Correctly understand caffeine and drink coffee reasonably and healthily

What is caffeine?
Caffeine: (Caffeine) is an alkaloid extracted from tea and coffee fruits. Moderate use of caffeine can dispel fatigue and excitatory nerves. Coffee, tea, soft drinks and energy drinks with caffeine are very popular. Therefore, caffeine is also the most commonly used psychotropic drug in the world. In North America, 90% of adults use caffeine every day. Many natural sources of caffeine also contain a variety of other xanthine alkaloids, including cardiotonic theophylline and theobromine, as well as other substances such as tannic acid.

(chemical formula C8H10N4O2 of caffeine)
The main source of caffeine in the world is coffee beans (the seeds of coffee trees), which are also the raw materials of coffee. The caffeine content in coffee largely depends on the variety of coffee beans and the method of making coffee, and even the caffeine content of coffee beans in the same tree varies greatly. Generally speaking, the amount of caffeine in a cup of coffee ranges from 40 mg in espresso to 100 mg in espresso. Deep-roasted coffee generally contains less caffeine than light-roasted coffee because roasting reduces the amount of caffeine in coffee beans. Arabica coffee usually contains less caffeine than medium-fruit coffee. Coffee also contains trace amounts of theophylline, but not theobromine.
Tea is another important source of caffeine. The caffeine content of each cup of tea is generally only half that of each cup of coffee, depending on the intensity of tea production. Certain varieties of tea, such as black tea and oolong tea, contain more caffeine than other teas. Tea contains a small amount of theobromine and slightly higher theophylline than coffee. The making of tea has a great influence on tea, but the color of tea can hardly indicate the amount of caffeine. The caffeine content of Japanese green tea is much lower than that of many black teas, such as Masayama race tea, which contains little caffeine.
Chocolate made from cocoa powder also contains a small amount of caffeine. Chocolate is a weak stimulant, mainly due to theobromine and theophylline contained in it. A typical 28g milk chocolate has about the same caffeine content as decaffeinated coffee.

Caffeine is also a common ingredient in soft drinks, such as cola, which was originally made from cola fruit. A soft drink usually contains 10 to 50 milligrams of caffeine. Energy drinks, such as Red Bull, contain 80 milligrams of caffeine per bottle. The caffeine in these drinks comes from the original ingredients they use or the additives obtained from decaffeinated coffee, and some are chemically synthesized. Guanana, the basic ingredient of many energy drinks, contains a lot of caffeine and a small amount of theobromine. The naturally occurring sustained-release excipients contain a small amount of theophylline.

Pharmacological effects of caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system stimulant and a metabolic stimulant. Caffeine is used as both a drink and a medicine. its function is to refresh and relieve fatigue. The exact dose of caffeine that everyone needs to produce an effect varies, depending on body size and caffeine tolerance. Caffeine can begin to work in the body in less than an hour, and the effect disappears in three to four hours for a mild dose of caffeine intake. Caffeine consumption does not reduce the amount of sleep required, it can only temporarily reduce the feeling of sleepiness.

Caffeine is safe for humans, but it is toxic to some animals, such as dogs, horses and parrots, because their livers are much less able to break down caffeine than humans.
In the case of long-term intake, large doses of caffeine is a drug that can cause "caffeine poisoning". Caffeine poisoning includes addiction and a range of physical and psychological side effects, such as nervousness, irritability, anxiety, tremors, muscle convulsions (hyperreflexia), insomnia and palpitations (most people take caffeine because of its irritating effects. Many students take caffeine pills when preparing for exams and those on night shifts. Under the strict definition of addiction, only a gradual increase in dosage is addictive, and caffeine dependence is more appropriate, but under a widely accepted definition, all chronic behaviors that are difficult to get rid of are called addictions. so it can also be described as caffeine addiction.) In addition, because caffeine can increase stomach acid, continuous high-dose intake can lead to peptic ulcers, erosive esophagitis and gastroesophageal reflux disease, so friends with poor stomach function are not suitable for drinking coffee.
How much caffeine a day is more appropriate
If you consume too much caffeine, usually more than 300 milligrams (equivalent to 2-3 cups of coffee) can lead to overexcitement of the central nervous system. Symptoms of caffeine overexcitement include irritability, nervousness, excitement, insomnia, blushing, increased urine, gastrointestinal disorders, muscle convulsions, distraction, irregular or rapid heartbeat, and restlessness.
Consuming extremely large doses of caffeine (500 mg or more) can be dangerous and even lead to death. Although it is almost impossible to die from drinking regular coffee, there are reports of deaths due to excessive use of caffeine pills.
The treatment of caffeine overexcitement is usually complementary, that is, individual symptoms are treated accordingly. However, if the patient's serum caffeine concentration is too high, it is possible to take peritoneal dialysis, hemodialysis and hemofiltration and other methods.
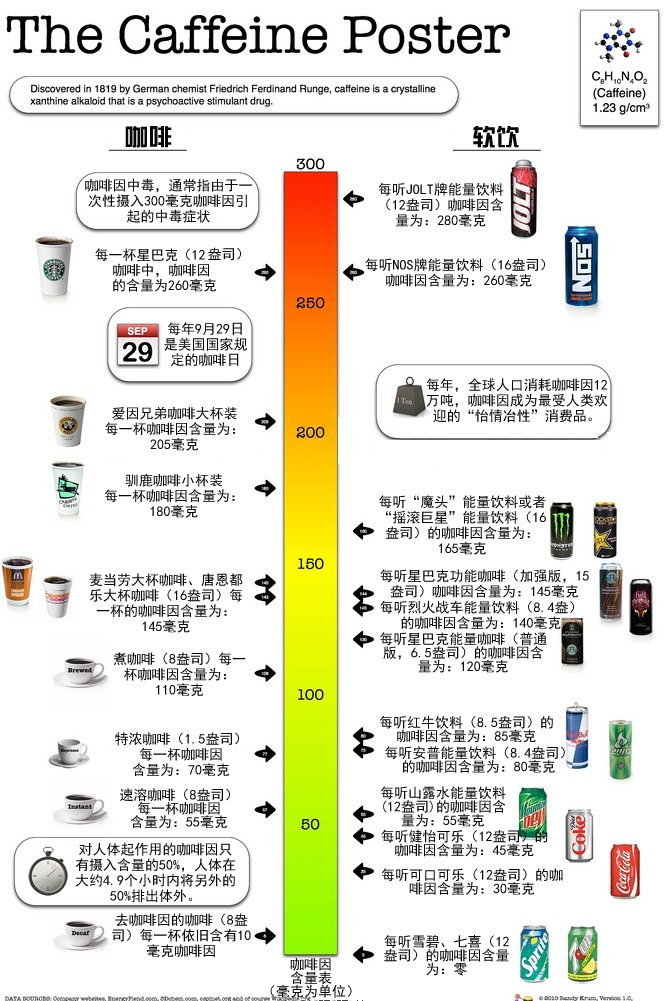
Diagram of caffeine content in daily drinks (picture data are for reference only)
What are the benefits of moderate intake of caffeine to the human body
Coffee is currently the longest-used but most misunderstood beverage. Many new research reports show that caffeine is not harmful to human health as thought in the past. On the contrary, some ingredients in coffee have many health effects on the human body. Are slowly discovered by scientists.
At present, it is known that the physiological responses of caffeine to the human body are as follows:
Can effectively fight free radicals that threaten our health: free radicals are the main cause of many diseases (such as cardiomyopathy, arteriosclerosis, stroke, emphysema, Parkinson's disease). Too much free radicals will affect the metabolism of the body, destroy cells and then affect organs and tissues.
Cardiovascular protection: contains high-ingredient polyphenol compounds, which are powerful antioxidants, which can delay the oxidation of LDL by up to three times, dissolve blood clots and prevent the formation of blood clots; coffee can also enhance vasoconstriction and avoid vascular dilatation and headache. In addition, a small amount of coffee can also enhance myocardial contractility, promote blood circulation and prevent cardiovascular disease.
Refreshing and refreshing: it can stimulate the central nervous system of the brain, prolong the awake time of the brain, make the mind clear, sharp, and focused, which can improve the efficiency of work and study.
Anti-melancholy: a small amount of caffeine can cheer people up, feel happy, and relieve depression.
Weight control: caffeine can increase the rate at which the body consumes calories. A study found that 100mg caffeine (about 1 cup of coffee) can accelerate fat decomposition, increase the body's metabolic rate by 3% to 4%, increase heat consumption and drink in moderation. Weight loss.
Promote digestion: caffeine stimulates the sympathetic nerve and increases gastric juice secretion. If you drink it in the right amount after a meal, it will help digestion.
Diuresis: coffee has a diuretic effect, which can increase the amount of urination, thus increasing the number of times to go to the toilet.
Improve constipation: coffee can stimulate gastrointestinal hormones or peristaltic hormones, produce laxative effect, can be used as a rapid laxative.
Reduce the risk of colorectal or rectal cancer: coffee contains natural antioxidants.
Pain relief: when caffeine is used as a drug, it can enhance the effect of some painkillers.
Enhance physical agility: caffeine also helps to lower the exercise threshold during exercise, increase body agility, and enable athletes to create better results.
Reduce the risk of gallstones: a new study from the Harvard School of Public Health found that people who drank 2-3 cups of coffee a day were on average 40% less likely to get gallstones than those who never drank them. In addition, the tannic acid contained in coffee has the function of astringency, hemostasis and odor prevention.
(source: network)
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

How much do you know about siphon pots? A simple and easy-to-use method of making coffee
Siphon pot (Siphon), commonly known as "plug wind pot" or "siphon", is a simple and easy-to-use method of coffee brewing, and it is also one of the most popular coffee brewing methods in cafes. Many people like the precision of siphon cooking with a touch of laboratory flavor, watching the water boil up and the coffee extracted into black drops, step by step in the hands of the coffee brewer. It means a lot to use.
- Next

Three cups of coffee a day can prevent the benefits of drinking coffee from gallstones
1. Drinking coffee regularly can prevent radiation damage. Radiation damage, especially the radiation of electrical appliances, has become a prominent pollution at present. two。 Coffee is good for the skin. Coffee can promote metabolic function, activate digestive organs, and has a great effect on constipation. Taking a bath with coffee powder is a kind of thermotherapy, which has the effect of losing weight. 3. Coffee has the function of relieving alcohol. After drinking coffee, you will
Related
- Detailed explanation of Jadeite planting Land in Panamanian Jadeite Manor introduction to the grading system of Jadeite competitive bidding, Red bid, Green bid and Rose Summer
- Story of Coffee planting in Brenka region of Costa Rica Stonehenge Manor anaerobic heavy honey treatment of flavor mouth
- What's on the barrel of Blue Mountain Coffee beans?
- Can American coffee also pull flowers? How to use hot American style to pull out a good-looking pattern?
- Can you make a cold extract with coffee beans? What is the right proportion for cold-extracted coffee formula?
- Indonesian PWN Gold Mandrine Coffee Origin Features Flavor How to Chong? Mandolin coffee is American.
- A brief introduction to the flavor characteristics of Brazilian yellow bourbon coffee beans
- What is the effect of different water quality on the flavor of cold-extracted coffee? What kind of water is best for brewing coffee?
- Why do you think of Rose Summer whenever you mention Panamanian coffee?
- Introduction to the characteristics of authentic blue mountain coffee bean producing areas? What is the CIB Coffee Authority in Jamaica?

