Is decaf healthier? Decaf Coffee Bean Features Advantages and Disadvantages Story
Professional coffee knowledge exchange More coffee bean information Please pay attention to coffee workshop (Weixin Official Accounts cafe_style)
[Coffee is delicious, remember not greedy cup] refers to coffee contains caffeine, appropriate caffeine can refresh, eliminate fatigue. Excessive caffeine can lead to "poisoning." Therefore, decaf coffee has also appeared on the market to satisfy the taste buds of coffee lovers. As more and more people now want to retain the antioxidant effects of coffee on the body but do not want to contact caffeine, Qianjie Coffee recently bought three decaf coffee beans, this issue will take you to discuss what decaf coffee is.

How do people find decaf?
It is said that Goethe, a famous German poet, is also a coffee lover, but he suffers from the pain of being unable to sleep after drinking coffee. The feeling of love but not closeness makes Goethe go to his friend Runge to analyze the composition of coffee beans and find out why coffee interferes with sleep. Around 1820, Longi found out that the factor affecting sleep was caffeine and developed a way to separate coffee beans from caffeine, so Lungi became the ancestor of decaffeinated coffee.
At that time, although Lungi found the factors that affect coffee sleep, the technology of extracting caffeine could not produce decaffeinated coffee in large quantities until 1903, when Ludwig Roselius, a German importer of coffee beans, found that as soon as the coffee beans were soaked in sea water, the caffeine content decreased a lot, so he hired a group of chemists to research and develop the technology of extracting caffeine, which made an important breakthrough in the extraction technology. Decaffeinated coffee is just beginning to be mass produced.
What is decaf?
In general, the weight ratio is used to measure the caffeine content of coffee beans. Arabica coffee beans have a caffeine content of 0.9% Mel 1.4% (an average of 1.2%), while Robsta has a caffeine content of 1.8% Rue 4% (average 2.2%). Decaf can be divided into natural decaf and artificially treated decaf (decaf).
The more common natural decaf coffee is Coffea Laurina, which has half the caffeine (0.6%) of regular Arabica. Unlike other artificially treated decaf coffees, pointed bourbon is genetically degraded, resulting in lower caffeine content and better flavor than the average Arabica coffee tree.
The common low-caffeinated coffee beans on the market are through the manual removal of caffeine from the beans, while for artificially decaffeinated low-caffeinated coffee, the EU standard for this type of low-caffeinated coffee is that the caffeine content after treatment does not exceed 0.1% of the raw bean, while the FDA standard of the US Food and Drug Administration is less than 3% of the original caffeine.

What are the common ways to handle decaf coffee?
There are many ways to remove caffeine, which can be divided into direct / indirect solvent treatment, supercritical carbon dioxide treatment, Swiss water treatment and mountain spring water treatment.
Direct solvent treatment (natural decontamination)
At the beginning, the direct solvent treatment method is to use dichloromethane solvent to directly contact coffee beans, and the direct solvent treatment method is also known as natural decontamination treatment. First, steam is used to open the stomata of the raw coffee beans, and the dichloromethane solvent is directly added to the coffee beans. After the solvent and caffeine are fused, the caffeine-filled solvents are washed out, and the coffee beans are boiled again to remove all residual solvents. The boiling point of dichloromethane is 39.8 degrees Celsius, so even if there are residual solvents in the cooking process, after baking, the solvents will all evaporate.
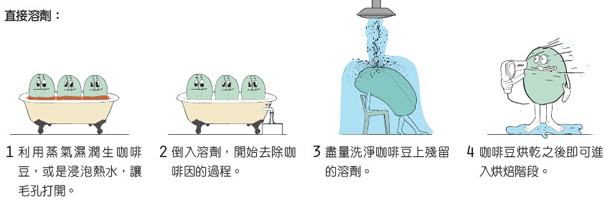
There are concerns about using dichloromethane as a solvent because it is suspected that long-term exposure increases the risk of cancer. But in fact, FDA limits the dichloromethane content of decaf to 0.001%, which is actually lower than that, with little side effect.
The process of using ethyl acetate as a solvent is the same, ethyl acetate usually comes from sugar cane, so when used, the direct solvent method is sometimes referred to as sugarcane decontamination. This method is usually used in de-causation in Colombia. But ethyl acetate is a highly flammable substance, so it is more dangerous.
Swiss water treatment method
This is one of the most traditional methods of extracting caffeine, using this commercially developed and efficient treatment.

The step of the Swiss water treatment method: soak the raw coffee beans in hot water, which is called "flavor filled water" (Flavor-charged Water) in the Swiss water treatment method. This water contains all the flavor factors that are necessary in the raw coffee beans, but lacks caffeine. This special water is the most important medium in the next decaffeinated process. The coffee beans are filtered out after the flavor is filled with water, which is filtered out by an activated carbon filter, and the rest is hot water full of pure flavor factors, and then re-soaked in hot water with pure flavor factors.
Carbon dioxide treatment
This treatment is to first let the coffee beans absorb water and expand, and the caffeine molecules are loose in the coffee beans. Add liquefied carbon dioxide and create more than 100 atmospheric pressure in water. Carbon dioxide is highly selective and does not "damage" the carbohydrates and proteins in coffee beans while dissolving caffeine, ensuring that the flavor of coffee beans is not destroyed. Liquid carbon dioxide that takes away caffeine can also be removed and recycled.
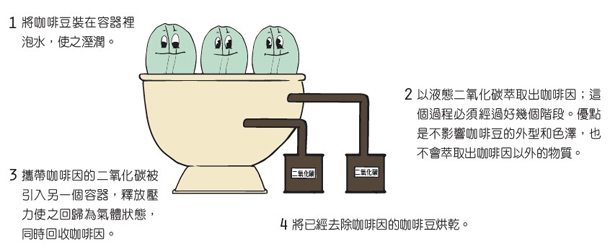
Coffee made from decaffeinated carbon dioxide has a lower burden on the human body, and according to the study, this method extracts more coffee than the direct solvent method, and the cost of this method is much higher than that of the direct solvent method.
Mountain spring water treatment
Similar to Swiss water treatment, another special kind of water is used to extract caffeine from glaciers. The company Descamex says it uses a special filter to remove caffeine. After treatment, you will get a caffeine-free aqueous solution, which also dissolves the solid substance of coffee and can be reused in the decaffeinated process.
Decaf coffee contains antioxidants and nutrients.
Caffeine is actually the largest source of antioxidants in Western diets; decaf coffee usually contains antioxidants in similar amounts to regular coffee, but they can be as low as 15%. This difference is probably due to a small loss of antioxidants in the decaffeinated process. So now more and more people choose decaf coffee because it not only has the effect of antioxidation, but also does not affect sleep.
The main antioxidants in regular and decaffeinated coffee are hydrogenated cinnamic acid and polyphenols. Antioxidants are very effective in neutralizing active compounds called free radicals. This can reduce oxidative damage and may help prevent diseases such as heart disease, cancer and type 2 diabetes.
In addition to antioxidants, decaffeinated coffee also contains small amounts of nutrients. A cup of decaffeinated coffee provides 2.4% of the recommended daily intake of magnesium, 4.8% of potassium and 2.5% of niacin, or vitamin B3. This may not seem like a lot of nutrients, but if you drink 2-3 cups (or more) of coffee a day, these amounts will increase quickly.

Is Decaf Coffee Really Bad?
Combined with the decaf treatment above, Front Street Coffee believes decaf coffee is not bad to drink because of the treatment. Because most decaf coffees choose cheap, commercial-grade beans as their ingredients. Modern decaffeination techniques are quite complex, and in most cases companies that produce decaf coffee naturally prefer high-caffeine varieties of coffee beans (such as robusta beans) when choosing raw materials. Like any coffee beans sold in coffee shops, decaf coffee can perform very well even after decaffeination if it starts with good Arabica beans from the green.
Here's a look at where the three decaf beans from Front Street Coffee come from, what decaffeination methods are used, and what differences in flavor.
Among the three decaf coffee beans from Front Street Coffee, Colombia Cymbidium Swiss Water Treatment is one of the decaf coffee beans on the shelf. Because Swiss water treatment is the most traditional method of decaffeination, it is also widely used in the market, and this decaf coffee bean can reflect the nutty and chocolate flavor of Colombia Whelan region, but also reflects the tonality of Castiglio fruit, iron pica and cardura acid characteristics.
Colombia Cymbidium Swiss Water Treatment Decaf Coffee
Country of origin: Colombia
Production area: Cymbidium
Altitude: 1750 m
Breeds: Iron Pickup, Cadura, Castillo
Treatment: Swiss Water Treatment
Level: Supreme
Season: 2020

Production area introduction
The Andes run through the province of Whelan in Colombia, while Cymbidium owns Mount Nevaddel. The area has mineral-rich soils, high elevations and a pleasant microclimate. Very suitable for the cultivation of boutique coffee.
Colombian coffee beans are well-known in the world, and the high-quality water-washed beans have always been the representative of high-quality coffee. Coffee beans exported from Colombia, after specific gravity inspection and manual picking of defective beans, are bagged after layers of strict inspection, so the quality of Colombian coffee can be guaranteed.
Colombia huila of Colombia belongs to the selected alpine coffee beans of the Colombian state company, which is known as the national treasure of Colombia. With its superior geographical and climatic conditions, Colombian coffee has always maintained high quality. Colombian coffee beans, which usually do not have a special market brand name, are from the National Coffee Farmers' Union of Colombia (national federation of colombia coffee growers) and have always been famous for their strict quality control and active promotion.

Coffee variety
In terms of varieties, this batch of low-caffeine coffee includes three varieties: iron pickup, Kaddura and Castillo. Iron pickup, one of the oldest Arabica species in the world, is loved for its delicious and sweet flavor, but it has been replaced by many high-yield coffee varieties in Colombia because of its low unit yield. Kaddura is a natural mutant of bourbon, its flavor is comparable to or slightly worse than bourbon beans, more importantly, super adaptability, no shade trees, direct exposure to the sun can also be full of vitality, commonly known as exposure coffee (Sun Coffee), can adapt to high-density planting.
Castillo, based on Colombian species, was crossbred with Kaddura until the tenth generation. Although it was not favored by practitioners in the industry at its debut, there has been no shortage of elegant and meticulous batches on the market in recent years.

Raw bean grade
This batch of raw coffee beans is Supremo. In the Colombian coffee bean system, Supremo is the highest grade, while the preferred Excelso is smaller and more common. Colombian coffee beans have a balanced flavor, rich taste, unique flavor and relatively full body, with a touch of vanilla and dark chocolate on the flavor when roasted moderately.
Baking curve
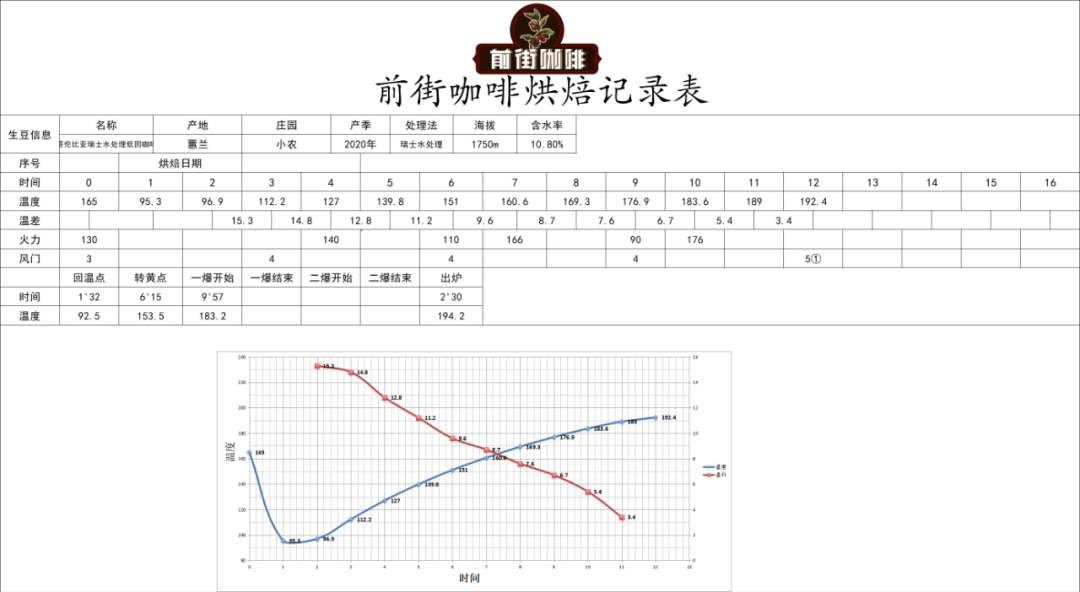
Test the flavor by cup

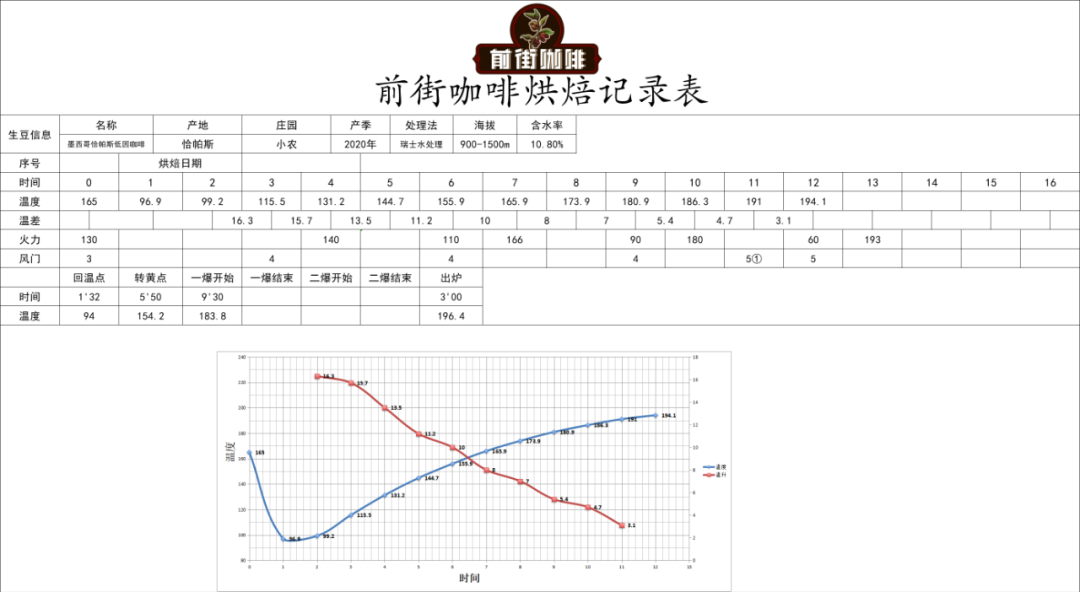
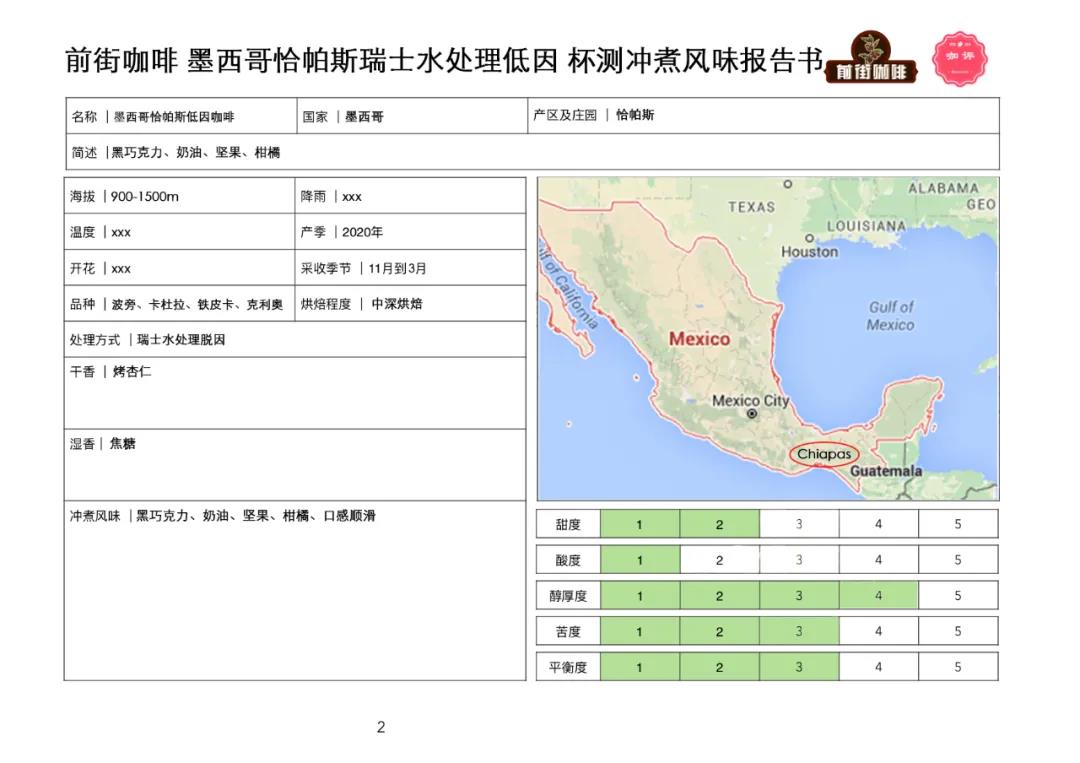
Mexican Chiapas Swiss Water treatment of decaf
Country of origin: Mexico, Mexico
Producing area: Chiapas Chiapas
Altitude: 900m-1500 m
Variety: bourbon, Kaddura, Tippika, Criollo
Treatment method: Swiss water treatment
Grade: HG
Production season: 2020

Production area introduction
Mexico has 12 major coffee producing areas, of which Chiapas is located in the south of Mexico, near Central America.
The coffee growing base in Chiapas is very strong. Therefore, the state is called the largest coffee producing area in Mexico, and its growers are experienced, enterprising and actively develop boutique coffee cultivation.
Chiapas coffee producing area is about 2500m above sea level, with many volcanoes and rich volcanic soil resources. High altitude and fertile volcanic soil give rise to the smooth taste and comfortable acidity of Chiapas coffee. The coast of Chiapas is affected by the northeast monsoon, with abundant rainfall in summer and rich water resources. So most of the coffee in this area is washed.
This batch of coffee is produced by the GRAPOS Cooperative, a coffee production organization based in the southern Mexican state of Chiapas, which was founded in 2007, when there were only 90 coffee farmers, and by 2016, the cooperative had grown to 3253 coffee farmers, covering the Soconusco, Siltepec, Porvenir and Tapachula sub-areas of Chiapas. GRAPOS coffee planting area of about 5560 hectares, 900-1500m above sea level, mostly small farmers intensive cultivation, per capita planting area of 3 hectares.
Coffee bean variety
The coffee varieties of this batch of coffee beans are composed of bourbon, Kaddura, iron pickup and Criollo. Iron pickup and bourbon belong to the same ancient Arabica coffee species, which are loved by people for their rich acidity and excellent flavor quality.
Kaddura is a single gene variant of bourbon. It was found in Brazil in 1937 that its production capacity and disease resistance were stronger than those of bourbon species, and the plants were shorter and easier to harvest. Unfortunately, it is the same as bourbon species that have periodic problems of production capacity fluctuation every two years.
Cleo is a natural mutant of the iron pickup, which is commonly found in countries such as Peru, Bolivia, Colombia and Mexico. Some countries in Latin America that grow coffee also call the iron pickup "Criollo". Can be seen as Cleo is a localized tin pickup.

Raw bean grade
Mexico adopts a raw bean grading system based on hardness. At the same latitude and on the same plot, the higher the altitude, the greater the temperature difference between day and night, the longer the coffee growing period, the harder the beans, the more nutrients absorbed in the beans, the more obvious the flavor substances will be. There will be more raw beans. The grade of this batch is HB (hard bean), and the growth altitude is 1200-1400m.
Baking curve
Test the flavor by cup
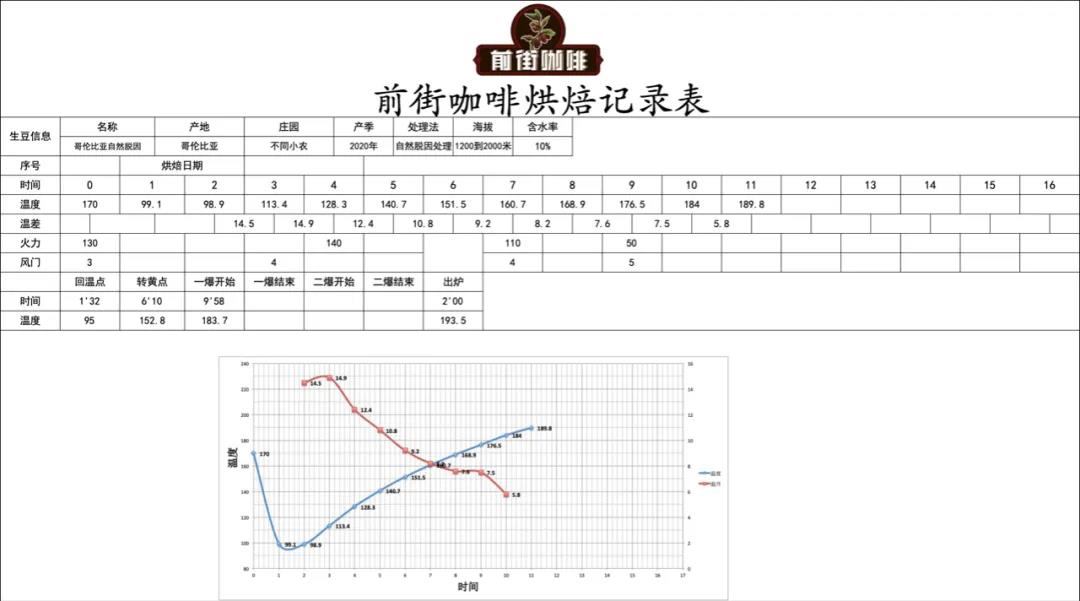
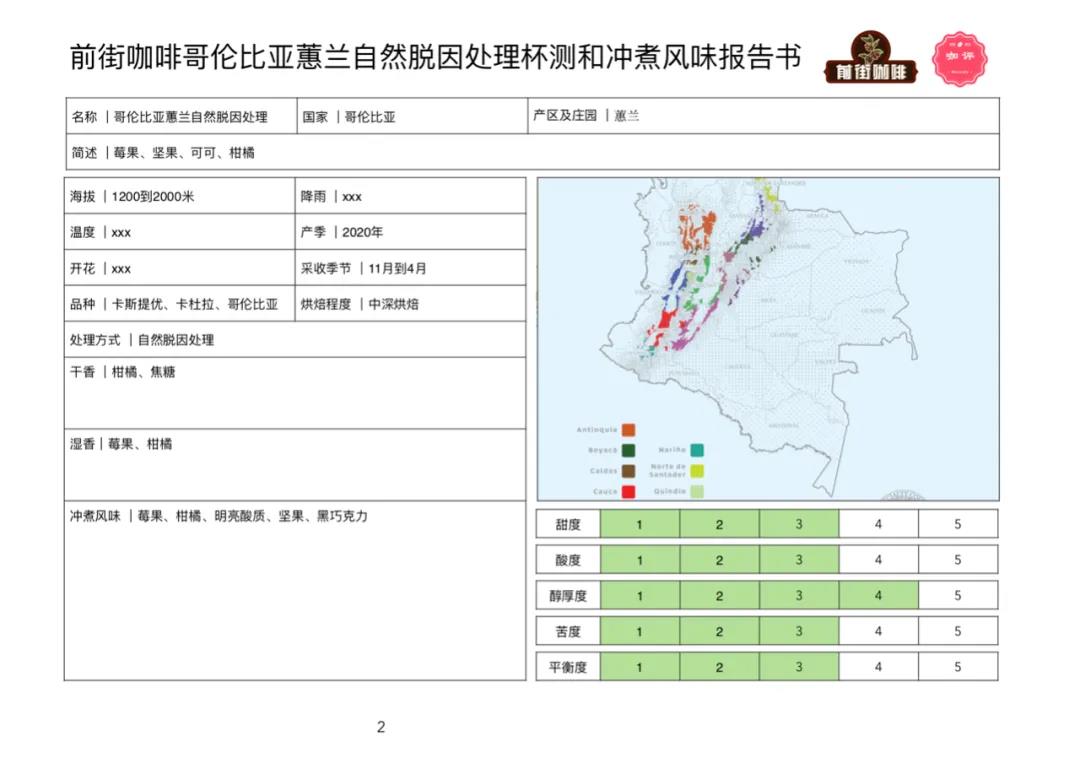
Columbia Cymbidium naturally decaffeinated coffee treatment
Coffee producing country: Colombia
Coffee producing area: Huilan
Planting altitude: 1200 to 2000 m
Coffee varieties: Castillo, Kaddura, Columbia
Treatment: natural de-causation treatment

Production area introduction
Huilan has a combination of excellent soil and geographical advantages for growing coffee, and some of the most complex and fruity Colombian coffees come from here. This area belongs to the selected alpine coffee beans of the Colombian State Corporation, which is known as the national treasure of Colombia. With its superior geographical and climatic conditions, Colombian coffee has always maintained high quality. There are more than 70, 000 coffee growers in the area, covering more than 16000 hectares (39500 acres). Colombian coffee beans, which usually do not have a special market brand name, are from the National Coffee Farmers' Union of Colombia (national federation of colombia coffee growers) and have always been famous for their strict quality control and active promotion.

The Laboyos Valley in the southern part of Colombia's Cymbidium province lies at the foot of the Andes. This huge mountain range is the source of the Magdalena River (Magdalena River), stretching north to the Caribbean coast. The valley itself is about 1300 meters above sea level. Coffee is grown in all the surrounding mountains, with an average farm area of about 6 hectares, with about 5000 trees per hectare. The soil is volcanic soil, which provides a lot of organic nutrients for this high-altitude coffee.
Coffee variety
The early varieties of coffee grown in Colombia were iron pickup and bourbon, which were replaced by Kaddura in 1970 because Kaddura was not only more productive per plant, but also more compact and could plant more coffee trees per unit area.
Kaddura, a single-gene variant of bourbon, was discovered in Brazil in 1937 with both production capacity and disease resistance.
In 1961, CENICAFE began to study the Timor variety of Robusta blood, and then Tim and Kaddura selected the Columbia Catimor series. After five generations of breeding, in 1982, CENICAFE released Colombia's first disease-resistant variety, named after the country: Colombian species Colombia. After the emergence of leaf rust in 1983, the Colombian species began to be planted in large numbers.

CENICAFE then continued its research and development, releasing the second resistant variety Tabi (a hybrid of iron pickup, bourbon and Timer) in 2002, Castillo, the most successful resistant variety to date, in 2005, and Castillo cultivation began in Colombia after a major outbreak of leaf rust in 2008.
Castillo is based on Colombia species and crossbred with Cadura until the tenth generation. Although it was not favored by practitioners in the industry when it first appeared, there are also elegant and meticulous batches on the market in recent years.
baking curve
Test the flavor by cup
How to brew decaf coffee in front of the street?
Filter cup: Kono filter cup
Water temperature: 88 ℃
Powder content: 15g
Powder / water ratio: 1:15
Degree of grinding: medium grinding (Chinese standard No. 20 screen pass rate 75%)
Cooking technique: three-stage extraction. Steam with 30 grams of water for 30 seconds, small water flow around the circle to 125 grams for sectional injection, water level drop is about to expose the powder bed, continue to inject water to 225 grams to stop water injection, and so on when the water level drop is about to expose the powder bed, remove the filter cup, (steaming starts timing) the extraction time is 2 minutes 39 minutes 30 ".

Columbia Cymbidium naturally decontaminated coffee brewing flavor: citrus, berries, bright acidity, dark chocolate, nuts.
Mexican Chapa Swiss water treatment decaf coffee brewing flavor: dark chocolate, cream, nuts, citrus, smooth taste.
Columbia Huilan Swiss water treatment decaf coffee brewing flavor: dark chocolate, caramel, nuts, mellow taste.
For more boutique coffee beans, please add private Qianjie coffee on Wechat. WeChat account: kaixinguoguo0925
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

Often drink coffee can lose weight coffee can detumescence lose weight so how to drink right?
Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) bulletproof coffee diet! Bulletproof coffee can really lose weight? you can lose weight by drinking one cup in the morning. Affected by westernization, more and more people like to drink coffee. When I have a cup of coffee with hamburgers and sandwiches for breakfast, I always feel that the energy of the day starts here, and a cup of coffee in the afternoon can be picked up.
- Next

The harm of decaf: it is more likely to develop heart disease and is not suitable for patients with hyperlipidemia.
Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information please follow the origin and development of decaf coffee in coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style): why are all Swiss water treatment decaf coffee sold? Are you a coffee person? Doctors warn that drinking decaffeinated coffee will not make you healthier, but may increase the risk of heart disease; pregnant women drink
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

