Fine coffee common sense the soul of caffeine coffee
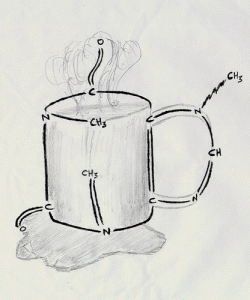
Chemical structure of caffeine
Caffeine can be said to be the soul of coffee and the most controversial issue. Caffeine is an alkaloid in coffee beans, which can stimulate the central nervous system, stimulate the secretion of epinephrine and enhance heart function in the right dose. Although caffeine has no odor, it has a remarkable bitter taste. Although some people want to judge the amount of caffeine by the same degree of bitterness of coffee, it is not completely successful, because the bitterness of caffeine accounts for only a small part of the bitterness of coffee, so there is not much influence on the bitterness of decaffeinated coffee.
It is generally believed that espresso is made under high pressure, very rich, aromatic, caffeine content will be relatively high. But the opposite is true. In fact, the content of caffeine (Caffeine) in raw coffee beans varies greatly from variety to variety (only if espresso uses the right mixture). The content of Robusta is higher, the average is about 2.2% of the dry matter, and the content of Arabica is less, the average is about 1.2%.
In recent years, low-caffeinated coffee beans have been cultivated in Java and Ivory Coast, with a caffeine content of only 0.2%. Caffeine can be removed by a variety of methods to make a variety of decaffeinated products. The caffeine content of decaffeinated instant coffee powder is less than 0.3%, and general commodities are controlled between 0.1% and 0.2%. Therefore, if you use some cheap, inferior, burnt robusta mixed coffee beans to make espresso, the espresso will be less healthy and the body will absorb too much caffeine. A moderate intake of caffeine is beneficial. It can help you concentrate and even help you have sex while protecting your body.
It must be made clear that when using the right stress and high-quality coffee beans, the daily intake must be limited to less than 5-6 cups; if you are using not-so-good beans at home, this intake must be reduced appropriately. After being digested by the human body, caffeine can be quickly absorbed and metabolized and excreted in the urine. The increase of caffeine in human blood depends on the content in the stomach. The most significant physiological effect of caffeine on the human body is the stimulation of the central nervous system. As for the dose required for the change of brain activity, which is much higher than the normal intake, the other more eye-catching physiological effects are the impact on blood pressure, cardiovascular and other issues.
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

Indian Coffee-the enigmatic Coffee of the mysterious country
Indian coffee with exotic spices our mysterious impression of India lies not only in its coffee, but also in tea, temples, yoga, sitaqin, or even more negative abnormal big cities, and so on. The reason why there are so many kinds of Indian beans on the market today must be attributed to the indomitable Indian coffee expert and importer Dr. Joseph Johns. Over the past 10 years
- Next

The Origin of Coffee in the Consulate of Kashgar, Xinjiang
Catherine Martney, wife of the British Consul General in Kashgar, Kashgar, is a brave English woman who has lived here with her husband for 17 years. In 1931, she wrote "the memory of a diplomat's wife to Kashgar" affectionately and in a delicate and warm tone. In 1898, an ordinary woman as far away as Great Britain
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

