Coffee roasting heat source heat conduction and convection

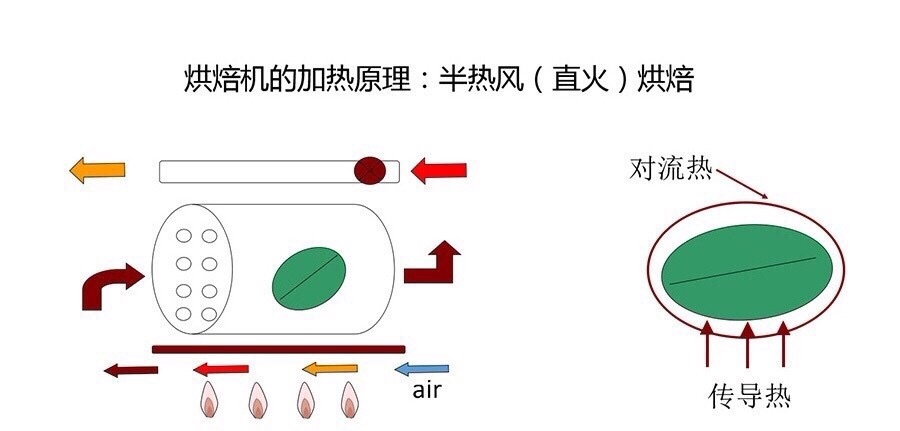
At present, the most widely used baking equipment is semi-direct fire (semi-hot air) baking, where the "half" is only relative to the baking heat source, not in terms of thermal efficiency distribution ratio, such as the probat roaster we use, in terms of thermal efficiency distribution, it is about 3 (direct fire): 7 (hot air) or 2:8, rather than 5:5. In this article, I try to analyze the characteristics of these two heat sources.
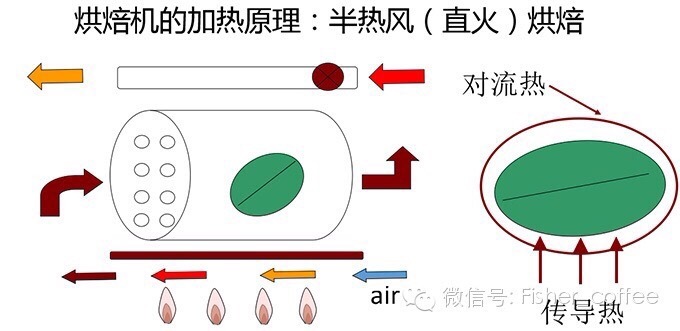
Heat conduction: usually refers to the heat transfer efficiency of the furnace wall of the baking equipment (drum) in direct contact with coffee beans. The heat source is different from the drum material, the efficiency of conducting heat and the radiant heat produced by the furnace wall are also different.

To take a simple example, like fried steak, the heat transfer is too fast, which may cause the steak to be scorched on the outside, and if the heat transfer is too slow, it becomes fast-boiled meat, and the steak is tasteless when chewed. Therefore, only by making rational use of the speed and efficiency of heat conduction, coffee beans can be roasted and their flavor can be brought into full play. What we often call "outer coke and inner tenderness" is the realm pursued by direct fire baking. This is why the traditional straight fire baking is like a sharp sword for bakers. The mastery of "heat" requires a lot of practice and experience to use freely, otherwise it is easy to hurt yourself. I tried a direct fire roaster from Fuji Royal in Japan, and it was a nightmare when the temperature rose too fast to make the coffee core taste obvious.
I made a few diagrams and added some references. On the left is the coffee bean, and the three temperature collection points are the surface, the shallow layer, and the center of the coffee bean. The temperature test data on the right come from the experimental data of probat.
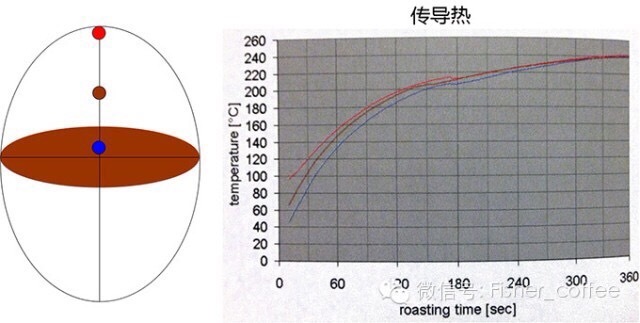
Heating characteristics of conduction heat
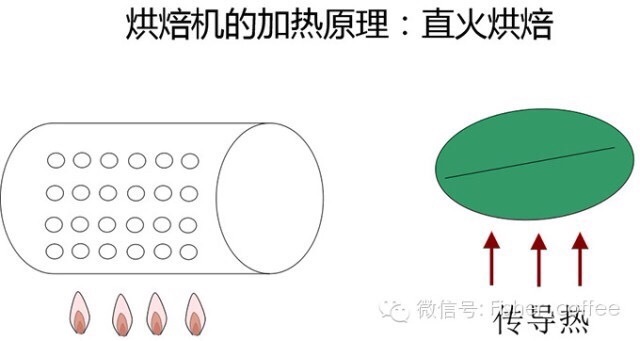
Convection heat: convection heat is the heating of coffee beans by circulating hot air, which is what we often call hot air heat. Full hot air machines are generally used in very large industrial baking equipment or smaller household baking equipment. The heating principle is similar to a microwave oven or an oven with hot air. Here is also a picture for reference.
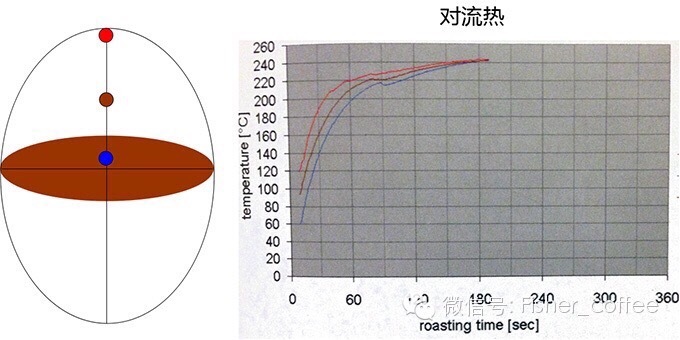
Heating characteristics of convective heat
It may be easier to get some answers by comparing the two pictures. First of all, the experimental premise of the two data graphs is 240 degrees. In other words, the experimental condition of conducting heat is that the furnace wall maintains a temperature of 240 degrees, which is inconvenient to test the temperature change of coffee beans, while the experimental condition of convective heat is that the hot air of 240 degrees continuously passes through the coffee beans, and the hot air temperature remains the same. to test the temperature change of coffee beans. In this way, it is easy to find out that convection heating is more efficient and faster, which is why large hot air baking equipment can finish baking in 3-5 minutes at the earliest. Of course, this is the basic knowledge that we are already familiar with, but we explain "why" in a scientific way. If you are still interested, you can do more comparison between the two pictures to get more baking characteristics of the two heat sources.
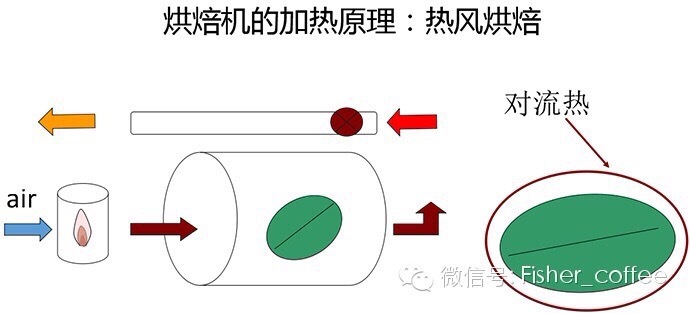
Of course, in the actual roasting process, it is very difficult for us to achieve a continuous and stable heat source, and in terms of coffee roasting and chemical change requirements, we do not need such a continuous heating method, which is why there are so many delicious coffees. but a completely different baking curve is used. What I want to say is that there is no fixed answer to good coffee, there are thousands of good ways, in terms of baking, we need to maintain a development mentality, keep trying and learning. With the development of coffee industry, the difference of brands comes from the difference of baking methods. Hope that we can gradually form our own baking characteristics in the development of the industry environment and the process of self-development.
The article comes from the original creation of FISHER
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

Hot knowledge! Summer teaches you to make a cold cup of coffee
It's already midsummer, still drinking hot coffee?! Don't let your taste buds get hot again, right? Make a cup of cold coffee to cheer you up. Cold coffee is not just iced coffee made of cold water and ice! That's too casual! It is actually cold coffee brewed with cold water and after 12 hours of contact with coffee powder, which is obviously stronger and fragrant, more caffeine and less bitter than ordinary hot coffee.
- Next

What is washing treatment?
1, choose beans: put the harvested fruit in a water tank and soak for about 24 hours. At this time, ripe fruit will sink, while immature and overripe fruit will float up and can be removed. 2. Remove the pulp: use a machine to remove the skin and pulp, leaving only the coffee beans wrapped in the endocarp. At this time, there is a layer of mucous membrane on the outside of the beans, and the process of washing is to wash this.
Related
- What is the meaning of lactic acid fermentation with coffee bean treatment?
- How to judge the state of foam by sound?
- How does the latte pull out the unicorn pattern? Come to get for a little trick to improve the flower pull!
- Will flower pulling affect the taste of the latte?
- Do you know the history of coffee?
- The difference between honey treatment and sun washing what is raisin honey treatment?
- What kind of milk can a novice use to make coffee foam to keep the foam longer? The correct method and skills of milking tutorial sharing
- Why do washed coffee beans taste sour? Flavor characteristics of washed Coffee
- Introduction to the skill of how to practice the size and height of water injection around the circle of hand-brewed coffee
- How do beginners practice coffee flower drawing from scratch?

