Brazilian coffee frost frost recovery and yield fluctuation of Brazilian coffee trees
With the development of new technology, the news of Brazilian coffee cream spread all over the world in a few minutes. Accordingly, coffee prices usually rise due to expectations of a global coffee shortage. Brazil produces nearly 25 million bags of 60 kilograms of coffee. This accounts for about 25% of the world's supply. Frost has far-reaching effects because it can reduce or completely eliminate most of the world's supplies in one day.
A coffee tree usually recovers from frost within a year-especially with proper care. Coffee frosts in Brazil usually occur in the south, where the vast majority of coffee has historically grown. June, July and August are the coldest seasons of the year in Brazil. In frost danger areas, low-lying areas are the most vulnerable because cold air flows down from the mountains and settles in the valleys. In addition, plots that are exposed to sunset in the sun are more resistant to cold temperatures than those that are cool for part of the afternoon. The reason is that the soil retains a lot of heat and releases it slowly throughout the night. A small rise in temperature is often enough to save plants. New technologies-such as tree-covered sprayers-are also used in emergencies where crops may be lost. Coffee trees less than a year old should be used by Pita Bread Plain, because they are easily frozen and cannot withstand serious damage.

There are two kinds of Brazilian coffee cream. The first is the traditional frost, which harms coffee trees and their next crop. The second type, called "black frost", is harder to identify, but has an impact on the productivity of coffee factories. In the latter type of frost, coffee trees are not affected by sub-zero temperature, but by a combination of wind and 2-5 °C temperature. Both types of frost reduce coffee production.
As the new technology allows the rapid spread of information about coffee frost in Brazil, there are corresponding doubts about production forecasts. Since losses are estimated to take time and the best indicator of future yield after frost is the degree of flowering, the market reaction is understandable. In addition, as more and more Brazilian coffee farmers go north to avoid frost problems, Brazilian coffee production does not fluctuate so sharply when frosts occur.

However, this will lead to a global coffee surplus, which may keep global coffee prices low. As Vietnam increases Arabica coffee production, coffee oversupply is likely to become the most pressing problem in the specialty coffee industry.
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev
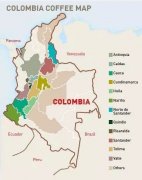
Columbia Coffee History, Climate, Environment, Coffee Flavor
Colombian coffee beans grow at high altitudes and are carefully cared for in the shade of banana and rubber trees. This kind of coffee is one of the best in the world. Rich, mellow, perfectly balanced. Colombia's arid mountains and well-drained, fertile volcanic soil provide ideal conditions for growing quality coffee. Coffee in Colombia is mainly grown in two regions, one
- Next
Rose Summer Flavor Panamanian Jade Manor Rosy Coffee varieties and their Origin and rise
Gesha, a plant variety grown at Hacienda La Esmeralda, a farmer in Panama, or geisha coffee has broken the record for green coffee in the past few years: a batch of coffee sold at auction in 2007 for $130 a pound. The Gesha and the record-breaking items come from the same field, crop and variety, but they are being auctioned.
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

