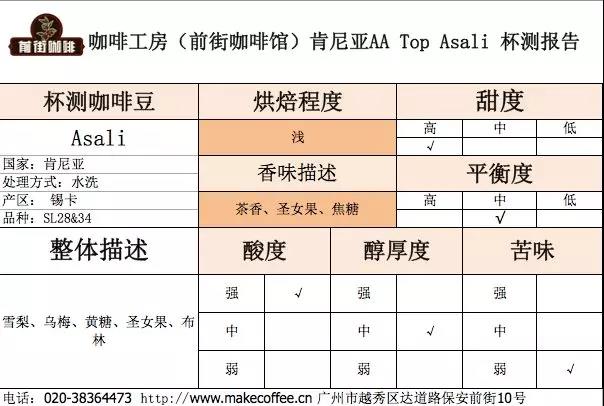
Coffee cup test report on Qianjie
Suggestion on brewing coffee in Qianjie
Filter cup: Hario V60
Water temperature: 90 ℃
Amount of powder: 15g
Powder / water ratio: 1:15
Degree of grinding: BG#6s (76% of the pass rate of Chinese standard No. 20 screen)

Qianjie coffee brewing technique: use 30 grams of water for steaming for 30 seconds, small water flow round the circle to 125 grams for segments, when the water level is about to expose the powder bed, continue to inject water to 225 grams to stop water injection, wait for the water level to drop and remove the filter cup when the powder bed is about to be exposed, (the time of steaming starts) the extraction time is 2 minutes 39 percent 00 ".
Flavor description: the wet fragrance has ripe tomato and flower aromas, imported virgin fruit and black plum flavor, bright acidity, clean and rich taste, outstanding sweetness in the middle, fruit juice, raspberry and yellow sugar on the finish, and green tea aroma.

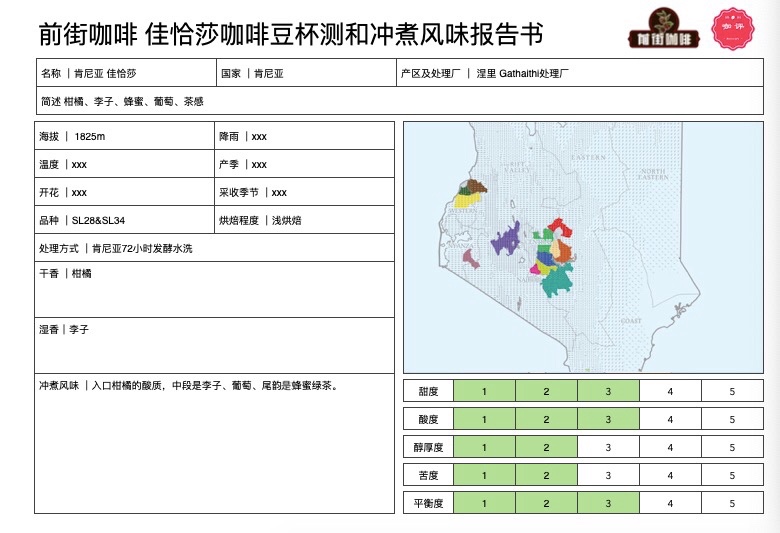
Qianjie Coffee-Kenya Gachasha Cooperative AB Coffee Bean
Producing area: Neri Gachasha Cooperative, Kenya
Processing plant: Gathaithi processing plant
Altitude: 1825m
Variety: SL28&SL34
Treatment: K72 washing
Suggestion on coffee baking in Qianjie
The front street baker uses Yang family 800N semi-direct fire, the amount of beans is 480g: the furnace temperature is 160 degrees Celsius, the throttle is 3, and the firepower is 120. Temperature recovery point: 1 temperature rising to 130 degrees, throttle opening 4. Baking to 6: 00 ", temperature 154.6 degrees, bean surface turns yellow, grass smell disappears completely, dehydration is complete.
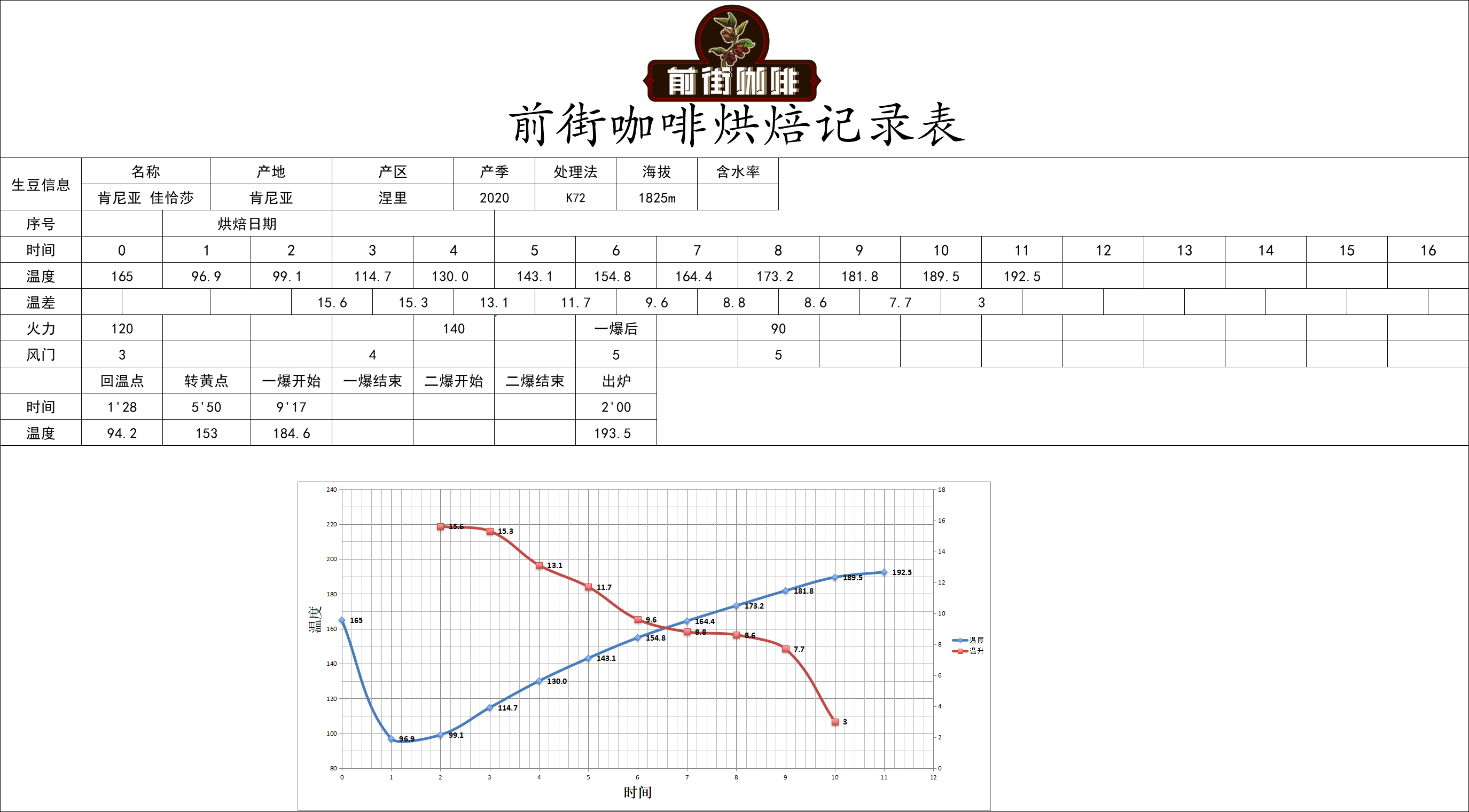
When the bean surface appears ugly Hu wrinkles and black markings, the smell of toast obviously changes to the smell of coffee, which can be defined as a prelude to an explosion. At this time, it is necessary to listen carefully to the sound of the explosion point, to 9: 28 ", the throttle remains the same, and the development time of the explosion is 2: 20". Put the pot at 193.8 degrees.
Coffee cup test report on Qianjie
Suggestion on brewing coffee in Qianjie
Filter cup: Hario V60
Water temperature: 90 ℃
Amount of powder: 15g
Powder / water ratio: 1:15
Degree of grinding: BG#6Q China Standard No. 20 screen pass rate 77%)

Qianjie coffee staged extraction, with 30 grams of water for steaming for 30 seconds, small flow circle injection to 125 grams for stages, water level drop is about to expose the powder bed, continue to inject water to 225 grams to stop water injection, and so the water level drop is about to expose the powder bed to remove the filter cup, (steaming starts timing) the extraction time is 2 minutes 39 percent 02 ".
Flavor description: obvious black plum and virgin fruit, almonds in the middle and honey at the end, juice-like taste and bright acidity.
For more boutique coffee beans, please add private Qianjie coffee on Wechat. WeChat account: kaixinguoguo0925
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

Introduction to the flavor characteristics and flavor description of Costa Rican hand-made coffee beans
For the exchange of professional baristas, please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) today to share with you a demonstration of the comparative brewing of Costa Rican coffee hand siphon. The protagonist is Moza, the musician series of raisins from Carnett Manor in the Tara Pearl region of Costa Rica.
- Next
The eight major producing areas and microclimate of Guatemalan coffee create a perfect flavor.
Have you ever wondered how many stories are behind this beautiful cup of coffee? This article discusses the micro-climate features that are closely related to Guatemalan coffee. After the impact of the Kuroshio movement, people gradually began to have professional knowledge and technology related to the coffee industry. In addition to the annual large-scale coffee-related exhibitions, baristas competitions, and the rapid development of baking equipment, we are interested in
Related
- Detailed explanation of Jadeite planting Land in Panamanian Jadeite Manor introduction to the grading system of Jadeite competitive bidding, Red bid, Green bid and Rose Summer
- Story of Coffee planting in Brenka region of Costa Rica Stonehenge Manor anaerobic heavy honey treatment of flavor mouth
- What's on the barrel of Blue Mountain Coffee beans?
- Can American coffee also pull flowers? How to use hot American style to pull out a good-looking pattern?
- Can you make a cold extract with coffee beans? What is the right proportion for cold-extracted coffee formula?
- Indonesian PWN Gold Mandrine Coffee Origin Features Flavor How to Chong? Mandolin coffee is American.
- A brief introduction to the flavor characteristics of Brazilian yellow bourbon coffee beans
- What is the effect of different water quality on the flavor of cold-extracted coffee? What kind of water is best for brewing coffee?
- Why do you think of Rose Summer whenever you mention Panamanian coffee?
- Introduction to the characteristics of authentic blue mountain coffee bean producing areas? What is the CIB Coffee Authority in Jamaica?

