What are the processing methods of fine coffee common sense coffee raw beans?
After picking, coffee fruits need to go through a series of processes before they can become what we call coffee raw beans. This series of processes are often referred to as the handling of raw coffee beans or the rough processing of raw coffee beans in the industry.
Before we talk about the classification of specific treatment methods, let's take a look at the structure of coffee fruits and raw coffee beans.
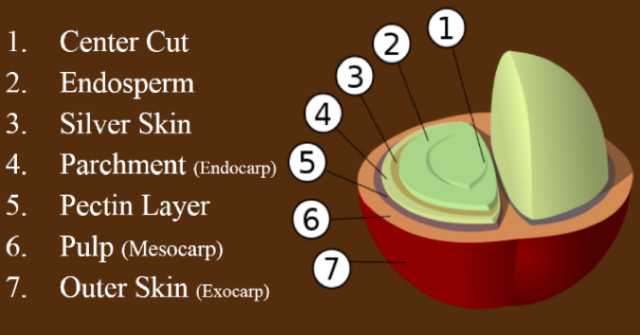
Coffee fruits from outside to inside are as follows:
❼ peel (exocarp)
❻ pulp (mesocarp)
❺ pectin
❹ parchment (endocarp)
❸ silver (a thin layer between parchment and raw beans, including the midline)
❷ coffee raw bean (endosperm)
❶ midline
Note: silver skin is the last protective film of raw coffee beans.
Ripe coffee fruit (left), and half-cut cross section (right)

Separate peel and flesh (right), with pectin and parchment raw beans (left)

Notice that the outside on the left is a yellowing transparent pectin, the middle S-shaped yellow is the silver skin wrapped with raw beans from the inside to the outside, and the parchment paper shell is between the silver skin and the pectin. The peel and flesh on the right side are one. Individual varieties of coffee fruit will be slightly thicker. Ripe coffee fruit is sweet to bite off, with a spicy taste of green pepper and spices.
The following picture shows an enlarged coffee bean with pectin, in which pectin, parchment, silver skin and raw beans are clearly distinguished.

[classification of processing methods ProcessingMethod]
According to whether the peel is removed or not, the treatment of coffee fruit can be divided into two ways: dry (DryProcessing) and wet (WetProcessing). Then according to the different treatment of pectin, and divided into more fine honey treatment, semi-washing and so on.
Dry treatment DryProcessing
Dry treatment is the most primitive treatment method; compared with wet treatment (water washing method), it needs less equipment, water source and manpower, and the treatment method is relatively simple. Covers the following different ways:
Sun-Dried/Natural sun exposure
PulpedNatural/Honey (Miel) honey treatment
Sun-DriedorNatural all-day sun
As the name implies, sun-drying means that coffee fruits are completely dried by the sun.
A good way of tanning should include:
❶ wind selects winnowing to remove light impurities, such as branches, leaves, grass, etc.
❷ screened sifting to remove impurities that are heavier or larger than coffee fruit, such as stones, soil clods, etc.
❸ flotation flotation further removes impurities and overripe and even dried coffee fruits according to specific gravity.
What we actually saw in Ethiopia was that after the coffee fruit was picked, it did not go through flotation, but was spread directly to the drying bed, and then workers went to inspect it to remove the overripe or immature coffee fruit before the coffee fruit was dried and blackened. And the remaining impurities (branches and leaves, etc.).
The pulp of PulpedNatural is dried naturally
A method of treatment that originated in Brazil (1991), which some people call Semi-washed, is classified as semi-washing, but individuals prefer Semi-Dried (because the coffee fruit is sun-dried without peel and pulp, and does not enter the later washing process).
Practice: remove the peel and pulp by machine and retain pectin for sun drying. The reason for this is to make up for the lack of effective grading and screening of coffee fruits with different maturity in the sun, which affects the quality of the final coffee beans.
Honey (Miel) Processing honey treatment
Honey treatment, which originated in Costa Rica in Central America (2003), is currently the most widely used in Central America. At first, it was in response to the needs of illy and Japanese customers, in order to find a producing country other than Brazil to expand the source of PulpedNatural treatment; later, as the new water regulations also forced more and more growers to turn to this relatively less water-intensive treatment. Its treatment method is basically the same as that of PulpedNatural, except that it is divided according to the proportion of retained pectin and the drying method:
WhiteHoney honey 80% mae 90% pectin was removed.
YellowHoney yellow honey retains 50% pectin and has no fermentation.
RedHoney red honey basically retains all pectin and has no fermentation.
BlackHoney black honey basically retains all pectin and dries at a slightly higher temperature at low altitude. It is covered with slight fermentation in the first 24 hours, and then the drying process is transferred to an African drying bed for drying.
GoldHoney Jinmi basically retains all pectin, drying at low temperature at high altitude and prolonging the drying time.
In individual estates, the treatment of individual batches will be different.
Wet treatment of WetProcessing
It is divided into two types: semi-washed Semi-Wash and full-washed Full-wash.
The final product of both methods is: coffee beans with parchment.
Main difference: remove pectin directly by machine or through fermentation tank to remove pectin layer.
Semi-washed: after peeling and pulping, the coffee fruit does not go through the fermentation tank, but through a special pectin removal machine to remove pectin.
Full water washing: after removing the peel and pulp of the coffee fruit, enter the fermentation tank and remove the pectin layer after 1-2 days of fermentation (the time varies according to the temperature and humidity of the site). There are different ways of enzyme and no enzyme.
Wet-Hulling wet planer
Wet planing (GilingBasah) is a unique treatment method of water washing system in Indonesia.
Dry with pectin and remove the parchment directly by machine when the moisture content is about 40.
[compare ComparisonofProcessingMethod with different processing methods]
Impact on the environment
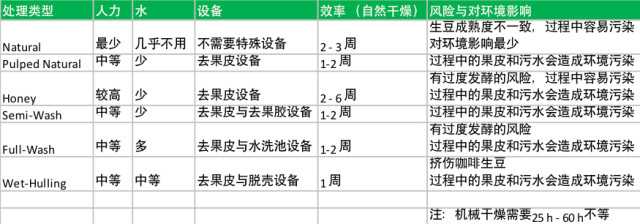
I hope you can understand that each treatment method has its own applicable conditions, including natural factors, manpower, material resources, etc.; as long as each method is properly controlled, it can deal with high-quality coffee raw beans with its own characteristics and flavor quality. (MQ / tr. by Phil Newell)
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

Coffee machine common sense how to adjust the Italian coffee grinder
It's a good choice to use an Italian coffee grinder in a coffee shop or at home. As long as you set the right data, you will have an unprecedented coffee experience, and the coffee you make will have constant quality and perfect taste. How to set up an electronic grinder when using a new variety of coffee beans, and how to maintain the constant quality of coffee. In the meantime, I will teach you how to
- Next

How to make Coffee menu and choose Coffee equipment when starting a Cafe
For a new coffee shop, choosing a coffee-making equipment suitable for your own coffee shop seems to be a complex matter, because you need to take into account the specifications, including the width, length and thickness of the equipment, and then consider the performance of the equipment. If you have the appropriate understanding, you will be able to choose the right equipment to facilitate your coffee service. To sum up, the equipment for making coffee can
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

