Reference Index of Coffee Bean grading Coffee Bean selection Kit
In fact, at present, there is no unified classification in the coffee industry, and each producing country is divided into its own levels. For example, Brazil sets No. 2 as the highest level and Jamaica sets No. 1 as the highest level.
Personally, because people have different preferences and tastes, grading does not fully represent the flavor of coffee, it is more about the quality of coffee, so coffee grade is not very important to me. I don't think you know good coffee until you taste it. Moreover, domestic coffee shops usually do not mark the grade, can only see Colombia coffee, mantenin coffee, Kenya coffee, etc., but do not see the grade. Therefore, taste was the absolute truth.
In general, however, the following three indicators can be used for grading:
(1)The size of coffee beans
Some people say that the size of the beans does not affect the flavor of coffee, like the Mattari of Yemen, although the particles of the beans are large and small, it is still the top of the coffee. However, in many production areas, the size of coffee beans is indeed a valuable indicator.
This classification is commonly used in Kenya, New Guinea, Puerto Rico, Zimbabwe, Tanzania and Uganda. In addition, many Brazilian coffees also use this classification method.
(2)Number of defective beans
This is the earliest classification method and is still used in many parts of Brazil. The method of identification is to randomly select 300 g samples, identify defective beans in the samples, and accumulate different scores according to the types of defects. After the evaluation, the grade is Gr2 to Gr8 according to the accumulated defect score, but there is no Gr1. If you want to buy first-class Brazilian beans, it will be a joke.

Image: defective coffee beans
Indonesian and Ethiopian coffee beans are graded in this way. The main classification of Indonesian beans is 6 grades: Gr1 ~ Gr6. In Ethiopia, there are 5 grades, among which Gr1 ~ Gr2 are reserved for washed beans, Gr1 represents 0~3 defective beans per 300g of raw beans, Gr2 represents 4~12 defective beans per 300g of raw beans, and the quality of sun-dried beans is Gr3, Gr4 or Gr5 in sequence.
(3)The origin of coffee beans
Coffee beans are processed from the fruit of the coffee tree, which grows between 25 degrees north and south of the equator (as shown in the figure below), that is, tropical and subtropical regions.
At present, there are more than 60 coffee producing countries, which are distributed in South America, Central America, West Indies, Asia, Africa, Arabia, South Pacific and Oceania.
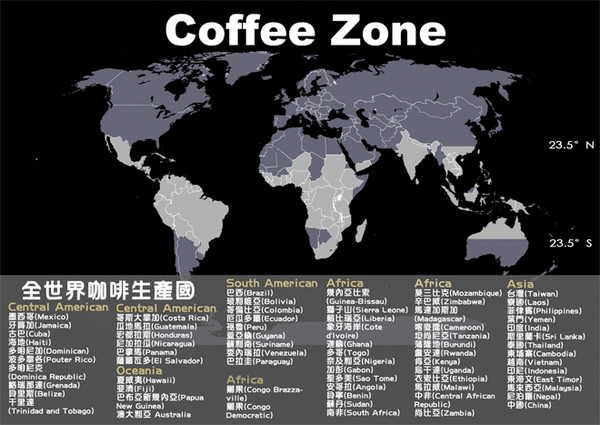
Photo: Coffee producing countries worldwide
The best quality coffee beans in the world are produced in Indonesia and Colombia. In terms of output, Brazil ranks first in the world, accounting for about 30%, followed by Central and South America centered on Colombia, Africa and Arabia, and the remaining 10% distributed in Asia and islands.
In addition, Guatemala, Costa Rica and El Salvador, Central American countries, are located in the rolling mountains. The farms in the territory are located in mountainous areas with different heights, so it is also possible to distinguish the quality of coffee by the height of origin.
(4)Coffee beans old and new
New coffee is called "new beans", referring to the green beans harvested that year. Green coffee beans produced the previous year are called "old beans." The beans harvested a few years earlier are called "old beans". Only the new beans produced in that year are high-grade products, because the taste and aroma of the new beans are relatively strong.

Comparison of Old and New Coffee Beans
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

Introduction to the secret treatment of coffee beans by Honey Process Coffee
Honey treatment, called Honey Process or Miel Process, is called Honey Coffee. It is used in coffee gardens in Costa Rica (Costa Rica), Panama (Panama) and Taiwan. Honey treatment is a kind of treatment which is between the sun treatment and water washing. It keeps the coffee clean, although the brightness decreases, but increases.
- Next

The treatment of raw coffee beans common sense of fine coffee beans
After the coffee fruit is picked, the coffee bean must be removed from the coffee fruit as soon as possible. There are generally several ways to deal with it: washing, that is, the coffee fruit is immediately picked when it turns red, the hard peel is removed by machine, the sticky berry is exposed, and then thrown into the pool to ferment. In about a day or two, the bacteria will eat most of the flesh attached to the seeds. The whole fermentation process needs to be monitored by the old master.
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

