Burundian Coffee Bean Flavor Story recommendation of Burundian boutique coffee beans in Burundi coffee producing area

Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style)
Qianjie Coffee has done a detailed introduction of African coffee producing areas before, interested partners can click to view. Today, Qianjie Coffee is mainly about Burundi, which is located in Africa. The charm of Burundian coffee lies in its distinct acidity and fruity aroma. When it comes to sour quality, we have to mention Ethiopian coffee and Kenyan coffee. By comparing the flavors of these African countries, Qianjie Coffee found that the sour quality of Burundi is not as light and bright as Ethiopia, nor as strong and thick as Kenya. Burundian acid is right in between.
Burundi is called the heart of Africa. Burundi is a landlocked country in Africa, located on the steep East African Rift Valley, with complex terrain, a crossroads between Central Africa and East Africa, and a watershed between Africa's two major rivers, the Nile River system and the Congo River system, known as the "Heart of Africa". Bloomberg began to grow coffee in 1930 and was introduced by Belgium, a colonial country. The local people originally had no habit of drinking coffee. In the early years, many farmers resisted to grow coffee. Under the exploitation of the colonial government, it is conceivable that the quality of coffee in those years would not be very good. Coupled with the long-standing ethnic problems in Burundi and producers' mistrust of purchasers, the improvement of coffee quality has been seriously hindered.
Since 1993, project mentoring from the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund has brought a turnaround for the coffee industry in Burundi, but in October of the same year, the first Hutu president was assassinated, social unrest and the development of the coffee industry was shelved. It was not until September 2006 when the Tutsi people of the party and government signed a ceasefire agreement with anti-government organizations that the situation in Burundi gradually stabilized and the development of the coffee industry began to enter a new stage.

The coffee project mentored by the World Bank has two major strategies: one is to expand the coffee washing treatment plant, and the other is to increase the total amount of coffee planted in an all-round way. Before 2007, when all washing treatment plants were under state control and were extremely inefficient and the quality of raw beans varied, the Government allowed private washing treatment plants to be set up in the same year, which was a real turning point for the coffee industry in Burundi. In 2011, Coffee Excellence held a coffee competition in Burundi for the first time, which attracted international attention, and farmers realized that growing coffee was rewarding.
Burundian coffee bean producing area
There are five main coffee bean producing areas in Burundi, namely Cayanza Kayanza, Ngoji Ngozi, Muyinji Muyinga, Qirundu Kirundo and Chirimilo Kirimiro.
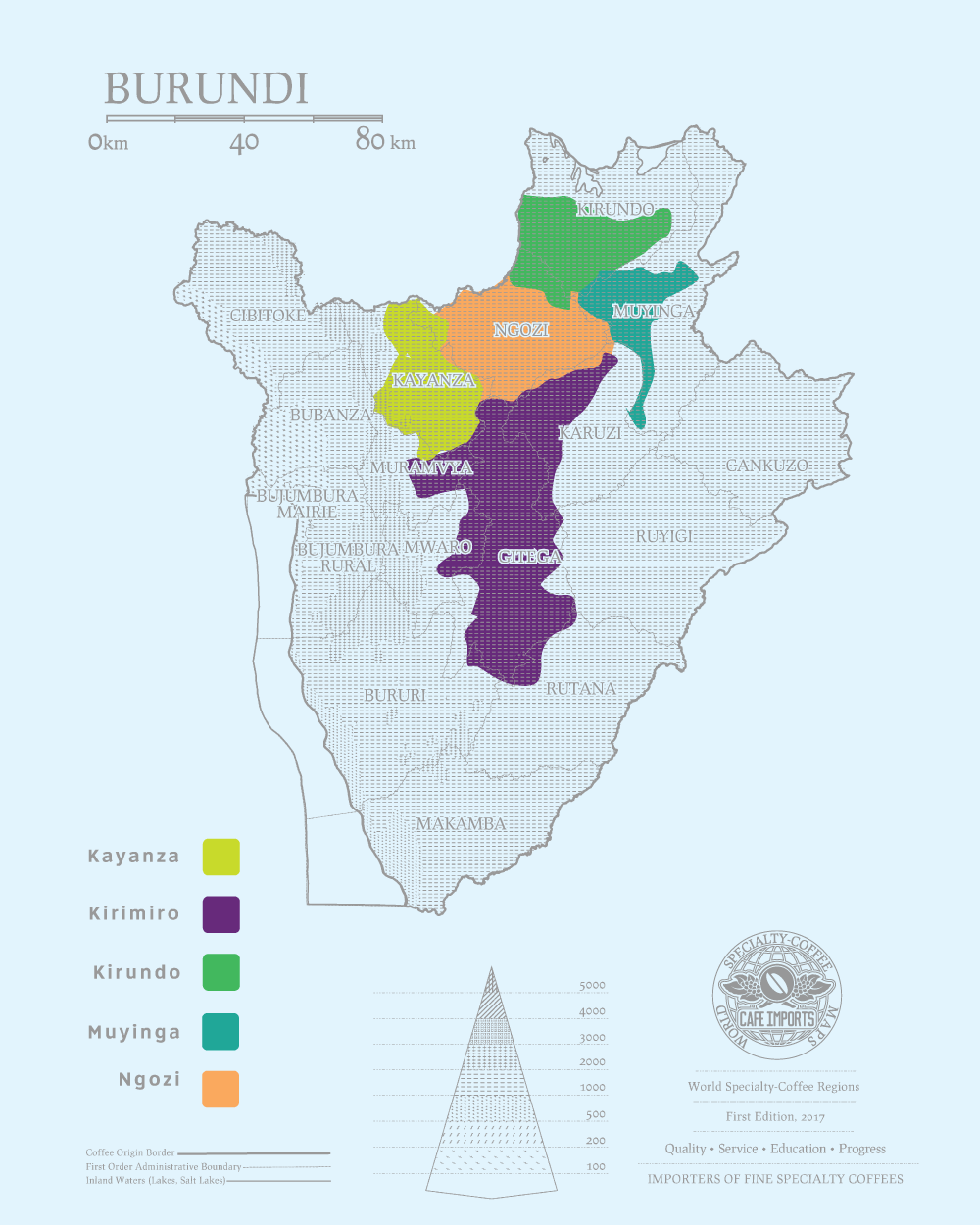
[Cayansa Kayanza, Ngoji Ngozi]
Both Cayansa Kayanza and Ngozi belong to Buyenzi of Buyongji, and their elevations are between 1700 and 2000m. The main rainy season begins in March and April, and the dry season begins in July after harvest, with an average annual temperature of 18-19 ℃. The low temperature at night lasts until early morning, which is the main reason for the compactness of bean fragrance and bean body in these two producing areas.
Coffee from Cayansa scored a high score of 91.09 in the 2015 COE competition. Ngoji's output is less than that of Cayanza, but it has also shown great potential for quality in recent years. In the 2015 COE competition, its best batches scored 88.92%, while other batches from the production area also scored more than 85%.
The production area is quite close to the border of Rwanda, the coffee production is low, and the elevation is between 1400 and 1700m. Due to the influence of the Cayansa production area, the production of high-quality products has gradually approached, and some washing methods have won the final results in the COE competition.
[Muyinyi Muyinga]
A coffee-growing region in northeast Burundi bordering Tanzania. With an average altitude of 1800 meters, the coffee flavor is slightly easier than that in the Cayansa producing area, which is not as rich as that in the Yangza producing area.
[Chirimilo Kirimiro]
Located in the mountains of central Burundi, the average temperature is 12-18 °C. The annual rainfall is about 1100mm, which is lower than that in other producing areas. In addition to COE award-winning coffee, this producing area also has a professional coffee laboratory that focuses on the quality control of exported coffee.
In addition to the above five major coffee producing areas, there are other producing areas. Qianjie Coffee selects Burundian coffee beans from the Rutana producing area, which is a cooperative organized by family-like small coffee farmers. There are 539 small coffee farmers' families, of which 148 are women. On average, each family grows 10,200 coffee trees (at least 1000 coffee trees per hectare), which shows its weak annual income and is a typical poor small coffee farmer family.
Treatment mode
Burundian coffee beans are mostly bourbon varieties as are neighboring Rwanda. Today, more than 800000 of Burundian families rely on coffee cultivation for a living, mostly in small-scale coffee plantations, planted at intervals from other crops, artificially planted, without mechanized equipment, and coffee is mainly treated by washing, with a small amount of sun-dried beans in recent years.
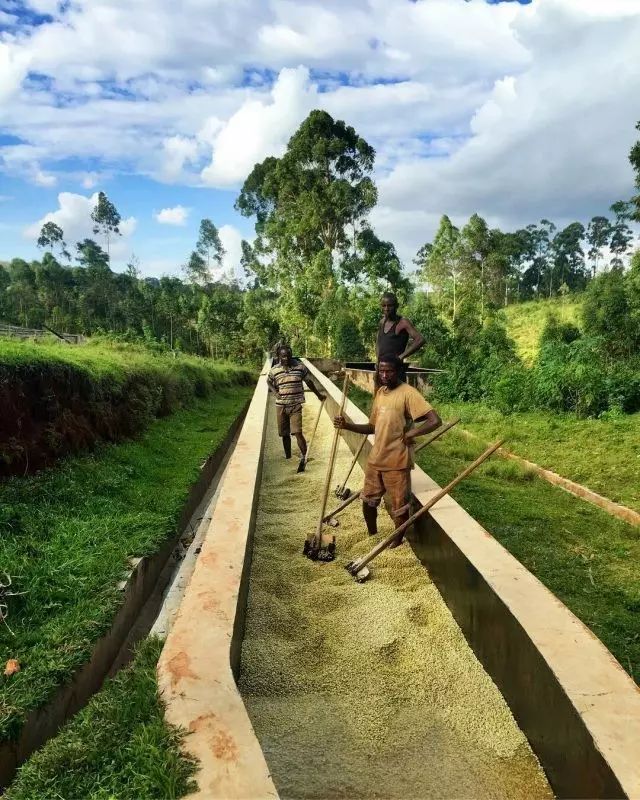

There are two methods of washing treatment in Burundi. One is hand-washed by farmers themselves and then handed over to the washing plant, which is called manual washing and marked as "washed". The other is to directly hand over the fruit to the washing plant and mark it as "fully washed".
Manual washing is completely manual removal of peel, pulp and pectin. Qianjie Coffee mentioned earlier that producers' mistrust of buyers, including mistrust of the processing plant, led to the Cajun Association thinking that the purchase price of the treatment plant was not true, and the price of directly trading the fruit was not good enough. I would rather handle the coffee myself and fight for more bargaining space with the processing factory. But the problem is that most farmers rely on bare hands, lack the use of tools, and often work on dusty roadsides, which inevitably affects the quality of coffee. However, since the opening of the spunlace treatment plant for privatization, the Burundian government has encouraged the harvest to be handed over to professional treatment plants.
Burundi has also developed a water washing treatment similar to that of Kenya-double water washing and fermentation. First, put the harvested fruit into a large tank, select the fruit with good density by buoyancy, then remove the peel and pulp by machine, enter the fermentation tank for about 18 hours, pour the fermented fruit into clean water the next day, and continue to ferment for 18 hours. a total of about 36-48 hours. Then wash the fruit clean, remove the pectin layer softened by hairspray, and finally enter the drying process. The first stage of drying should be shaded and air-dried to avoid direct exposure to hot sunlight, the moisture content will be less than 40%, move to the scaffolding for natural sun exposure, and the moisture content will reach 11%.

Production area: Bubanza
Variety: bourbon
Altitude: 1400-1700m
Grade: AA
Treatment: washing
Flavor: honey, kumquat, violet, light acidity, smooth taste, saturated aroma, rich and long-lasting finish

Baking suggestion
When Qianjie Coffee gets the raw beans of Burundian coffee, it can be said that there is almost no defective beans, and the size and water content are quite even. the high altitude growth environment makes Burundian coffee beans produce brighter acidity and lemon flavors. it also has the flavor of passion fruit, pineapple, flower and honey.
Therefore, Qianjie Coffee decided to use the method of shallow baking, which can fully show the flavor and sweetness of Burundian fruit. Burundian coffee has a high density of raw beans, and the firepower adjustment should be especially careful. After 1 minute, the initial firepower will be relatively large, until the early stage of dehydration, the firepower will be adjusted early, so that the taste and aroma of the coffee become uniform.
After high maturity baking, the bean noodles show a very bright baking color, the taste is full of wild, leaving a strong flavor and aroma. The dry fragrance is very strong, which is not inferior to that of Kenya. When you enter the mouth, you can feel very rich, vanilla-like taste, a little wild feeling, coffee is full-bodied, the acidity is lower than Kenya, the finish is lighter than Kenya, with the inherent characteristics of East African beans, but also quite unique.
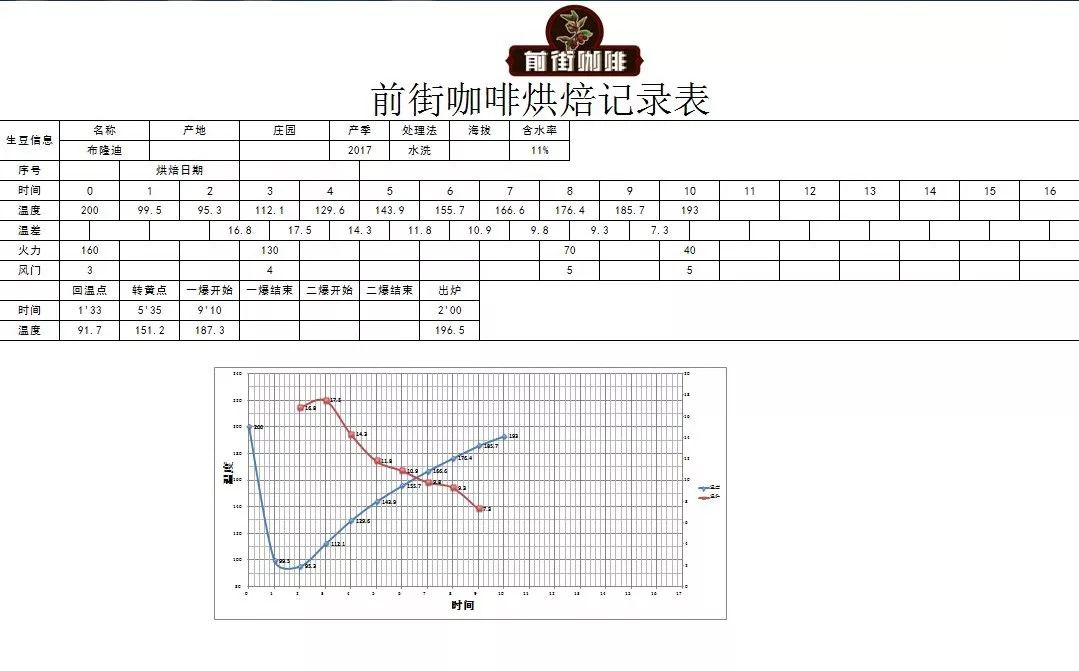
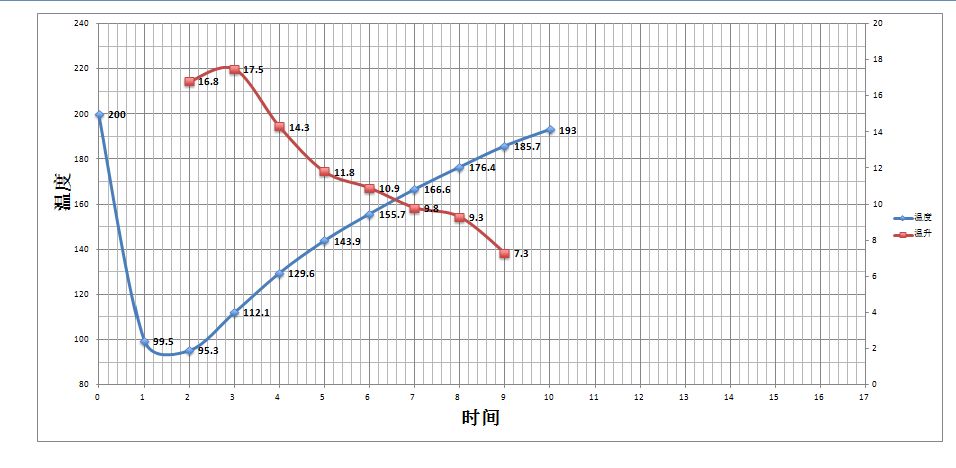
Yangjia 800N, raw bean 550g, specific operation:
Put the furnace temperature to 200 degrees Celsius, set the throttle to stew for 1 minute, adjust the firepower to 160 degrees, keep the throttle unchanged, adjust the firepower to 160 degrees, drop to 130 degrees, bake to 5: 35 ", the temperature is 152 degrees, the bean table turns yellow, the smell of grass disappears completely, dehydration is completed, throttle tune 4.
In the 9th minute, ugly Hu wrinkles and black markings appear on the bean table, and the smell of toast obviously changes to the smell of coffee, which can be defined as a prelude to an explosion. at this time, listen clearly to the sound of an explosion point, to 9: 10 "to start an explosion, the small firepower remains the same. The throttle is fully open at 5 degrees (the firepower should not be so careful that there is no cracking sound) 40 degrees, 196.5 degrees into the pot.
Test the flavor by cup
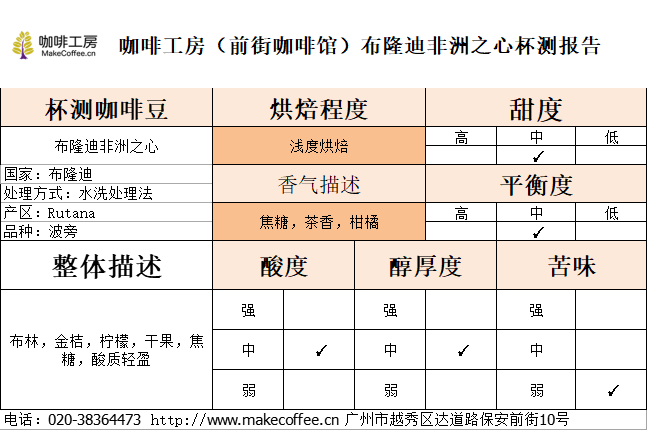
Dry aroma: citrus, cream, caramel
Wet incense: lemon, vanilla
Entrance: Brin, kumquat, lemon, dried fruit, caramel, light acidity, smooth taste, saturated aroma, rich and lasting finish.
How to brew Burundian Heart of Africa Coffee beans in Front Street Coffee
Qianjie Coffee: V60 filter cup, 15g powder, 90 ℃ water temperature, 1:15 powder / water ratio, grindability (Chinese standard No. 20 sieve pass rate 80%)
Qianjie coffee should be reminded that when you get freshly roasted coffee beans, don't brew them for three or four days before brewing, then the flavor of the coffee will really come out.
Qianjie coffee is extracted by stages, that is, three-stage water injection, 30 grams of water stuffy steam for 30 seconds, the second small flow circle water injection to 125 grams of water cut off, waiting for the water to drop and then slowly water injection, the speed is uniform, the water level should not be too high, again water injection to 225 grams stop, extraction time 2 minutes (including steaming time).
Brewing flavor: it smells of mandarin and tea, imported black brine, mandarin flavor, rich taste, and the sweetness of nut caramel in the middle and back. The taste is full of wild, strong taste and aroma remain in the mouth, and the finish is rich and lasting.

For more boutique coffee beans, please add private Qianjie coffee on Wechat. WeChat account: kaixinguoguo0925
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

The mellow flavor of Dominican coffee introduces the characteristics of Dominica coffee manor.
Coffee in Dominica is grown in highlands and lowlands, and its taste is slightly different. The upland is sour, but the taste is rich; the lowland is less sour and tastes smoother. Boutique coffee has become popular in recent years. High-quality coffee beans produced by some Dominican estates have a rich aroma, mellow taste and moderately bright sour taste, and have been bought with the more famous Puerto Rico beans or teeth.
- Next

Introduction of Ugandan Coffee production area
It has a low ripe fruit aroma, such as the taste of red wine, and a thick mellow thickness, which is similar to some Kenyan beans with low tone, but with a mild soil flavor, so it is quite different from other East African countries in flavor characteristics. on the contrary, it is somewhat similar to Asian Indonesian Sulawesi Tonaga coffee and Java manor coffee. With baking between City+ and Full City+
Related
- Detailed explanation of Jadeite planting Land in Panamanian Jadeite Manor introduction to the grading system of Jadeite competitive bidding, Red bid, Green bid and Rose Summer
- Story of Coffee planting in Brenka region of Costa Rica Stonehenge Manor anaerobic heavy honey treatment of flavor mouth
- What's on the barrel of Blue Mountain Coffee beans?
- Can American coffee also pull flowers? How to use hot American style to pull out a good-looking pattern?
- Can you make a cold extract with coffee beans? What is the right proportion for cold-extracted coffee formula?
- Indonesian PWN Gold Mandrine Coffee Origin Features Flavor How to Chong? Mandolin coffee is American.
- A brief introduction to the flavor characteristics of Brazilian yellow bourbon coffee beans
- What is the effect of different water quality on the flavor of cold-extracted coffee? What kind of water is best for brewing coffee?
- Why do you think of Rose Summer whenever you mention Panamanian coffee?
- Introduction to the characteristics of authentic blue mountain coffee bean producing areas? What is the CIB Coffee Authority in Jamaica?

