How are the boutique coffee beans graded? Coffee origin Ethiopian coffee bean grade discrimination
Sometimes we will see English and numbers, G1, G2, G3, AA, PB, SHB, SHG, HB and so on. Today, we will introduce the coffee bean grade of Ethiopia. It uses G1, G2, G3, G4, G5 and so on. To grade it. So what are their standards? Coffee beans are usually graded according to defect rate, bean size, altitude, raw bean density, treatment standards, and so on. Due to historical reasons, trade interests, climate and topography and other factors, each country's producing areas can not be evaluated and classified according to a unified standard or simply on the basis of altitude. Nor can we compare a certain level of one country with that of another country.
Before the emergence of the Ethiopian Mercantile Exchange (Ethiopia Commodity Exchange, referred to as ECX), Ethiopia's coffee export grade was set by the CLU department of the Ministry of Agriculture (Cupping and Liquoring Unit), mainly based on the number of defective beans in 300g.
ECX defines all coffees as unwashed and washed as three types:
a. The number of defects in Speciality is less, and the cup test has high flavor quality.
b. Commerical does not reach the boutique grade, but it is higher than the domestic consumption grade (Local / Domestic).
c. Local / domestic (Local / Domestic) coffee with relatively poor flavor caused by a large number of defective beans (unripe beans), out of season and poor storage.
Among them, boutique and commerce are aimed at the export international market. ECX divides the coffee bean grade into nine grades according to the total score of physical attribute characteristics and cup test flavor characteristics, of which the physical feature score accounts for 40% and the cup test mass score accounts for 60%.
Physical characteristics (40%):
Washing treatment: number of defects (20%), appearance size (10%), color (5%), smell (5%)
Non-washing treatment: number of defects (30%), odor (10%)
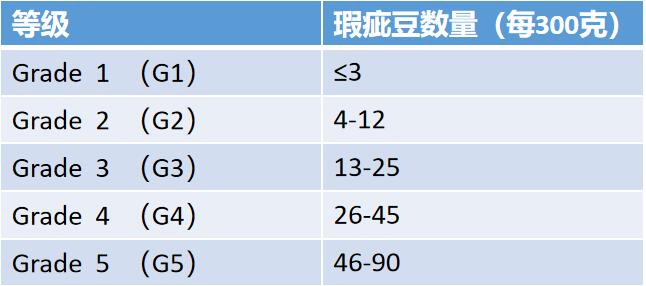
The first is the number of defective beans.
Grade 1; less than 3 defective beans are required.
Grade 2; less than 4-12 defective beans are required
Grade 3; 13-25 defective beans are required.
Grade 4; less than 26-45 defective beans are required
Grade 5; less than 46-90 defective beans are required
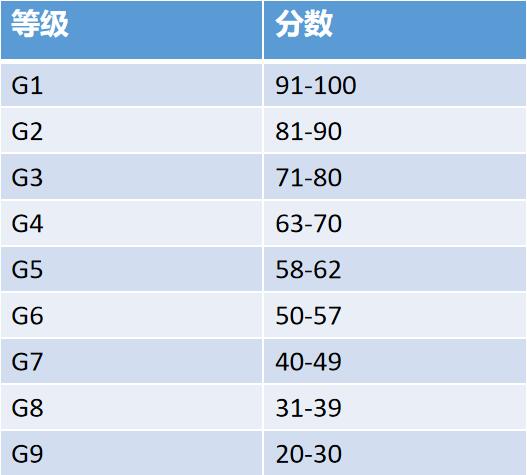
2. Cup test quality (60%)
Grade fractional washing non-washing
Grade 1 Tech 100-91
Grade 2Bing 81-90
Grade 3Tech 71-80 points
Grade 4Bing 63-70 points
Grade 5Tech 58-62
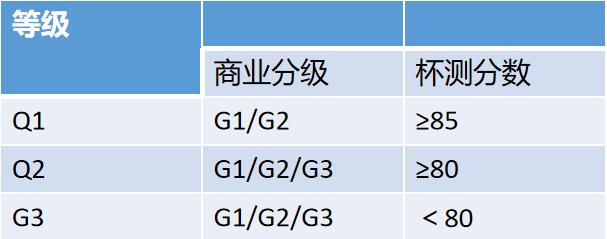
Then the G1-G3 was tested again according to the SCAA standard, and its flavor properties were evaluated in more detail, and the G1 and G2 with no less than 85 points were rated as Q1; among them, G1 and G2 were rated as Q2 for those between 80 and 85, and G3 for all G1Magi G2 G3 below 80; Q1 and Q2 were classified as exportation of boutique coffee beans. G4-G9 remains unchanged and is classified as commercial grade export together with G3.
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

According to the characteristics of Honduran coffee beans, is Honduran Shirley barrel fermented coffee beans good?
Honduras, whose full name is the Republic of Honduras, is a mountainous country in Central America. Bordering Guatemala, El Salvador and Nicaragua, it lies between the Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, with a coastline. This used to be where the Indians lived. Columbus landed here in 1502 and named it Honduras (meaning abyss). It was colonized by Spain at the beginning of the 16th century. Proclamation on September 15, 1821
- Next

What is the coffee grading system in Kenya? Classification characteristics of eight grades of Kenyan coffee beans
Kenya, as a neighbor of Ethiopia, where coffee originated, is very famous for its coffee. People in the coffee industry all think that Kenyan coffee is one of its favorite products. This is because Kenyan coffee contains every feeling we want from a good cup of coffee. It has a wonderful and satisfying aroma.
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

