Sidamo Lion King hand Chong parameters temperature grindability Powder / Water ratio recommended Flavor and taste description
For professional baristas, please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style)
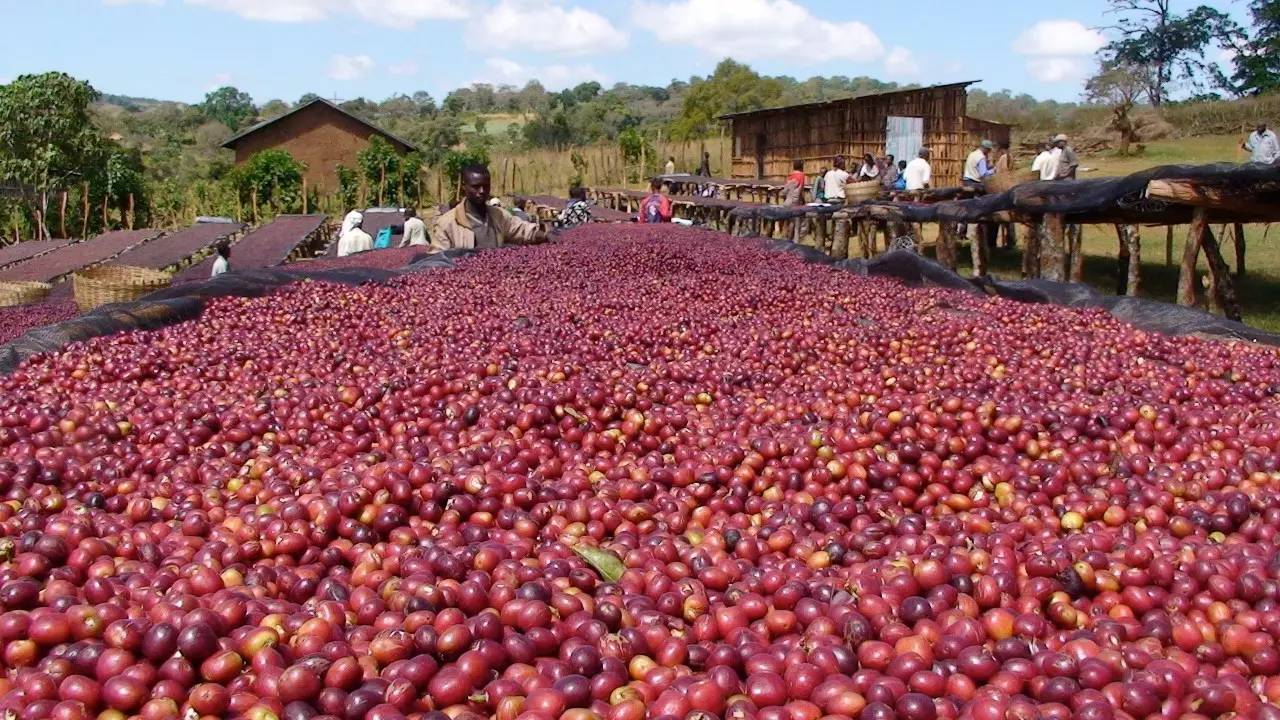

Ethiopia
Name: Ethiopia
Location: East Africa
Capital: Adis Abba Addis Ababa
Religion: dominated by Christianity
Language: Amharic
Time zone: GMT+3
Measurement: metric (Metric)
Currency: bill Birr (1 $≈ 20 birr)
Agricultural products (export): coffee, flowers and sesame are the main cash crops
Port: Port of Djibouti (Djibouti, now the main export port)
Average annual temperature: 15-20c in highland and 25-30c in lowland
Average annual rainfall: 1000-2000 mm
Soil: 50% volcanic soil (volcanic)-25% sedimentary soil (sedimentary)-25% other
Ethiopian geographical location source James Elford's Blog
Ethiopia, which is located in a country full of wonders, is the source of all the Arabica coffee we have never drunk.
The recorded historical evidence of coffee in Ethiopia can be traced back to the 4th-5th century AD, when coffee spread to Yemen in the Arabian Peninsula as people fought and migrated because of the inter-ethnic war. later, with the rise of the Ottoman Empire and the spread of Islam, Europe began to have cafes and the gradual formation of coffee shop culture, and then Central America began to grow coffee. India and Indonesia in Asia began to grow coffee commercially on a large scale. It took us hundreds of years to reach the third wave of boutique coffee.
The origin and spread of Ethiopian coffee originated from the Makira primeval forest.
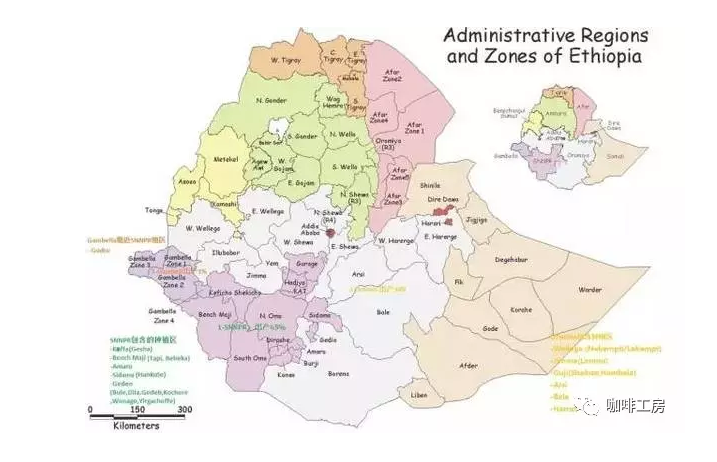
The administrative division of Ethiopia
Ethiopia is a federal republic. Since 1995, a new division system has been used in administrative areas.
9 autonomous prefectures of ●
● 2 municipalities directly under the Central Government
The autonomous prefecture is divided into Zone region, Woreda County and Kebele Township.
Note: most of our common coffee names are Woreda County or Kebele Township level.
Ethiopian administrative division data come from Wikipedia
The climate of Ethiopia
Ethiopia's climate is polarized, half of the humid rainforest and half of the Gobi desert.
This is also the reason why coffee cultivation is mainly distributed in the southern tribal states SNNPR and Oromia, Oromia.
Tuesse climate distribution
Worldclim, the source of annual precipitation
The main rainfall season in Ethiopia is 6, 7, 7 and 8 months, and the annual precipitation in the main growing areas of coffee is 1000-2000 mm.
Chart average annual temperature source worldclim
Ethiopia has the coldest weather in December and January, and the hottest in April and May.
The average annual temperature in the main growing areas of coffee is between 15 and 30.
Coffee cultivation in Ethiopia
Since Ethiopia changed the administrative division around 1995, the greatest impact on the coffee area is that the original Sidamo Sidamo province is divided into the new Sidamo Sidama (the original minority), and most of it is classified into the Oromia Oromia state. And Yega Xuefei, which used to belong to Sidamo Province, is now classified as the new Gedeo of Gaidio District. Now there will be a mixture of Ethiopian coffee products in circulation in the market with the names of new and old regions. Here we take the new regional division as the benchmark, combined with the administrative region to understand Ethiopia's coffee growing map.
Ethiopia's coffee cultivation is divided according to scale and pattern (Note 1)
● forest coffee (8-10%), coffee trees coexist with other crops in pristine forests without any artificial care, and farmers pick coffee fruits regularly.
● semi-forest coffee (30-35%), the coffee planting area is between the forest and the range of farmers' lives. Coffee trees, like forest coffee, are naturally produced varieties. Farmers will manage the coffee planting areas and plant other cash crops.
● garden coffee (50-55%), coffee trees are planted around farmers' living areas, and most of them are grown by farmers themselves.
● plantation coffee (5-6%), large private grower with more processing facilities and production capacity
Ethiopia's Nine Fine Production Areas
Ethiopia has the most diversified coffee cultivation system in the world, including forest coffee, semi-forest coffee, pastoral coffee and plantation coffee. 90% of Ethiopia's coffee is grown in pastoral, forest and semi-forest areas, but large-scale industrial cultivation is rare in Ethiopia, perhaps to produce so much quality.
Forest coffee: refers to wild coffee in the virgin forest, protected by the local government, there are special personnel to pick.
Semi-forest coffee: farmers regularly enter the forest to prune shade trees or coffee branches to increase light and yield, but even so, annual yields are not high.
Pastoral coffee: refers to small farmers in their own fields mixed coffee and other cash crops, and mostly planted under the elephant leg plantain, it is also formed in its unique landscape. But this is Ethiopia's dominant mode of production.
Plantation coffee: refers to the current state-owned enterprises, specialized in improving the efficiency of mass production cultivation.
These four cultivation systems are distributed in the following nine major production areas in Ethiopia: Kimma, Sidama, Yegashefi, Hara, Limu, Iruba, Kimbi (Lekanti), Tiebi and Bebeka. On the whole, the flavor of each producing area has its own characteristics. Basically, the beans in western Tiebi, Bebeka, Iruba and northwestern Tana Lake are obviously larger, and the game is heavier but the fruit acid flavor is lower. The central Limu, south-central Yejia Xuefei, Sidamo, rich fruit flavor, floral and sour fragrance, relatively stable quality. Eastern Harrah combines western game and south-central fruit flavors, but there are also great differences between good and bad.
The genes of Ethiopian ancient superior varieties are very complex, coupled with the multi-processing methods of sun, water and semi-water washing, so the flavor presented will be complex and changeable. It may not be an exaggeration to call it "the smell of kings."
Yejia Xuefei (fine production area): altitude 1,800 ~ 2,000 meters| Garden coffee system|
Yegashefi is affiliated with the Sidama region and is separated due to its unique flavor. In addition to the town of Yejia Shefei, it also includes three sub-producing areas around Wenago, Kochere, Gelena and Abaya. Therefore, Yirgacheffe A, Wenago A, Kochere A, Gelena/AbayaA will be more expensive than the namesake B in the new Yergacheffe grading system. In addition to washing and sun exposure, the recently introduced semi-washed Yega Shefi is also worth a try.
Sidamo (fine production area): altitude 1,400 ~ 2,200 meters| Garden coffee system|
The flavor is similar to Ye Jia Xue Fei, delicate washed or sun-dried West Damo, the same flower fragrance and orange fragrance, the price is not inferior to Ye Jia Xue Fei. The varieties of these two regions are similar, with medium seeds but also small seeds with short plants, which farmers often sell separately. Common Kurmie, poor disease resistance;Wolisho; tall and robust;Deiga, medium tree, these three species are the main force of the fine sun series Biloya and Aretha.
Lime (fine production area): altitude 1, 200~2000 meters| Pastoral, forest, semi-forest, plantation coffee system|
The output is small, mainly exported to Europe and the United States market, Taiwan is not easy to buy, but Europe and the United States are very popular, there are three treatment methods of washing, sun and semi-washing. Lim's body viscosity will be significantly lower, flower and citrus flavor performance is also inferior to Yega Shefi and Sidamo, but more grass and brown sugar aroma, fruit acid bright.
Hala (fine production area): altitude 1,500 ~2400 meters| Garden coffee system|
Hara is an ancient city in the east, but coffee is not grown in the Urban area. The so-called Hara coffee refers to the coffee produced by Haraji High and Low in the Great Hara area. Since the annual rainfall is only 1,000 mm, all solar treatment is adopted. Flavor Upper Hara Coffee is famous for its special [mixed fragrance], which is typical of ancient early morning flavor. She is tied with Yega Shefi [double star].
If Harrah's defective beans are picked clean, it's easy to drink berry fruit with a pleasant, fermented aroma. However, due to various factors, the quality of Hara coffee has been unstable in recent years, and the grading system is not true, so be sure to test or try it when purchasing.
Jinma (commercial soybean production area): altitude 1,350 ~ 1,850 meters| Forest/semi-forest systems|
Kimma is the capital of the Kafa Forest or Kafa Province. The English spelling is very messy. Most maps are jimma, but coffee sacks are spelled Djimmah. This is Ethiopia's largest coffee producing area, accounting for 1/3 of exports.
Kafa Forest is known for its primitive wild varieties. Jinma is the distribution center of kafa in this area. Farmers used to pick from forest areas and transport them to Jinma. Then they mixed hundreds of varieties together and sold them as commercial beans, resulting in the aroma of many delicious varieties being masked.
Although the washed gold marmalade lacks the orange fragrance and floral charm of Yejia Xuefei, the flavor spectrum is quite clean and clear, similar to Central American fine products. Commercial-grade fine gold ma is very common in Taiwan. If you are lucky, you can buy high-quality and inexpensive gold ma. You can drink the fragrance of lemon peel, which is not inferior to West Damo. Overall, Kimma has a better flavor than the Brazilian bulk commercial bean Sandos, making it a good mid to low priced formula bean.
Iruba (commercial soybean production): Altitude 1,350 ~ 1,850| Forest/Semi-Forest Coffee System|
This area is located in the west of Ethiopia, just bordering Sudan, is the most convenient western production area, coffee gene complexity is only second to the coffee forest, beans are significantly larger than Yega Shefi and Sidamo, fruit acid flavor is low, viscosity is good, flavor balance, coffee here is mostly transported to Jinma mixed, rare independent sale.
Kimbi, Lekati (commercial soybean producing area): Altitude 1,500~1,800| Forest/Semi-Forest Coffee System|
There are sun-dried and washed beans in this area, beans are similar to Hara's long body beans, and there are also a small number of high-quality beans popular in Europe and America. Most of them are known as poor haras, fruit acids and fruity flavors due to erubaba, bright flavors.
Tiebi, Beibeika (bulk commercial bean production area): altitude 500~ 1,900 meters| Pastoral/Forest/Semi-Forest Coffee System|
The two producing areas are very close, Tibi is in the north of Bebeka, with enterprise-oriented coffee plantation, and in recent years, the pastoral system has been promoted to increase agricultural income, with an annual output of about 3,000 tons. Both have wild coffee, yield is not high, flavor is very different from Harrah and Yerga Sherphine, low fruit acid is the biggest feature, suitable for making formula beans, there are sun and water washing.
Lake Tana (alternative production area): elevation 1,840 meters| forest systems|
Monastery coffee, the annual production of coffee in the surrounding forests is very small, less than 10 tons, in fact, can not be called the production area, the lake area is full of Eastern Orthodox monasteries, churches, religious murals and myths, creating the world's most "divine" coffee.
European monasteries pioneered local coffee farming, which was later run by coffee communities or cooperatives in the villages surrounding the town. There are no special plantations here, coffee trees are naturally scattered in forests and fields. During harvest season, Ethiopian coffee trading companies come to town to buy coffee beans collected by farmers.
In addition to the town of Yejia Shefei, it also includes three sub-producing areas, namely Wenago, Kochere and Gelena/Abaya.
1. Planting system and environment The mountain villages in Yejia Xuefei producing area are cool and foggy, spring all the year round, gentle breeze in summer, cool but not hot, rain but not damp, and winter is not cold. It is the best environment for planting Arabica. There are no large coffee plantations here. Coffee farmers grow coffee mixed with other crops, usually under banana trees, forming a unique landscape.
2. Treatment method Ethiopia's traditional sun treatment method is relatively rough and heavy, which is criticized by people. In 1959, Yejia Shefei production area introduced South American washing treatment method, most production areas are generally used washing treatment, that is, coffee fruit peeling, fermentation, washing process after removing pectin layer, and then drying.
Since 2006, some coffee processing plants in some producing areas have adopted exquisite overhead solarization, which involves intensive manual labor to isolate the coffee fruit from contact with the ground and prevent the dirt from being produced in the process of solarization, creating an unusually clean fruit flavor. After more than two weeks of sun exposure, the dark brown coffee cherries are professionally stored, waiting for the full flavor to ripen. Before sale, the dried cherry pulp and sheepskin are removed, and then the immature beans and overfermented beans are eliminated. Strict control greatly improves the quality of sun-dried beans.

The Lion King insolates the Guji producing areas in Sidamo Province, Ethiopia.
The coffee flavor of Sidamo is very diverse, because of the different soil composition, regional microclimate and countless native coffee varieties, the coffee produced in each urban area has obvious differences and characteristics. Sidamo producing area (Sidama) is located in the south of Ethiopia. The industry here is dominated by agriculture, and the coffee-growing area is located around the East African Great Rift Valley (Great Rift Valley). The coffee flavor of Sidamo is very diverse, because of the different soil composition, regional microclimate and countless native coffee varieties, the coffee produced in each urban area has obvious differences and characteristics. Sidamo producing area (Sidama) is located in the south of Ethiopia. The industry here is dominated by agriculture, and the coffee-growing area is located around the East African Great Rift Valley (Great Rift Valley).
Guji is located in the southeast of the Gedeo area where Sidamo is produced, in the wilderness of 2100 meters above sea level, but it is higher than that of Yega, with the highest elevation of more than 2600 meters, much higher than the average Sidama, and a larger area. Guji coffee tends to have sweet blueberry aromas with lemon aromas, rich floral and fruit aromas, peach fruit honey and surprisingly bright acidity and full berry aromas.
1. After picking beans without special screening and treatment, uneven appearance and maturity are mixed together, the process is relatively rough, so the quality of coffee beans is unstable and prone to defective beans.
two。 Coffee farmers usually find an open space near their home to deal with it, so there are often a lot of impurities or dirt on the ground, and coffee is easy to get smelly.
The improved method of tanning, that is, to improve the two shortcomings of the traditional way:
1. When picking beans, only fully ripe crimson coffee cherries are picked. Before exposure, the beans will be screened for defects in the processing plant to make the beans look more average in size and maturity.
two。 Next, use tall wooden frames or whole scaffolding for the sun to avoid the risk of beans smelling on the ground. In the process of exposure, take good care of the beans so that the coffee beans can be evenly exposed to water; every three to five days, coffee workers will manually screen out defective and moldy beans. Therefore, by the end of the exposure, before the beans enter the market to remove the peel and flesh, a bright crimson coffee cherry is already a grade with few defects. The coffee beans after harvest must enter the treatment program immediately, otherwise they will begin to ferment, making the coffee beans have a bad smell. There are two methods of treatment: "solarization" and "washing", which will cause different flavors. Sun-dried beans have a complete natural mellow flavor, gentle aroma and more gum; washing rules have a good mellow taste, high aroma and lively sour taste.
[sun Sidamo]: the bean body is smaller than Longberry, and it is yellowish in green. in the sun drying field of Sidamo, the coffee is placed in a hemp net wooden rack, and the workers take turns to stir the coffee manually in the sun. Sidamo is usually marked with G4 exit, while water-washed Sidamo is mostly exported at G2 level because of the better sun treatment process.
[washed Sidamo]: coffee raw bean green is slightly gray, some places are thick and some places are small, the acidity is soft and strong, mellow, sweet and spicy, it is one of the courtyard coffee in the highlands of southern Ethiopia. Unlike ordinary African coffee, Sidamo has clear acidity, smooth taste and delicate floral smell.
Hand on the Lion King of Sidamo. 15g powder, medium fineness grinding (sugar size), v60 filter cup, 90 degrees water temperature, 30g water injection for the first time, steaming for 30 seconds, water injection to 105g water cut off, wait for the powder bed water to reach half, then water injection, slow and uniform water injection until 225g water, finally shake the filter cup to increase the extraction, the ratio of water to powder is 1:15, and the extraction time is 2:04.
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

Introduction to the recommended flavor of Yega Xuefei coffee bean washing Cochel G1 hand temperature grindability powder / water ratio
For professional baristas, please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) Coffee beans details: country: Ethiopia Grade: G1 production area: Yejia Chuefei Baking degree: shallow Baking method: washing Variety: local Native Flavor: Jasmine Flavor, Lemon, Bergamot, Honey, Grapefruit Cochel is located in 25 southeast of Ethiopia.
- Next

Introduction of Sidamo hand Chong Huakui parameters temperature grindability Powder / Water ratio Flavor and taste description
For the exchange of professional baristas, please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) Sakui processing plant is located in buku abel village, 2200 meters above sea level. From the beginning of cultivation, it has been chosen as a noble family environment-humus-rich reddish brown soil, and it has been given shade and care to Enset tree species, so that Sakui can receive sufficient sunlight and produce rich flavor without consuming too much nutrients.
Related
- Detailed explanation of Jadeite planting Land in Panamanian Jadeite Manor introduction to the grading system of Jadeite competitive bidding, Red bid, Green bid and Rose Summer
- Story of Coffee planting in Brenka region of Costa Rica Stonehenge Manor anaerobic heavy honey treatment of flavor mouth
- What's on the barrel of Blue Mountain Coffee beans?
- Can American coffee also pull flowers? How to use hot American style to pull out a good-looking pattern?
- Can you make a cold extract with coffee beans? What is the right proportion for cold-extracted coffee formula?
- Indonesian PWN Gold Mandrine Coffee Origin Features Flavor How to Chong? Mandolin coffee is American.
- A brief introduction to the flavor characteristics of Brazilian yellow bourbon coffee beans
- What is the effect of different water quality on the flavor of cold-extracted coffee? What kind of water is best for brewing coffee?
- Why do you think of Rose Summer whenever you mention Panamanian coffee?
- Introduction to the characteristics of authentic blue mountain coffee bean producing areas? What is the CIB Coffee Authority in Jamaica?

