The characteristics of taste and flavor of Guatemalan coffee introduction to the varieties and grades of coffee in Guatemala

Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style)
In the coffee-producing regions of Latin America, Guatemalan coffee beans are famous for their bright acidity and smoky sensation. The taste is smooth and the flavor is very special, so Guatemalan coffee beans are also known as "cigarette coffee". Then the next Qianjie article will talk about the flavor characteristics of Guatemalan coffee beans.
History of coffee cultivation in Guatemala
According to Qianjie, local farmers in Guatemala knew how to grow and drink coffee as early as 1747. In 1750, Father Jesuit introduced coffee trees to Guatemala. In 1845, with the establishment of the Guatemalan Coffee planting and Promotion Committee, coffee became an important cash crop in Guatemala. Under the strong promotion of the government, coffee accounted for 90% of Guatemala's total exports in 1880. in order to obtain greater production, those in power targeted indigenous land, forcing them to sell their land and move to more barren places.
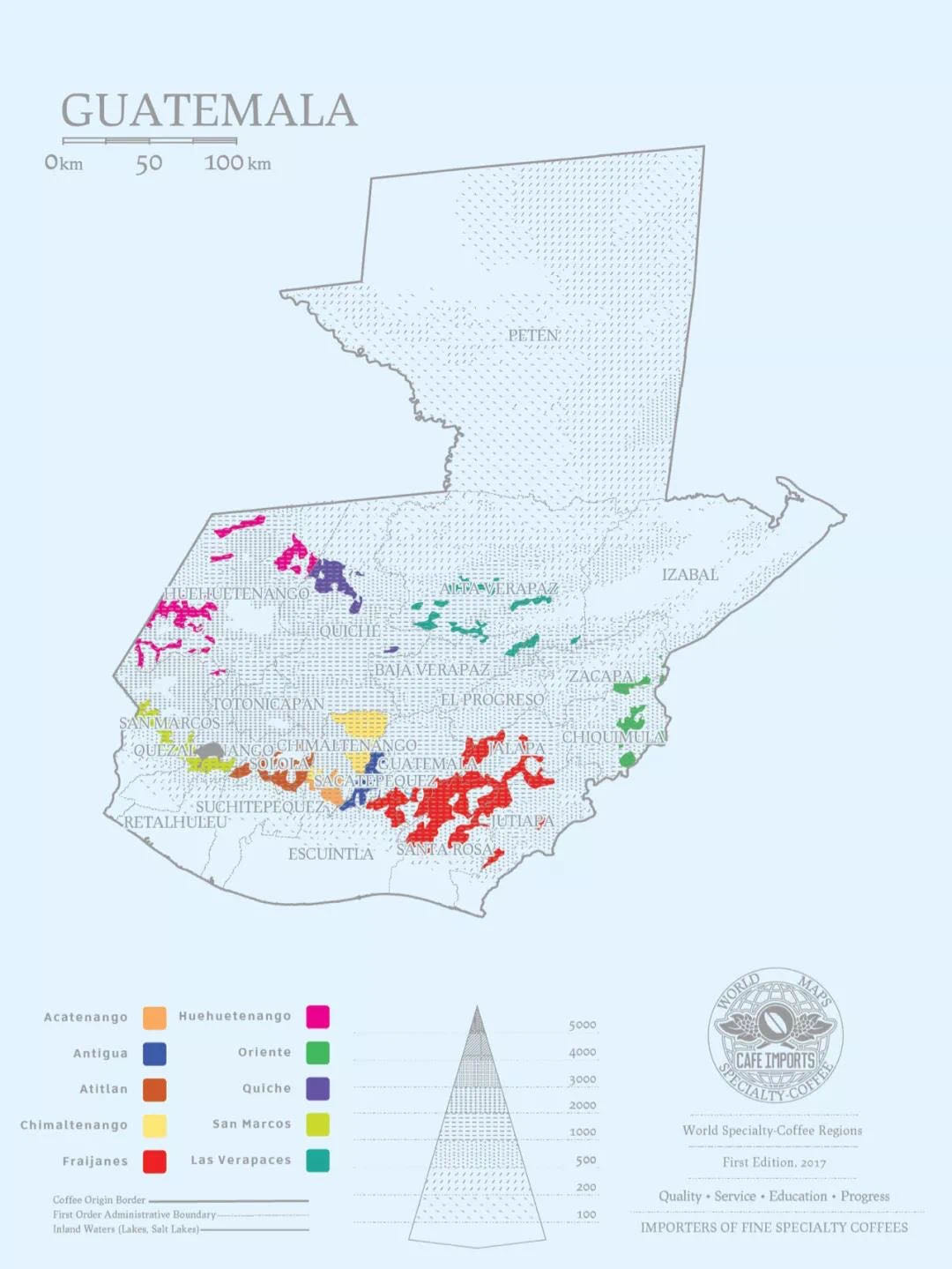
So to this day, most of the coffee production in Guatemala takes place in the south. According to Qianjie, there are eight major coffee producing areas in Guatemala at present, and the flavor of coffee produced in each area is different, but to sum up, Guatemalan coffee shows a mild and mellow overall texture and elegant aroma. With a special and pleasant acidity similar to fruit acid, Guatemala has become an aristocrat in coffee. For example, Guatemala Antigua coffee beans in the front street coffee shop are very popular with coffee fans. Coffee growing areas in Guatemala
As Qianjie Coffee said above, there are eight coffee growing areas in Guatemala, and each producing area will affect its flavor because of its different regional distribution. Then Qianjie Coffee will briefly describe the characteristics of the following eight producing areas.
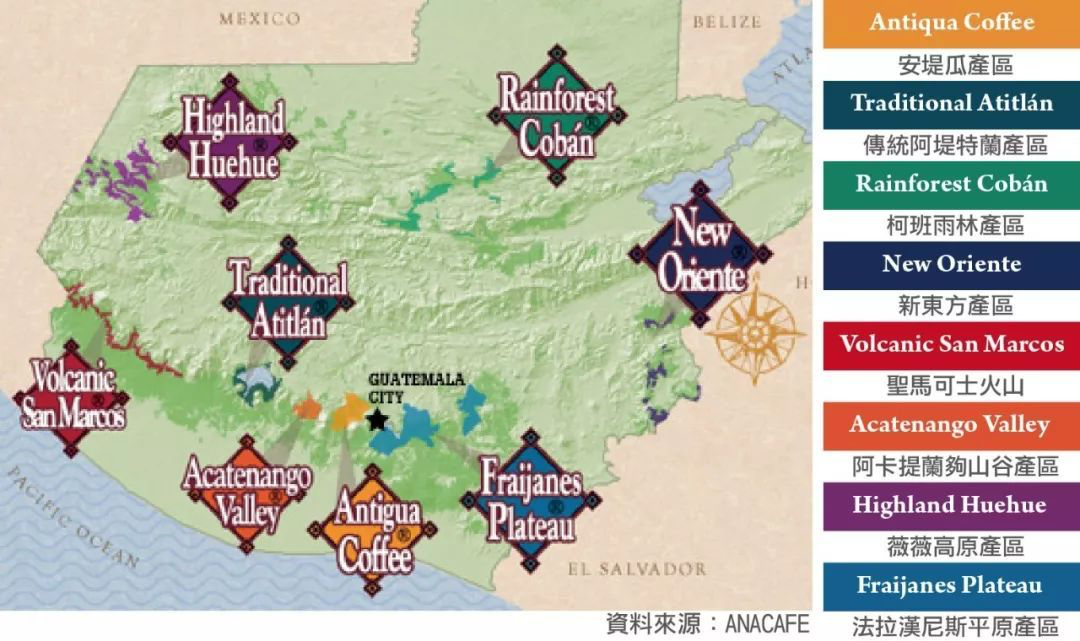
Antigua (Antigua)
The old capital and ancient city, close to the capital, is the most famous of all coffee producing areas in Guatemala, of course, the corresponding is expensive, so now there are a lot of fake Antigua coffee beans in the boutique coffee market; the highest price is the bourbon grown coffee fruit grown in the volcanic soil with the most characteristics of Antigua.
Flavor: balanced between sweet and sour.
Altitude: 1500-1700m
Arkat Nango Valley (Acatenango Villey)
The eighth coffee-producing area in Guatemala, as far as Qianjie knows, was the early supply area for Antigua. It is next door to Antigua. The valley is majestic. Coffee-producing areas are planted along the volcanic valley, and the valley retains warm and humid air. Coupled with the temperature difference between day and night, it is very suitable for growing coffee fruit.
Flavor: good sweetness, delicate acidity, flavor and aroma are widely loved by coffee fans.
Altitude: 1300-2900m
Koban Rainforest (Rainforest Coban)
The rainfall in this area is very heavy, the climate is cool and cloudy all the year round, and the soil contains calcareous and clay. The treatment after harvest often affects the quality of coffee in this area, but as long as it is handled well, the flavor will be very full and charming.
Flavor: good on the palate, with notes of chocolate and tropical fruits.
Altitude: 1300-1500m
Mount San Marcos (Volcanic San Marco)
The level of coffee in this area fluctuates greatly, the rainfall is abundant, and the coffee fruit will blossom densely as soon as it rains, so it depends on luck to dry the coffee in the sun after harvest, which leads to the instability of coffee quality in this area.
Flavor: with obvious acidity and sweetness, properly handled coffee fruit will have a full and unique aroma.
Altitude: 1400-1800m

Lake Attilan (Traditional Atitlan)
The soil of Lake Attilan is very fertile. The highest coffee is produced at 1950 meters, and most of it extends from the slope to the edge of Lake Attilan, which is still 1500m above sea level. It is also the largest and most famous high-altitude lake in Guatemala.
Flavor: thick fragrance and sticky.
Altitude: 1500-1750m
Wei Wei Plateau (Highland Huehue)
This area is the highest average elevation in Guatemala and belongs to the volcano-producing area of Guatemala, but this area is rugged and remote from the capital, thanks to the dry hot wind from Mexico blowing here. it makes it possible to grow coffee fruits at 2000m on the Vivi Plateau.
Flavor: the acid is bright and delicate, with floral scent and changeable flavor.
Altitude: 1500-2000m
Farrakhan Nice Plain (Fraijanes Plateau)
This area belongs to the volcanic producing area, high altitude, the soil is rich in pumice, and can even be ignited. Its coffee flavor is balanced, but it has more unique aroma than Antigua. Qianjie believes that its coffee flavor is outstanding because of the soil characteristics and changing temperature and humidity in the area.
Flavor: it has a unique aroma, balanced flavor, mild acidity and strong taste.
Altitude: 1400-1800m
New Oriental (New Oriente)
The region is close to neighboring Honduras, the climate is similar to Koban, but some areas are hotter, the New East belongs to the volcanic region, but its flavor is very different from other volcanoes.
Flavor: the aroma is obvious, with chocolate and spice.
Altitude 1200-1700m

Planting conditions of Guatemalan coffee
Guatemala borders Mexico to the north, Honduras and El Salvador to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It is blessed with tropical rain, volcanic geology, plateau valleys and changeable micro-climate. Therefore, it is also very suitable for growing Arabica coffee beans.
The northern and eastern coastal plains of Guatemala have a tropical rain forest climate, while the southern mountains have a subtropical climate. The year is divided into two dry and wet seasons, with the wet season from May to October and the dry season from November to April of the following year. The narrow and fertile flatlands on the Pacific side of Guatemala have a tropical climate. The central plateau is also the cultural center of Guatemala. according to Qianjie Coffee, the temperature at 1300-1800 meters is mild all year round, with daily temperatures between 18 and 28 ℃. Higher places tend to be colder in January and February.
The annual precipitation is 2000-3000 mm in the northeast and 500-1000 mm in the south. The average elevation of Guatemala is high, with coffee belts distributed over 1500 meters and between 14 and 16 degrees north latitude, it is the easiest to grow extremely hard beans, and they are all washed. 45% of the coffee beans belong to the fine grade, and the proportion is quite high. There are also a few Robusta varieties of coffee beans.

Grading of Guatemalan coffee beans
Qianjie Coffee also mentioned above that the coffee growing area in Guatemala is suitable for the growth of very hard beans because of its high altitude, so the coffee grading in Guatemala is also based on the hardness and altitude of coffee beans. This is also because the higher the altitude of coffee growth, the higher the density of the fruit and the more unique the flavor. The following are the rating criteria for Guatemalan coffee beans (ranked from high quality to low quality):

SHB (extremely hard beans): planted at 1500-1700 meters above sea level
HB (hard beans): planted at 1350-1500 meters above sea level
SH (slightly hard beans): planting altitude is 1200-1350 meters;
Extra Prime (extra high quality water washed beans): plant 1000-1200 meters above sea level
Prime (high quality water washed beans): planted at an altitude of 850-1000 meters;
Good Washed (good quality washed beans): plant 700-850m above sea level.
Guatemalan coffee treatment
According to Qianjie Coffee, it is known that most of the coffee fruits in Guatemala are treated by washing, and only a few are treated by the sun.
In the previous articles on Qianjie Coffee, it was also mentioned that washing treatment is a treatment that can best reflect the most primitive flavor of a coffee bean, and it is also the beginning of understanding the flavor of this producing area, so the rations beans introduced by Qianjie Coffee are mainly washed. For example, Vivette Nan fruit rations beans in Qianjie Coffee Guatemala are treated with water washing. The rule of sun treatment is to add aroma and fermented feeling to the basic flavor of the producing area.
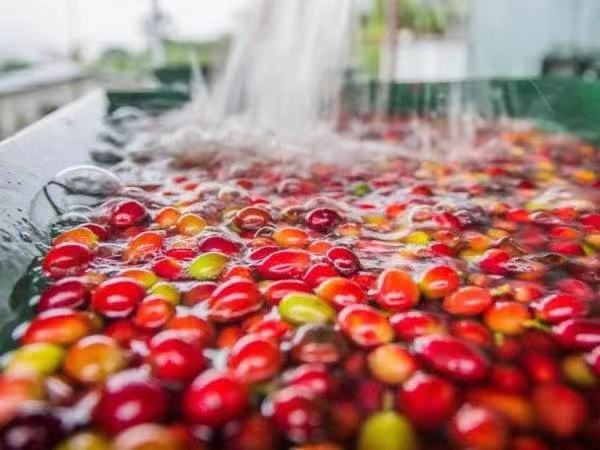

Washing treatment process
1. Harvest. After ripe coffee fruit, first pick out impurities and inferior beans and screen floating beans, so far they are all the same as the sun method.
two。 Remove the flesh. The fresh fruit is sent to the pulp screening machine (pulping machine) to remove the peel and pulp, and the immature fruit will be screened at this stage because it is not easy to separate the pulp. After the pulp screening machine, all that is left is pectin, sheepskin and seeds.
3. Ferment and remove pectin. Transfer the peeled seeds with pectin into the fermentation tank. Although the name is water washing, it does not really wash away the pectin, but through the fermentation process, the pectin is removed by biodecomposition. The fermentation process is about 16-36 hours, during which the pectin must be stirred frequently to accelerate the separation of pectin from the seeds. Water washing fermentation produces acids such as citric acid, malic acid and acetic acid, which seep into raw beans, making the beans sour more sour than in the sun. After the fermentation is completed, it is really washed-- wash the beans again.
4. Dry. After washing, you also need to be insolated or machine-dried to reduce the water content to 12%. Washing method because the flesh has been removed, so in the drying process, do not have to worry about easy mildew like the sun method. Dried sheepskin raw beans, which are not as hard as the sun-cured peels with pulp, can be obtained by hulling.
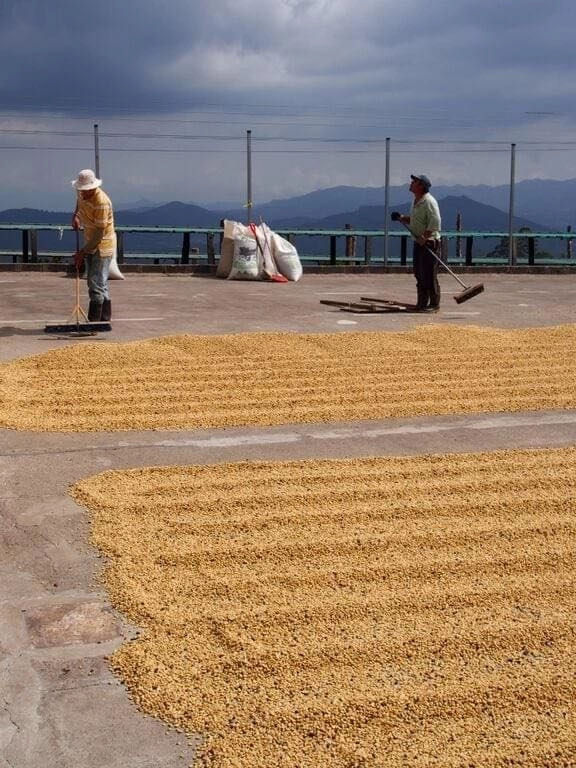
Sun treatment process
1. Harvest ripe coffee fruit
two。 Preliminary selection of impurities and inferior beans
3. Select floating beans: pour the coffee fruit into the sink, the ripe and full fruit will sink to the bottom of the sink, and the immature or incomplete fruit will surface.
4. Sun drying: the ripe coffee fruit sunk at the bottom of the sink is pulled out and spread in the exposure field for sun drying, reducing the moisture from 70% to about 10-12%. Turn the fruit several times a day to dry evenly, and cover it at night to avoid moisture.
5. Remove the shell: after exposure for about two to four weeks, the outer layer of the coffee seed has been dry and hard, and then use the sheller to remove the shell.
6. Packaging and transportation: the shelled coffee beans will be packed in a bag, which is also what we generally call raw beans. Finally, after different roasting processes and brewing changes, it can show the taste changes of millions of kinds of coffee.

Guatemalan coffee varieties
According to Qianjie Coffee, Guatemala mainly grows individual coffee beans of bourbon, iron pickup, Kaddura and Kaduai.
Bourbon: it's a natural variant of the iron pickup. The coffee fruit appears wine red when it is ripe, and the body of the coffee bean is round. Planted in bourbon at high altitude, it usually has a better aroma and bright acidity, and tastes like red wine.
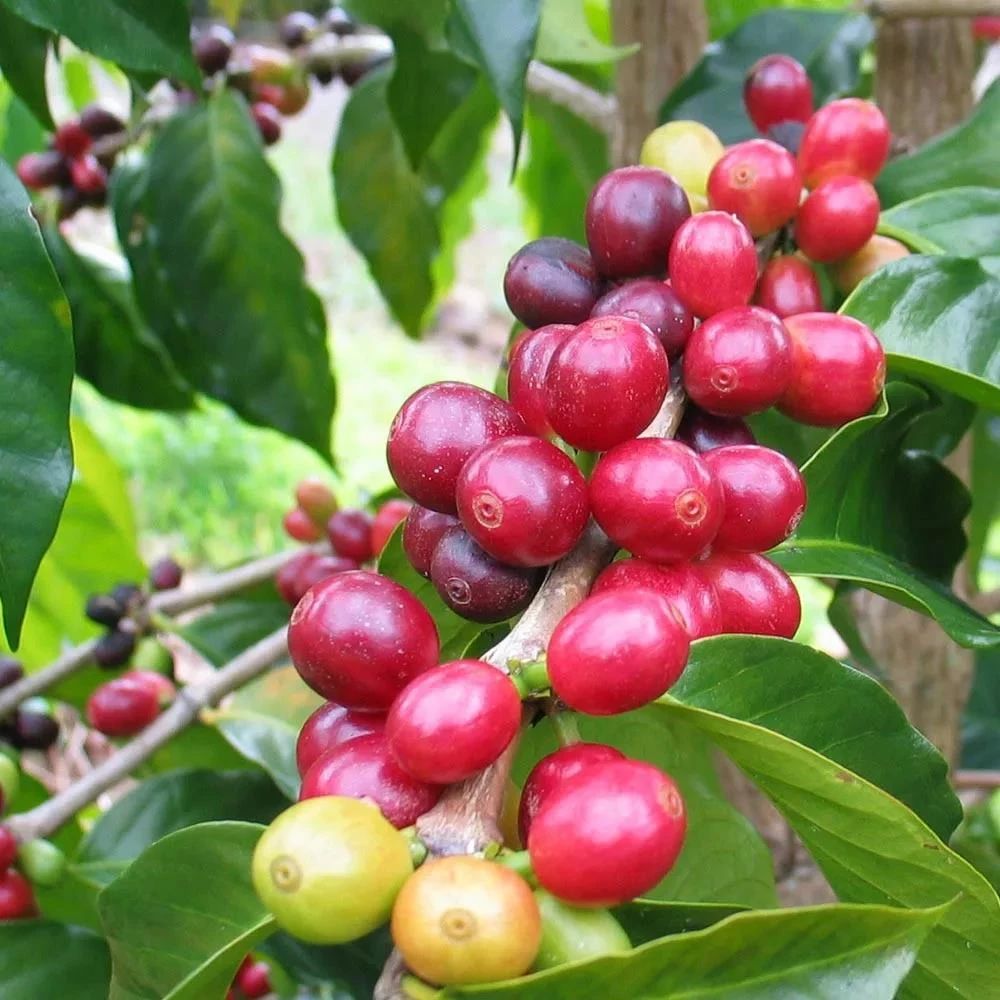

Iron pickup: iron pickup has excellent taste and is recognized as a boutique coffee variety, but its output is extremely low and vulnerable to rust, which requires more manpower management. Tieka Coffee, native to Ethiopia and southeastern Sudan, is the most widely cultivated variety of coffee in the Western Hemisphere. The plant is strong, but it is not resistant to light. The top leaf of the iron pickup is red and copper, which is called Tongding coffee.

Kaddura: a natural variety of bourbon, it was discovered in Brazil in 1937. Its tree is not as tall as bourbon and smaller. Due to inheriting the blood of bourbon, the disease resistance is relatively weak, but the yield is higher than that of bourbon. Although found in Brazil, Kaddura is not suitable for growing in Brazil, so it is not planted on a large scale in Brazil, but is popular in Central and South America, such as Colombia, Costa Rica and Nicaragua. Kaddura is planted on a large scale.
Kaduai: coffee variety artificially crossed by Kaddura and New World (Mondu Novo). Kaduai inherits Kaddura's small trees, which do not need shade, are easy to grow and easy to pick. It also has a better ability to resist natural disasters than the New World. It has a good acidity in flavor. Kaduai generally presents two types of red fruit and yellow fruit.
The above is the relevant information about Guatemalan coffee beans organized by Qianjie Coffee. Next, Qianjie Coffee will introduce all the Guatemalan coffee beans in Qianjie at present.
Front Street Coffee Guatemala Vivette Nan Fruit (ration beans)

Country: Guatemala
Producing area: Vivette Nanguo
Altitude: 1500-2000m
Variety: Bourbon Kaddura Kaduai
Treatment: washing treatment
Bean shape: the bean body is more uniform.
Flavor: nuts, lemon peel, berries, citrus
Front street coffee Guatemala Antigua flower god coffee beans

Country: Guatemala
Producing area: Antigua
Altitude: 1200m
Variety: bourbon, Kaddura
Treatment: washing treatment
Flavor: berries, citrus, light flower aromas, soft acidity, chocolate finish
The above are the brief news of Qianjie Coffee, the two Guatemalan coffee beans, and Qianjie does a lot of baking and brewing tests every time a new coffee bean is put on the shelf, and takes out the best roasting and brewing data for coffee fans to taste. Next, Qianjie will share the roasting and brewing data of Guatemala Antigua Flower God coffee beans for coffee fans' reference.
[Qianjie Coffee Baking suggestion]
This coffee has a round body, yellowish green, good evenness and medium moisture content, so Qianjie bakers aim to be medium-baked, preserving bright acidity to show floral and fruit aromas, and improving richness and balance on the other.

Baking machine: Yang family 600g semi-straight fire
Enter the pot at 200 degrees Celsius, adjust the firepower 160 degrees Celsius after opening the throttle for 30s, keep the throttle unchanged, the temperature return point 1 "36, keep the firepower, 4: 50" seconds the bean watch turns yellow, the smell of grass disappears completely, enter the dehydration stage, the firepower is reduced to 140 degrees, the throttle is adjusted to 4, the 4th'50 "dehydration is completed, the firepower is reduced to 140 degrees, 8 degrees 39. At 32 ", ugly wrinkles and black markings appear on the bean surface, and the smell of toast obviously changes to the smell of coffee, which can be defined as a prelude to an explosion. At this time, listen carefully to the sound of the explosion point, start to explode at 8: 37", adjust the firepower to 80 degrees, the throttle should be fully opened 5 (the firepower should be very careful, not so small as to be free of bursting sound), develop 1: 50 "after an explosion, 195.3 degrees into the pot.
[suggestion on brewing coffee in Qianjie]
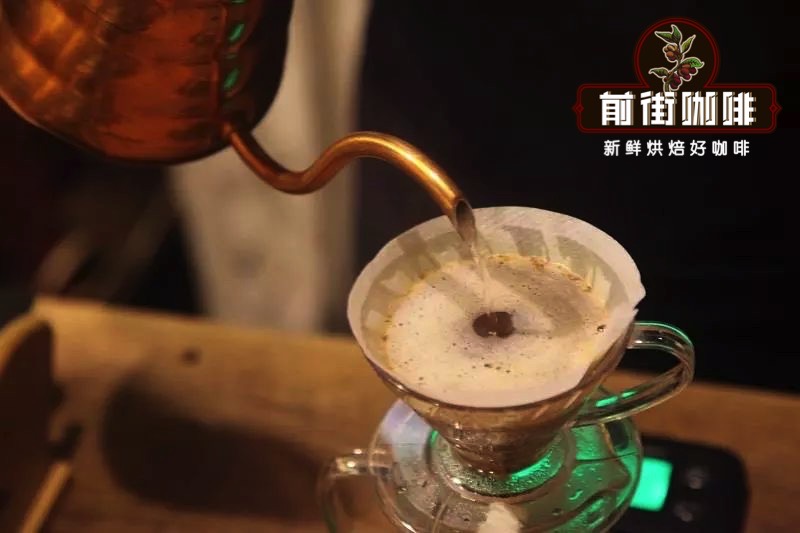

Filter cup: V60 filter cup
Amount of powder: 15g
Powder / water ratio: 1:15
Temperature: 90 degrees
Degree of grinding: BG#6S
[Qianjie coffee brewing technique]
Segmented extraction.
Steaming 30 grams of water for 30 seconds, injecting water to 125 grams in sections, continue to inject water to 225 grams when the water level is about to expose the powder bed, remove the filter cup when the water level is about to expose the powder bed, and the extraction time is two minutes.

[flavor description]: floral aroma, citrus acid, caramel, slightly smoky taste
For more boutique coffee beans, please add private Qianjie coffee on Wechat. WeChat account: kaixinguoguo0925
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

Suvira West Island Coffee beans Fine Coffee beans on the oldest Island of Indonesia
For information, please pay attention to the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) Sulawesi Coffee often appears on the sacks of Ce1ebes, Toraja, Kalossi three English names. Celebes, the old name of Celebes under Dutch rule, has long been changed to Sulawesi; Toraja is interesting because it is neither a place name, a city name, nor a variety name.
- Next

What is the difference in flavor between Rwandan coffee and other coffee in Africa? Rwanda coffee bean flavor
For information, follow Coffee Workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) Rwanda: this small East African country should not be ignored by roasters and coffee lovers. It is known as the hometown of thousands of mountains, and its high-quality, high-altitude coffee coexists with its poverty. It is not the largest coffee producer in Africa; in 2016, it harvested only 220000 bags (60 kg) of coffee, while
Related
- Does Rose Summer choose Blue, Green or Red? Detailed explanation of Rose Summer Coffee plots and Classification in Panamanian Jade Manor
- What is the difference between the origin, producing area, processing plant, cooperative and manor of coffee beans?
- How fine does the espresso powder fit? how to grind the espresso?
- Sca coffee roasting degree color card coffee roasting degree 8 roasting color values what do you mean?
- The practice of lattes: how to make lattes at home
- Introduction to Indonesian Fine Coffee beans-- Java Coffee producing area of Indonesian Arabica Coffee
- How much will the flavor of light and medium roasted rose summer be expressed? What baking level is rose summer suitable for?
- Introduction to the characteristics of washing, sun-drying or wet-planing coffee commonly used in Mantenin, Indonesia
- Price characteristics of Arabica Coffee Bean Starbucks introduction to Manning Coffee Bean Taste producing area Variety Manor
- What is the authentic Yega flavor? What are the flavor characteristics of the really excellent Yejasuffi coffee beans?

