Are the advantages and disadvantages of decaf coffee different in taste? will the effect of decaf on weight loss affect sleep?

Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style)
It has become a habit for many friends to start work with a cup of coffee in the morning. With the development of the coffee industry, more and more novel coffee processing methods have emerged. Qianjie Coffee currently has several types of anaerobic and barrel-treated coffee beans, which are also very popular in stores and Tmall stores. In addition to the diversity of processing methods, there are more and more subdivisions of coffee categories, such as decaf coffee, which is to be introduced in Qianjie Coffee today. For some of the more sensitive people, a little caffeine is enough to have a negative effect. At this time, decaf coffee is a good choice for people who are ultimately more sensitive, or people who deliberately quit caffeine.
A guest asked Qianjie Coffee, can decaf also be a boutique grade? If you use micro-batches of selected beans to carry out the low-cause program, will it still taste good? And how to remove caffeine? There are many misconceptions about the quality and health effects of decaf. Today, Qianjie Coffee will discuss with you what decaf is.

The story of decaf
It is said that Goethe, a famous German poet, is also a coffee lover, but he suffers from the pain of being unable to sleep after drinking coffee. The feeling of love but not closeness makes Goethe go to his friend Runge to analyze the ingredients of coffee beans and find out why coffee interferes with sleep. Around 1820, Longi found out that the factor affecting sleep was caffeine and developed a way to separate coffee beans from caffeine, so Lungi became the ancestor of decaffeinated coffee.
At that time, although Lungi found the factors that affect coffee sleep, the technology of extracting caffeine could not produce decaffeinated coffee in large quantities until 1903, when Ludwig Roselius, a German importer of coffee beans, found that as soon as the coffee beans were soaked in sea water, the caffeine content decreased a lot, so he hired a group of chemists to research and develop the technology of extracting caffeine, which made an important breakthrough in the extraction technology. Decaffeinated coffee is just beginning to be mass produced.

What is decaf?
Decaf Decaf is the abbreviation of decaffeinated coffee (decaffeinated coffee). There are many ways to remove caffeine from coffee beans. Except for caffeine content, the nutritional value of decaffeinated coffee should be almost the same as that of ordinary coffee. However, depending on the method used, the taste and smell may become slightly mild and the color may change. This makes decaffeinated coffee more enjoyable for people who are sensitive to the bitterness and smell of regular coffee.
Does decaf beans mean no caffeine at all? No, decaf actually eliminates about 97% of the caffeine, not all the caffeine. Although there is still caffeine, decaf caffeine is less likely to affect most people than regular espresso.
Decaf is not a demand for coffee in the 21st century.
The refreshing effect of caffeine can be said to be the main reason why people can't do without it. Caffeine is a central nervous system stimulant, caffeine intake can make people feel less tired, as well as improve attention, reduce pain and other effects.
As a matter of fact, decaffeinated coffee is not a new demand in the 21st century. As early as the beginning of the 20th century, Kaffee Hag, the first company in the world to sell decaffeinated coffee (later acquired and renamed Caf é Hag by American merchants), developed this product.
It's just that not many people drank decaf at that time. Until the end of World War II, ── Robusta; Coffea canephora, a coffee bean with high caffeine content, rose. However, due to the heavy use of Luodou, many people can not stand high concentrations of caffeine, increasing the demand for decaf coffee.

▲ Science monthly
Most of the common coffee in our life comes from Coffea arabica, which accounts for about 60% of the global production. Because the coffee brewed has a variety of aroma and rich sour taste, it is mostly made into a variety of boutique coffee.
Robusta beans, on the other hand, have a strong smell and bitter taste, so they are often mixed or instant coffee, with a global production of nearly 40%. In addition, Arabica beans contain about 1.2% to 1.5% caffeine, while Robbosa beans are nearly twice as high, about 2.2% to 2.7%.
After World War II, more and more coffee products made from Luodou were used, but because of the high caffeine content, it was easy for consumers to feel uncomfortable, so many manufacturers began to invest resources to develop decaf coffee products.
In general, Arabica coffee beans contain 1.1%-1.7% caffeine, while robusta beans contain 2%-4.5% d caffeine.
How to remove caffeine
The common way to remove caffeine is to use "extraction". Generally speaking, raw coffee beans are extracted to remove caffeine before drying and baking. The common extraction methods can be divided into three categories: solvent extraction (solvent decaffeination), carbon dioxide treatment and water treatment.
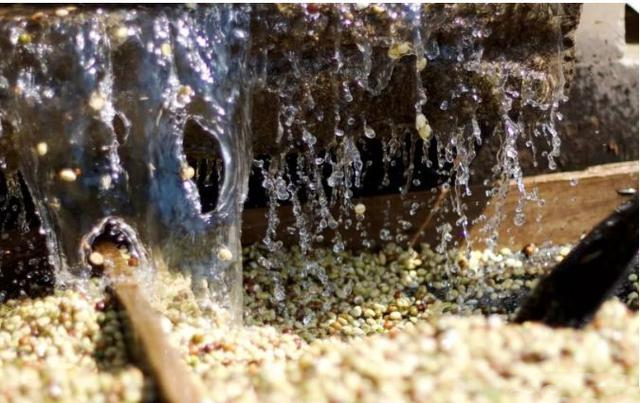

Solvent extraction method
According to the different treatment steps, solvent extraction can be divided into "direct solvent extraction" and "indirect solvent extraction". Because caffeine binds to chlorogenic acid (Chlorogenic acid, CGA) in beans, it is necessary to separate caffeine molecules from dried coffee beans by absorbing enough water before starting extraction.
The direct extraction method is to directly steam the dried raw coffee beans and soak them in the solvent. After the caffeine is dissolved, the raw beans are removed and heated to volatilize the solvent and water.
The indirect extraction rule is to boil the raw beans in hot water, dissolve caffeine and various odor molecules, and then fully mix the boiled coffee beans with the solvent to let the caffeine dissolve into the solvent. after removing the solvent, rinse the raw beans with the remaining water so that the odor molecules can return to the beans, and finally drain and dry.
When it comes to caffeine extraction solvents, dichloromethane dominated the decaf industry before the 1970s and is recognized as the best solvent to use. In addition to the quite good extraction effect, its colorless, boiling point 39.6℃ is easy to volatilize and non-flammable, which makes the process quite effective and safe. But ironically, dichloromethane was eventually abandoned not because it was found to be carcinogenic, but because it was suspected to be one of the culprits of the hole in the ozone layer.
When dichloromethane was out of fashion, it was replaced by ethyl acetate. Ethyl acetate will occur naturally in nature, and many fruits themselves contain a certain proportion, so there is no doubt about safety. In 1982, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved ethyl acetate for caffeine removal, but because many foods contain ethyl acetate, it is impossible to directly explore its health effects, so there is no clear licensing standard for residues.
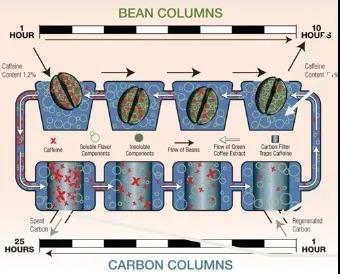
Carbon dioxide treatment
The carbon dioxide treatment is similar to the direct solvent method, which soaks the coffee beans in warm water, replaces the solvent with high-pressure liquefied carbon dioxide, extracts caffeine, and then returns to room temperature to become a gas.
The coffee produced by decaffeination with carbon dioxide has a lower burden on the human body, and according to the study, this method can extract more coffee than the direct solvent method, but the cost of this method is much higher than that of the direct solvent method.

Water treatment method
In addition to developing the expensive supercritical fluid method, another group of people developed a way to extract caffeine with water as a solvent without losing the smell of coffee. This method is much cheaper and easier to operate than the supercritical fluid method, and the most common water treatment method is the Swiss Water treatment (Swiss water process) developed by the Swiss company Coffex in the late 1970s.
In Swiss water treatment, raw coffee beans are soaked in hot water, and caffeine has been partially removed during the soaking stage. The soaked solution is then filtered with activated carbon and finally poured back into the coffee beans. This series of steps will be more effective in removing caffeine. In addition to not requiring the use of chemical solvents, the soaked solution can also be reused in different batches of treatment procedures, but coffee still loses a lot of flavor in the filtration process.

The disadvantage of this method is that it is much more expensive to produce than the above two solvent methods, and the extracted caffeine is directly filtered out and cannot be used for other commercial purposes.
Mountain spring water treatment
This is the use of another special kind of water, water from glaciers to extract caffeine. The company Descamex says it uses a special filter to remove caffeine.
After treatment, you will get a caffeine-free aqueous solution, which also dissolves the solid substance of coffee and can be reused in the decaffeinated process.
This treatment and the Swiss water treatment are both methods that do not use chemical solvents, so some consumers regard it as a safer and healthier choice.
Can decaf also be fine coffee?
It is often recognized that decaf coffee is insipid and boring. Although caffeine itself does not have any smell, the most important flavor substance of coffee beans will be lost in the process of processing, and the loss of flavor has nothing to do with the act of removing caffeine.
The biggest challenge for decaf companies is to find a way to extract caffeine without sacrificing the flavor of the beans. This has always been a very controversial topic in the boutique coffee industry.

The most common treatment is to remove caffeine directly with a solvent, which directly destroys the flavor of coffee, because the target of removal is not only caffeine. These delicious substances in coffee will be consumed in large amounts in the processing process, resulting in a huge negative impact on the flavor of coffee. Lower-quality coffee beans are often treated with solvent because the bean itself does not taste very good.
But these remarks do not mean that there is no low-caffeine boutique coffee, the use of good quality coffee beans, and the use of less flavor loss of caffeine treatment to remove caffeine, can also get good quality coffee. The low-caffeine coffee beans obtained by Swiss water treatment will be less damaged in flavor, but its treatment cost is higher, so it is less used to treat decaf.
Swiss water treatment retains the solid solution of coffee beans, which extracts caffeine by "specially filtering out the activated carbon of caffeine". This step retains the flavor of the coffee origin and batch processing, and in order to confirm that the flavor is retained, Swiss Water will perform a cup test before and after the de-caine procedure.

How do you roast decaf?
How to bake sweet coffee is decaf? The decaf process involves adding water to raw coffee beans to extract caffeine and then drying it again. The decaffeinated process is carried out as gently and carefully as possible to remove caffeine without affecting its flavor as much as possible.
This means that the pre-explosion baking process needs to be done in a milder way. During the roasting process, decaf coffee will follow a similar temperature curve, but the heating rate is a little different, because decaffeinated coffee also has decaffeinated treatment, so the degree of calorie retention of coffee beans is also different.
Need to adjust the amount of roasted beans and boiler preheating time for low-caffeine coffee. Decaf is usually roasted with a milder baking curve than usual, such as a lower and slower heating rate, and a curve that slows down after the heating rate reaches its maximum until the end of the baking.

There are two keys to maximize sweetness in decaf roasting: prolonging the time and lowering the temperature. The goal is to slightly caramel before the first explosion.
When roasting to the first explosion, the reaction of decaf coffee will be very different from that of ordinary coffee. Once decaf coffee begins to release heat, its development will be different, and the energy maintained in coffee beans will not be very tight. The special cellular characteristics of decaf may pose a challenge to bean bakers. On the one hand, beans are easy to overbake and overdevelop; on the other hand, because they can't maintain the same amount of calories in beans, you can't just roast beans like ordinary coffee and wait for them to cool down.
Therefore, look for high-quality raw beans. Ensure that the first explosion has sufficient but not excessive caramelization, and skillfully control the baked beans after the first explosion to achieve the correct balance of sweetness, sour and bitterness. To make delicious and sweet coffee, you still need to keep baking to accumulate experience.
For more boutique coffee beans, please add private Qianjie coffee on Wechat. WeChat account: kaixinguoguo0925
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

Will decaf use 100% Arabica beans? Does Starbucks have decaf beans?
Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information Please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) when talking about low caffeine, we only think of two things: one is that the pressure to drink is very low, and the caffeine content is less than 0.1% of the dry weight of coffee beans; second, most of the common low-caffeine coffee beans have a light flavor, losing the wonderful aroma and fruit feeling of coffee beans.
- Next

What is coffee bean decaine? Decaf beans recommend where to sell decaf coffee in Guangzhou
Professional coffee knowledge exchange more information about coffee beans Please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) as early as the Stone Age, humans have begun to use caffeine. Early people found that chewing the seeds, bark or leaves of certain plants can relieve fatigue and refresh. It was not until many years later that people found that using hot water to soak these plants can increase caffeine.
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

