Introduction of Coffee Flavor and Taste characteristics of Yunnan Coffee Bean Variety Katim Catimor

Chinese Coffee History
With the help of modern technology, we can know that tea contains caffeine. That means that we Chinese fell in love with caffeinated drinks as early as 1300 years ago, and even in 780 AD, the Cha Sheng-Lu Yu's Cha Jing opened up China's unique global tea culture. However, it was not until the end of the 19th century that another caffeine crop, coffee tree, was introduced to China. That is to say, the history of coffee in China is only more than 200 years.

The earliest Chinese literature of Coffee in China can be traced back to the Chronicles of the four continents compiled in 1840 by Lin Zexu, a national hero in the late Qing Dynasty. According to the book, Yemeni coffee is exported as a native product, while "Yunaisdi" (United State, United States) is an importer.
Interestingly, the history of coffee consumption in China can be traced back to years earlier than the Chronicles of the four continents. In 1836, Li Dou, a dramatist of the Qing Dynasty, recorded that the Danes opened China's first coffee shop near the thirteen lines in Guangzhou, which was then known as the "black house". It is also written in the Guangdong Tongzhi during the Jiaqing period that "black wine is drunk after a meal, and this wine can be consumed."
The "black wine" mentioned above was the name for coffee at that time. Coffee, an imported product, was not only called "black wine" at that time. At that time, because there was no unified translation method, all kinds of written records are quite interesting now: Jiafei, Jiafei, yoke Torreya grandis, Kao Fei, Kao Fei, Gao Li and so on.
During the period of the Republic of China, more and more Chinese people had the habit of drinking coffee, especially the earliest trade ports, such as Shanghai. At present, Shanghai has the largest number of cafes in China. At that time, the cafe was more of a meeting place. Lu Xun, the author of "Young Leap soil" in our primary school Chinese textbook, likes to go to the public coffee cafe at 998 North Sichuan Road in Shanghai. he loves not coffee, but the atmosphere of the cafe.
In recent years, China is also on its way to catch up with the third wave of coffee. Friends also began to explore the planting areas, varieties, roasting and extraction methods of coffee beans. And Qianjie Coffee has been with you along the way, giving you the science of every bean, the story behind each producing area and the way we deal with it.
History of Coffee cultivation in Yunnan
The Chronicles of Binchuan County recorded: "in the 30th year of the Qing Dynasty (1904), Tian Deneng, a French Catholic missionary, was sent by the Dali Diocese Church to bring French Lu Hongru and Sichuan Deng Peigen to preach in the Binchuan area." in 1904, French priest Tian Deneng, ordered by the Dali Church, went to build a church in Zhukula Village, Pingchuan Town, Binchuan County, Dali. Father Tian Deneng had a habit of drinking coffee, so he introduced an Arabica coffee tree and planted it next to the church.
Some people say that the Arabica coffee tree was imported from Vietnam, but there is nothing to test. Some people say that the tree was planted in 1892; others say it was 1902.
Among them, the History of Catholicism in Yunnan recorded: "the name and address of the church: Catholic Church, Pingchuan, Pingchuan Zhu Kula, founded: Guang Xu 30 years (1904)." These documents prove that Father Tian Deneng first appeared in Pennsylvania in 1904 and funded the construction of the church in Zhukula. This history is controversial, but it never says exactly in which year Arabica coffee trees were planted in Yunnan.
Yunnan coffee producing area
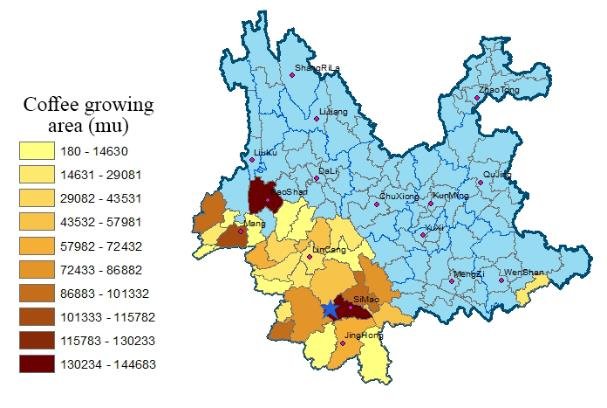
When it comes to coffee growing areas in China, it can be divided into three producing areas and two parts. The first part is the coastal areas of Fujian Province and Hainan Province, both of which grow robusta beans because of their low average altitude and high temperatures, which are not suitable for growing Arabica beans. In Yunnan, most areas are 1000-2000 meters above sea level, and the topography is mainly mountain slopes, with undulating terrain, fertile soil, sufficient sunshine, rich rainfall and large temperature difference between day and night, which are ideal planting conditions for Arabica beans.
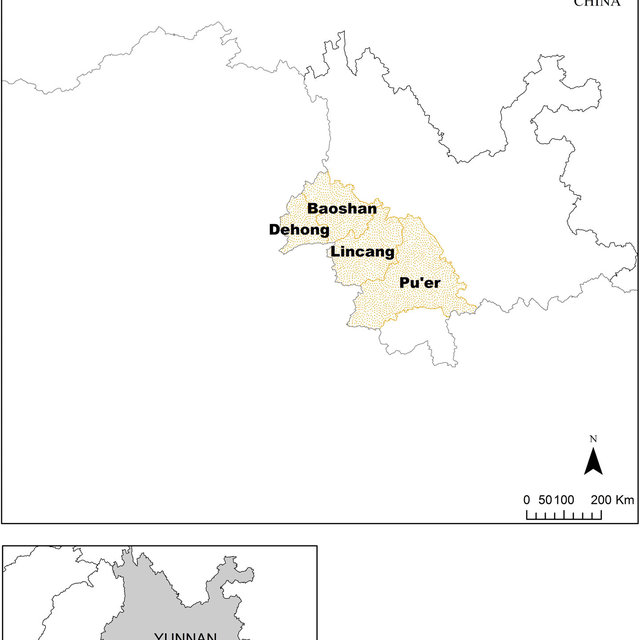
Yunnan coffee producing areas are mostly concentrated in the west and south, mainly distributed in: Lincang, Baoshan, Pu'er, Dehong.
[Lincang]: Lincang City is located in the southwest of Yunnan Province, with the Tropic of Cancer running through the south, Pu'er to the east, Dali to the north, Baoshan to the west, and Myanmar to the southwest. Lincang City is named because of its proximity to the Lancang River. It is a bright pearl in the southwest border of the motherland. The annual average temperature in Lincang is between 16.8 ℃ and 17.2℃. The dry and wet season is obvious and the sunshine is sufficient.
Baoshan: the cultivation of Baoshan small-grain coffee in Yunnan has a long history. Baoshan small-grain coffee can be said to be a national geographical indication product, and it is one of the coffee with good quality in the whole country and in the world.
The average temperature of Baoshan is 21.5℃, and the highest is 40.4℃, which is basically frost-free all the year round. It is recognized as the best producing area of small-grain coffee. The small-grain coffee cultivated here is famous at home and abroad for its strong but not bitter, fragrant but not strong, well-proportioned small noodles, mellow and fruity.
[Pu'er]: although Pu'er is famous for its tea, its coffee planting area has reached 789000 mu, with an output of 58600 tons of coffee beans and a total output value of 2.469 billion yuan, making it the largest coffee planting base in Yunnan. Its climate, geography and soil conditions are unique for growing coffee.
[Dehong]: with a typical climate of tropical rain forest in South Asia, no severe cold in winter, no heat in summer, short frost period and small temperature difference, it is recognized by domestic experts as the most suitable area for growing small-grain coffee in China. The coffee produced has a unique flavor and good quality, and has a high reputation in domestic and foreign markets. Among them, Hougu Coffee has become one of the first-class coffee enterprises in China.
Yunnan coffee bean varieties

When it comes to Yunnan coffee, we have to mention Yunnan small grains. Yunnan small grain originally got its name from the iron pickup, which is the Arabica small seed. The oldest variety in Yunnan is iron pickup, but because of its poor disease resistance, coffee farmers began to cut down good varieties of coffee with good flavor and plant them with poor flavor, but the yield was very high. S288, which is resistant to leaf rust, was introduced at the beginning, and Katim with higher yield was introduced in the later stage. Nowadays, you can see two beans from Yunnan on the bean list of Qianjie coffee. One is the Yunnan Huaguo Mountain of Tippika, and the other is the Yunnan small grain of Katim.
[Qianjie Coffee Yunnan Huaguoshan Coffee]

Producing area: Baoshan, Yunnan
Altitude: 1200m
Treatment method: washing
Variety: iron pickup
[Qianjie Coffee Yunnan small Coffee]

Producing area: Baoshan, Yunnan
Altitude: 1200m
Treatment method: washing
Variety: Katim
Katim.

Katim Catimor, from the cross between Timor timor and Kaddura caturra, was developed in 1959 by the Portuguese Coffee Leaf Rust Research Center (CIFC). Its research direction is disease resistance and high yield. Katim coffee beans are characterized by high yield, short plants, dense planting and red-brown new leaves. Inheriting the Robusta robusta gene from Timor timor, Katim catimor can better resist coffee berry disease and coffee leaf rust, and has stronger resistance to diseases and insect pests, but it is often criticized for its performance in the cup. Katim coffee beans are characterized by fast ripening and high yield, requiring adequate fertilizer supply and shade. In addition, Katim catimor's high yield corresponds to a relatively shorter commercial life, with an average of only ten years.
When growing at low altitude, the cup test performance of Katim coffee beans has no obvious advantages and disadvantages compared with other commercial varieties. Planted above 1200 meters above sea level, the flavor of Katim catimor Cup is obviously inferior to that of Bourbon bourbon, Kaddura caturra and Kaduai catuai.
Katim coffee beans were first developed in 1959 and were popularized in Brazil in the 1970s and 1980s. With disease resistance and high yield, it occupies a place in Central and South American coffee varieties. The occasional outbreak of coffee leaf rust crisis in Central and South America has also contributed to the use of Katim coffee beans. Unfortunately, because the Timorese species (also known as the Alabasta species) is the product of a natural cross between the Tibica Arabica species and the Robusta species, although the latter can give it disease resistance, the delicate taste of the Arabica varieties has disappeared.
Katim CIFC7963 (F6) is widely popularized and planted in Dehong, Baoshan, Pu'er, Xishuangbanna, Lincang, Wenshan, Yuxi and other coffee growing areas in Yunnan Province, as well as Panzhihua in Sichuan Province and neighboring Myanmar, with a total promotion area of more than 200,000 mu. Cooking suggestion
Qianjie Coffee recommends that when these two cups of Yunnan coffee are washed, they tend to be balanced, requiring neither too much acidity nor too much modification of the tail section. The amount of coffee powder is 15g, the ratio of powder to water is recommended at 1:15, the flavor can be clearer at 1:16, the filter cup is kono filter cup, the temperature of brewing water is 88 degrees Celsius, the aim is to make the acid softer and the size of fine grinding / fine granulated sugar (the pass rate of sieve 20 is 80%).
The use of three-stage extraction: steaming with 30 grams of water for 30 seconds, small water injection around the circle to 125 grams for stages, when the water level is about to expose the powder bed, continue to inject water to 225 grams to stop water injection, wait for the water level to drop and remove the filter cup when the powder bed is about to be exposed, (the time of steaming starts) the extraction time is 2 minutes 39 percent 00 ".

Flavor: Huaguoshan iron pickup coffee beans you can drink obvious baked nuts, soft acidity, overall balance fragrance, solid dark chocolate aroma, light orange peel. You can taste nutty aromas of small Katim coffee, with herbs, chocolate, caramel and a hint of acidity in the finish.

Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) more boutique coffee beans please add private Wechat Qianjie coffee, WeChat: kaixinguoguo0925
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

How does the rare Hawaiian Coffee Flavor describe the Flavor of Solar Iron pickup in Hawaii Cafu producing area
For the exchange of professional baristas, please follow the Coffee Workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) country: Hawaii Product name: Hawaii Card Fog tanning Iron production area: card Fog treatment: tanning treatment altitude: 500m-620m Variety: Typica Grade: Prime Card Fog in the Big Island area of Hawaii, in the southeast of the famous Kona coffee bean growing area. In the fog.
- Next

Colombian coffee "Emerald Mountain" flavor taste and roasting degree suggest hand-picked coffee only
For the exchange of professional baristas, please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) across the natural Andes, where Colombian coffee is rich. The hilly area of more than 1700 meters is the hometown of the Jade Mountain. Moderate rainfall, sunshine-morning the difference is warm and cold strong night the land drainage is good, nutrient-rich volcanic ash specific cool climate below 2000m
Related
- Detailed explanation of Jadeite planting Land in Panamanian Jadeite Manor introduction to the grading system of Jadeite competitive bidding, Red bid, Green bid and Rose Summer
- Story of Coffee planting in Brenka region of Costa Rica Stonehenge Manor anaerobic heavy honey treatment of flavor mouth
- What's on the barrel of Blue Mountain Coffee beans?
- Can American coffee also pull flowers? How to use hot American style to pull out a good-looking pattern?
- Can you make a cold extract with coffee beans? What is the right proportion for cold-extracted coffee formula?
- Indonesian PWN Gold Mandrine Coffee Origin Features Flavor How to Chong? Mandolin coffee is American.
- A brief introduction to the flavor characteristics of Brazilian yellow bourbon coffee beans
- What is the effect of different water quality on the flavor of cold-extracted coffee? What kind of water is best for brewing coffee?
- Why do you think of Rose Summer whenever you mention Panamanian coffee?
- Introduction to the characteristics of authentic blue mountain coffee bean producing areas? What is the CIB Coffee Authority in Jamaica?

