Peruvian Coffee background and current situation Peruvian Coffee grading system Peruvian Coffee treatment
Historical background and current situation of Peruvian coffee
Coffee was actually grown in Peru in the mid-17th century, but most of the coffee was collected by the government to pay off the national debt. Because Peru owed money to Britain, about 2 million hectares of land was produced to repay Britain, including coffee cultivation.
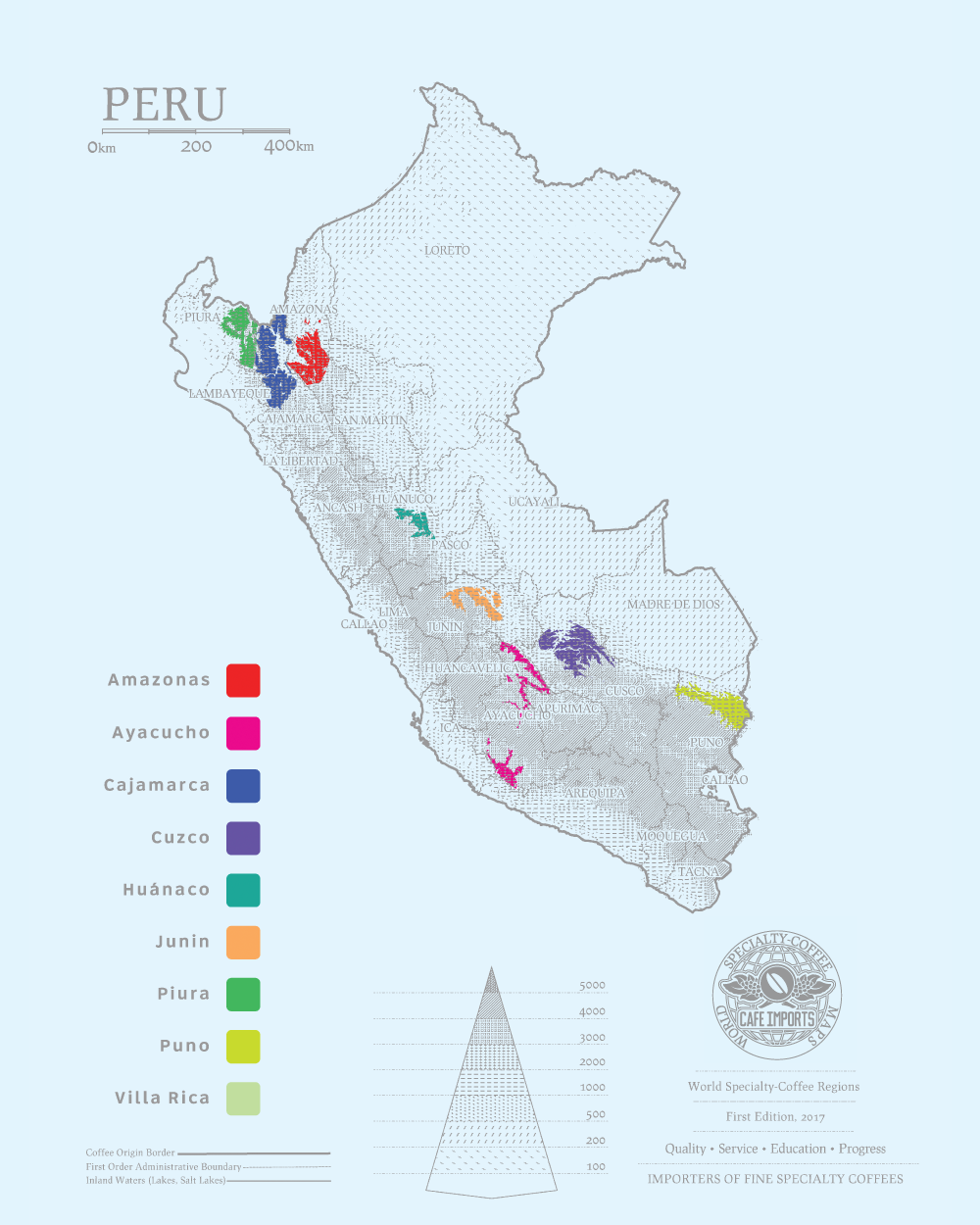
Later, with the end of this event, the land slowly returned to the hands of farmers, and with the encouragement of the Peruvian government, coffee began to be cultivated in large quantities. The cultivation area was surrounded by the Andes Mountains, where the fine coffee was cultivated at an altitude of 1200 to 1800 meters. The fertile soil was matched with the alternation of dry season and rainy season, and the temperature difference between day and night could be between about 2 degrees Celsius and 20 degrees Celsius. The climate and environment are very suitable for coffee growth, which is also one of the reasons why Peru has gradually become a coffee exporter. Its export value accounts for about 28 per cent of Peru's total exports, and it has been cultivated on 380,000 hectares by 160,000 families.
As in many Central and South American countries, farms became smaller and more dispersed as large lands owned by Europe were sold or redistributed throughout the 20th century, providing farmers with independence but also limiting their access to resources and expanding commercial markets. However, unlike many other countries where the coffee economy is dominated by smallholders, Peru lacks organizations or infrastructure to provide financial or technical support to farmers-a gap that external organizations and certification try to fill. The country has a sizable supply of certified organic coffee, as well as Fairtrade, Rainforest Alliance and UTZ certified coffee.
Peruvian coffee flavor characteristics
Peruvian coffee bean appearance color is a bit like half sun color for its characteristics, alcohol moderate, high quality balance, acidity palatability is one of its characteristics, another slightly stone fruit taste, taste mild acid.
Peruvian coffee grading system
Grading in Peru is usually done by altitude classification for high mountain beans and green bean size classification for low and medium altitudes. Origin also uses "number of defects" as an auxiliary classification, while buyers use custom "cup test quality" as an auxiliary classification.
Strictly High Bean (SHB): over 1350 m.
High Bean (HB): 1200-1350 m.

Peruvian approach
Peru because of abundant water resources, the traditional treatment method to wash mainly, then is the sun treatment. At Vela Ethan's coffee estate, new treatments include red honey, double anaerobic fermentation + washing or anaerobic fermentation + sun. For example, in the first stage of double anaerobic fermentation + washing process, coffee beans with Exocarp are placed in a closed barrel for 14 hours-peel removal-leaving part of pulp and peel for second fermentation for 24 hours-washing with water for three times-drying-shelling) During anaerobic fermentation, the temperature is controlled between 18-22 ℃, and the drying temperature is also controlled at 30-35 ℃.
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev
Kundinamaka Coffee Bean Flavor introduction to Coffee producing areas of Candinamaka, Colombia
Around 1860, the province of Cundinamarca began to grow coffee on the western slope, and then slowly moved northwest over the next decade or two. This area is the second Colombian province to start export, and production peaked during World War II. There used to be many very large estates here, some with more than a million coffee trees.
- Next
What's St. Martin's coffee like? The characteristic Flavor of San Martin Coffee producing area in Peru
Coffee is Peru's main export. However, crops are affected by climate change, which reduces acreage and promotes the spread of disease. To meet these challenges, farmers have two parallel strategies: they diversify production by adding new crops such as cocoa or vegetables, and invest in organic agriculture to protect the environment and get higher prices. The latter makes Peru a complete
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

