Is the high acidity of coffee beans good or bad? sour coffee beans are recommended by brands _ what are caffeic acid?

Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style)
The traditional impression is that coffee is bitter and unpalatable, and if you add acid, it is a cup of rotten medicine. Qianjie makes it clear to you that this is not the case. Today's coffee is no longer the impression in the past, the development of boutique coffee now, pay attention to the original flavor of coffee. The acid of coffee is not bad, of course, acid also has good and bad acid, and good acid can have a pleasant feeling!
Beginner friends who have not come into contact with individual coffee may wonder why the coffee is sour. If the coffee is sour, is it a bad coffee that has expired? In fact, this acid is not the other acid, coffee contains hundreds of acidic compounds. Today, we will mainly introduce the acids in several kinds of coffee that affect the taste.

How does coffee get sour?
The acidity of coffee has a lot to do with the variety of coffee and the depth of roasting, while coffee is acidic because coffee beans fully absorb the acid of pulp in the process of growth and treatment. The taste of raw coffee beans is the same as fruit, a variety of soil will also affect the growth and flavor of fruits, different soil quality, climate, water, altitude and so on, so that beans from different areas have their own unique taste.
[citric acid]
Citric acid is an important organic acid. Citric acid in coffee is one of the products of coffee tree respiration. The amount of citric acid can be used to judge whether raw beans are fresh or not. As the maturity of coffee cherries increases, the content of citric acid will decrease and will be converted into more sugar. Citric acid reached its peak in shallow baking and was decomposed continuously in the later stage of baking.
[malic acid]
Malic acid exists in apples, Hawthorns, grapes and other fruits. The concentration of malic acid in raw beans is lower than citric acid. After baking, the concentration is reduced to only 0.1% of the raw bean weight. Malic acid is generally classified as aromatic acid.

[tartaric acid]
Tartaric acid exists in many plants, such as grape and sour horn. It is one of the main organic acids in wine and one of the sources of astringency in coffee.
[acetic acid]
Acetic acid, also known as acetic acid, glacial acetic acid, is an organic acid. Typical fatty acids are the source of sour and pungent odors in food. In coffee, it mainly comes from the fermentation step in the process of coffee post-treatment, so the content of acetic acid in washed coffee is generally higher than that in sun-cured coffee in the process of water-washing fermentation. The pressure in the roaster during the baking process can significantly increase the content of acetic acid, maintain the volatile acidity and improve the quality of coffee. A small amount of acetic acid makes the coffee fermented, but if excessive, it will make the coffee bitter in vinegar.
[chlorogenic acid]
Chlorogenic acid is a common acid in all raw coffee beans, accounting for 6% and 8% of the net weight of coffee. Coffee is the plant that contains the most chlorogenic acid in the world. Chlorogenic acid is an important source of coffee acidity and bitterness, and has a slight nerve stimulating effect on people. Chlorogenic acid is one of the main acidic substances in coffee. Chlorogenic acid has two isomers, monocaffeoic acid which is decomposed during baking and dicaffeoic acid that will not be decomposed. Among them, dicaffeoic acid can make coffee bitter and metallic. During baking, chlorogenic acid is broken down into quinic acid and caffeic acid, which increase the astringency and taste of coffee.
[phosphoric acid]
Phosphoric acid is found in Kenyan coffee with a high concentration of inorganic acid, which makes Kenyan coffee unique and excellent acidity. The phosphoric acid in coffee accounts for only about 1% of the total coffee substance, and mainly comes from phytic acid hydrolysis in the soil. In baking, the content of phosphoric acid increases with the deepening of baking degree. Phosphoric acid increases the brightness and sweetness of coffee.
There are a variety of acids in coffee, and these are the most important acids.
Brand recommendation of sour coffee beans
Sour coffee recommended


[Qianjie Coffee Wash Yega Xuefei]
Country: Ethiopia
Producing area: Yega Xuefei
Altitude: 1800-2000 m
Treatment: washing treatment
Baking: shallow baking
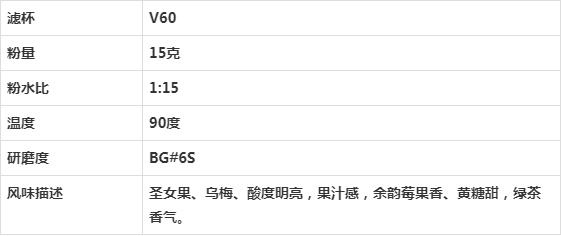

[front Street Coffee Asalia, Kenya]
Producing area: Sika Thika, Kenya
Processing plant: Asali honey processing plant
Altitude: 1500-1750 m
Variety: SL28-SL34
Treatment: Kenya 72-hour treatment
Baking degree: shallow baking


[front Street Coffee Panamanian Flower Butterfly]
Producing area: Pokuit
Altitude: 1600 m
Varieties: rose summer, Kaddura. Kaduai
Baking: light baking
This is the coffee bean recommended by the editor today. If you like it, try it.
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

What are the recommendations for sour coffee beans? introduction to the taste characteristics of shallow roasted coffee beans
Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information Please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style). On weekdays, you can get in touch with all kinds of guests at the bar. A considerable number of these guests are unaccustomed to sour coffee beans, while usually sour coffee is roasted.
- Next

Sour coffee beans are recommended. Kenyan coffee is sour. Sour coffee beans are more expensive.
Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) the source of sour Kenya beans friends like sour coffee beans should like Kenya, it is not as elegant as the acidity of Yega Xuefei, but has a very outstanding sour, round, sweet and thick taste. This is due to planting in Kenya.
Related
- Detailed explanation of Jadeite planting Land in Panamanian Jadeite Manor introduction to the grading system of Jadeite competitive bidding, Red bid, Green bid and Rose Summer
- Story of Coffee planting in Brenka region of Costa Rica Stonehenge Manor anaerobic heavy honey treatment of flavor mouth
- What's on the barrel of Blue Mountain Coffee beans?
- Can American coffee also pull flowers? How to use hot American style to pull out a good-looking pattern?
- Can you make a cold extract with coffee beans? What is the right proportion for cold-extracted coffee formula?
- Indonesian PWN Gold Mandrine Coffee Origin Features Flavor How to Chong? Mandolin coffee is American.
- A brief introduction to the flavor characteristics of Brazilian yellow bourbon coffee beans
- What is the effect of different water quality on the flavor of cold-extracted coffee? What kind of water is best for brewing coffee?
- Why do you think of Rose Summer whenever you mention Panamanian coffee?
- Introduction to the characteristics of authentic blue mountain coffee bean producing areas? What is the CIB Coffee Authority in Jamaica?

