Do American coffee beans taste good?
American coffee occupies a large position in the coffee industry, such as Panama, Colombia and Guatemala are all rich in high-quality coffee in the Americas, not to mention that coffee has become more and more high-quality in the past decade, and consumers have higher and higher requirements for the quality of coffee. Several countries in the Americas that are rich in high-quality coffee are places where everyone is haunted. The names of Panama and Rosa shocked the whole boutique coffee circle, and created the reputation of Panamanian coffee today. If you want to find another coffee-producing country comparable to Panama, you might as well start from neighboring countries, starting from Panama, to the northwest, that is, another famous coffee-producing country in the Americas-Costa Rica. Costa Rica is geographically bordered by Nicaragua in the north and Panama in the south. It was declared a permanent neutral country on November 17, 1983. According to the Constitution, Costa Rica has no army, only police and security forces to maintain internal security. It is the first country in the world without an army. Although Costa Rica is an agricultural country, it has achieved a relatively high standard of living, a general expansion of land ownership, a boom in tourism and a diverse culture because it is the cultural confluence of Central and South America. It has been nearly 200 years since Costa Rica began to promote coffee cultivation on a large scale in the 1820s. Coffee beans, as one of the most important export agricultural products of Costa Rica, are strongly supported and protected by the state.
Costa Rica is located in the Central American isthmus and belongs to North America. In the previous article, the front street coffee mentioned that Costa Rica is close to Panama, with Nicaragua in the north, the Caribbean in the northeast and the Pacific Ocean in the south. Influenced by ocean currents such as the Pacific Ocean and monsoons, Costa Rica has formed a unique microclimate. The whole year of Costa Rica is divided into dry season and rainy season, which is from April to November, and from December to March of the following year. Coffee trees planted in Costa Rica generally blossom from April to June and are harvested at the same time from July to February. The rainy season provides sufficient Rain Water to help coffee trees grow, and the fruit is picked during the dry season to facilitate the harvest of coffee fruits with the same maturity, as well as long-term sun drying conditions for sun treatment.

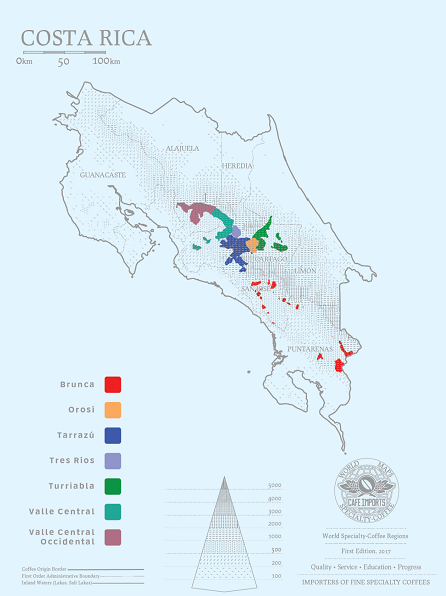
Despite its small size, Costa Rica is one of the most species-rich countries in the world, rich in natural resources and, as its name suggests, "rich coast". The coastal landscape of Costa Rica is plain, and the central part is cut off by rugged mountains. Among them, there are seven representative producing areas: West Valley in the western valley, Central Valley in the central valley, Tarrazu in Tarazhu, Tres Rios in Sanshui River, Orosi in Europe, Brunca in Brenka, and Duli Alba Turrialba. Among them, Tara Zhu is the most representative, which is located in the south of San Jose, the capital of Costa Rica, and is the most valued coffee producing area. Most of the best coffee in Costa Rica comes from secondary production areas. Take the result of the Costa Rica COE Excellence Cup in 2020 as an example, nine of the top 26 coffee beans came from the Tarazhu producing area, and three of them won the top three respectively. It is conceivable that the Tarazhu producing area is a veteran of producing high-quality coffee.

The common treatment methods in Costa Rica are washing treatment, sun treatment and typical honey treatment. The peel and pulp of coffee fruit were removed by washing, and the pectin layer was removed by pool fermentation and dried in the sun. In the sun treatment, the fruit was kept completely and dried in the sun, and then the pectin part of the peel and pulp was removed. The honey treatment is between the two, honey treatment is like the first two steps of washing treatment, first flotation coffee fruit, remove peel and pulp. However, the pectin layer was not removed by pool fermentation, but by retaining pectin in the sun. By retaining the amount of pectin, it is divided into yellow honey, red honey and black honey. Because the pectin part is sticky and slippery, and its sugar content is high, in the process of processing, the pectin wraps the coffee raw beans like honey, so people vividly call this layer of coffee pectin "honey", so it is named "honey treatment".
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

Iced latte what is the ratio of iced latte coffee to milk and ice cubes
Making espresso is a necessary skill for every barista, and almost every cafe produces espresso. We often talk about espresso is a series of coffee drinks based on espresso. Today, let's make an iced latte with milk coffee, which is the easiest to make in espresso. Iced latte looks like a very simple
- Next

Introduction of coffee varieties in Colombia-introduction of coffee beans produced in the main producing countries in the world.
Like Brazil, Colombia, as the world's main producer, has excellent geographical conditions that are tailor-made for coffee cultivation. Colombia has changed from marijuana as the pillar to coffee as the pillar. With the strong support of the government, especially after the sweep of leaf rust, Colombia has also begun to diversify its coffee varieties. As in other areas, the iron pickup
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

