Nutrition and composition of coffee beans

Many people like to enjoy breakfast in the morning to a cup of strong coffee to refresh, in the afternoon tea time to taste the cake and with mellow coffee boost, but like to drink coffee we also need to understand the composition of coffee beans, in order to understand their own intake of nutrients, but also to know the impact of coffee ingredients on the body and coffee flavor changes.
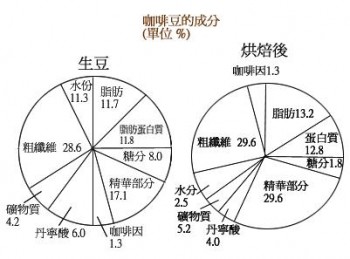
The nutrition and ingredients of coffee beans can be roughly divided into 8 different nutrients and ingredients. The following introduces the ingredients of coffee beans one by one and explains the effects of these ingredients on the body and coffee flavor:
Caffeine: source of bitterness. Appropriate amount of caffeine will increase the metabolic rate of cells, stimulate the central nervous system, cardiovascular, respiratory system, gastrointestinal, muscle, kidney…and so on.
Tannin: Source of sour taste. Boiling will decompose to produce pyrogallol acid, too much tannic acid will cause coffee taste astringent.
Fat: The fat contained in coffee beans can be roughly divided into acidic fat and volatile fat, which are described as follows:
Acid fat: fat contains acid, its strength will vary according to the type of coffee.
Volatile fat: The source of coffee aroma, it will emit 40 aromatic substances, but also will evaporate due to contact with air.
Protein: Source of calories. However, coffee protein is not easy to dissolve, so the intake of calories is limited.
Sugar: Source of sweetness and color of coffee. After roasting, the sugar in the green coffee beans will be converted into caramel. Caramel and tannins combine to make coffee astringent and sweet.
Coarse fiber: source of coffee color. The fibers of raw beans will carbonize after baking. When carbon fiber combines with caramel, it forms the color of coffee.
Minerals: Slightly astringent source. A small amount of lime, iron, phosphorus, sodium carbonate and so on.
Water: Raw beans contain about 11% water, leaving about 2.5% after baking.

Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

[coffee common sense] the difference between Italian VS hand brew, Italian coffee and hand brew coffee
Yes, there are thousands of kinds of coffee. I just want to divide them into two categories, one is called espresso, the other is called non-Italian. Why are they classified in this way? When we drink a cup of coffee, we need to know where it comes from. Then the magical thing appeared, these two kinds of coffee making utensils have the difference in principle! Today, we will help you organize the coffee from the point of view of brewing equipment.
- Next

Coffee Story| A coffee "technology control" unknown life (1)
Camel coffee shop although small, layout is very reasonable to love coffee is equal to choose a full of temperature and aroma of life style, if unfortunately become a coffee technology control? Congratulations, you have successfully embarked on a hard and happy road of burning money. It's a warm, fragrant scene, a floor-to-ceiling window with bright yellow lights, and someone sipping coffee.
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

