Introduction to the Flavor characteristics of Indonesian Coffee
When it comes to the boutique coffee producing areas in Indonesia, Sumatra is the only one that can blurt out. The Indonesian coffee beans on the front street include not only Mantenin from Sumatra, but also beans from West Java, another boutique coffee producing region. This coffee bean is very different from the Indonesian coffee flavor that many people remember. It has no full-bodied coffee flavor with herbs and spices, on the contrary, it is more soft and sour tropical fruit. In this article, Qianjie Coffee introduces this coffee bean from West Java.
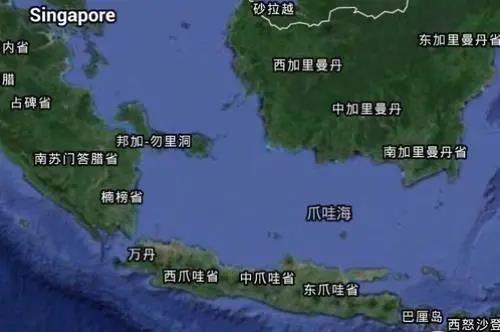
The coffee producing area introduces West Java as the first-level administrative district of Indonesia. Located in the western part of Java, facing the Java Sea to the north and the Indian Ocean to the south, including offshore islands, covering an area of 46300 square kilometers, Java has a tropical rain forest climate, which is hot and humid all the year round. The plains along the northern coast have the highest temperatures, while the mountains are much cooler. High humidity often creates a debilitating climate. From November to March of the following year is the northwest monsoon period, rainy and cloudy; from April to October is the southeast monsoon period, with more sunny days and less rainfall. The average annual rainfall in Jakarta is about 1760 mm (69 inches). The average daily maximum temperature in Jakarta is 30 ℃ (86 ℉) and the lowest is 23 ℃ (74 ℉). In the highlands of Tosari (Tosari, 1735 m (5692 ft) above sea level), the average temperature is 22 ℃ (72 Murray 47 ℉). Because volcanic ash periodically fertilizes the land, the soil in Java is very fertile. Java plays an extremely important role in the history of coffee. Unlike most other Indonesian coffee, Arabica coffee grows on small farms for initial processing. Java coffee is grown on large farms or plantations. most of them are operated by the government and are washed in modern ways. The variety, which belongs to S795 and is called Jember by local people, is artificially cultivated. Qianjie will choose this coffee bean on the shelves because it shows the delicate aroma of Java, with relatively soft acidity, delicate taste and good balance. Java coffee has a better aroma and acidity than coffee from Sumatra and Sulawesi.
History of coffee cultivation mocha coffee spread to India around 1600 and was planted in Ceylon in 1658. It has never had a good harvest. The Netherlands was introduced from India to Java for coffee cultivation in 1699 and the first seedlings were exported to the European Dutch East India Company (Dutch acronym VOC Vereeningde Oost-Indische, founded in 1602) in 1711. Within 10 years, exports of JAVA coffee grown in Indonesia have increased to 60 tons per year. Indonesia is the first country outside Yemen and Ethiopia to grow coffee widely. Coffee was monopolized by VOC for more than 60 years (1725-1780). In the early days of Dutch rule, iron pickup coffee beans were grown, and coffee seeds were introduced from Ceylon (modern Sri Lanka). In the 17th century, the Dutch colonial government first grew coffee in Batavia, extending south to Sukabumi. And a wide range of central East Java, West Java and parts of Sumatra and Sulawesi Island, open the noble marketing of coffee. Coffee trees from Java were exported to the Netherlands in 1711, cultivated in greenhouses in Amsterdam and sent to Versailles in France in 1715. since then, the Netherlands and France spread coffee to Asia and the Americas, which is called New World Coffee.

In the late 19th century, Dutch colonists established large coffee plantations on the Ijen plateau in eastern Java. In the 1920s small farmers throughout Indonesia began to grow coffee as a cash crop. However, the disaster occurred in 1876, when coffee leaf rust swept through Indonesia, destroying most of the tin card varieties. In the late 1880s, most coffee plantations were destroyed by insect diseases, and the plague spread to central and East Java. At the beginning of the 20th century, Arabica coffee was severely damaged by leaf rust, destroying most of the Dutch coffee variety system, so the Indonesian Coffee and Cocoa Institute (ICCRI) was established in 1911, continuing the knowledge base of coffee trees and cocoa cultivation introduced by the Dutch in the 16th century. ICCRI pioneered coffee and cocoa research activities with a national mandate to implement coffee and cocoa research activities to produce innovative technologies suitable for farm-to-coffee and cocoa processing. Far more professional than the SCAA Association, it is recognized as an international research institution in the world.

ICCRI provides services to coffee and cocoa farmers and aims to address persistent problems and enhance technology transfer. It is composed of more than 300 employees, covering three main responsibilities, research and service, business and support staff. There are 36 researchers, including 12 PhDs, 7 masters and 17 college researchers. The researchers were classified as 11 major research scientists, 9 research scientists, 11 associate scientists and 5 assistant scientists. And provide relevant data and information to small farmers, private and real estate companies, national and regional governments, associations and other stakeholders. Java Coffee was nationalized on separate estates and vigorously piled up new varieties of Arabica coffee beans, which were handed over to small farmers through the government and various development projects. More than 90% of Indonesian coffee is grown on small farms with less than 1 hectare per capita. Most of the production is organic, of which 19 farmers' cooperatives and exporters have obtained international certification for organic coffee. More than 20 varieties of Arabica coffee are grown commercially in Indonesia. It can also be roughly divided into six categories: iron pickup is an original variety introduced by the Netherlands. Most of the tin cards were destroyed by coffee leaf rust in Indonesia in the late 1880s. However, iron pickup mutants of Bergandal and Sidikalang can still be found in the high elevations of Sumatra. H ibrido de Timor (HDT), also known as "Tim Tim, Tim'" is a mixture of Arabica and Robusta. It seems to be a single coffee variety from 1917 to 18, which was planted in Aceh in 1979. Linie S: this strain was originally in India and evolved from Bourbon. The most common are smur288 and smur795, which are often found in Aceh, Flores and Lindong. Ethiopian lines Ethiopian line, which includes Rambung and Abyssinia, was brought to Java in 1928. Has been planted in Aceh. Another group of Ethiopian variants, called "USDA", was found in Sumatra and spread to Indonesia in the 1950s. Caturra variety: Caturra is a bourbon mutant coffee that originated in Brazil. Catimor: is to enhance the flavor of Arabica and Robusta cross breeding. There are many types of Catimor, including "Ateng-Jaluk", which is currently under study to determine whether this variety is suitable for planting in Aceh and can achieve excellent cup test results.
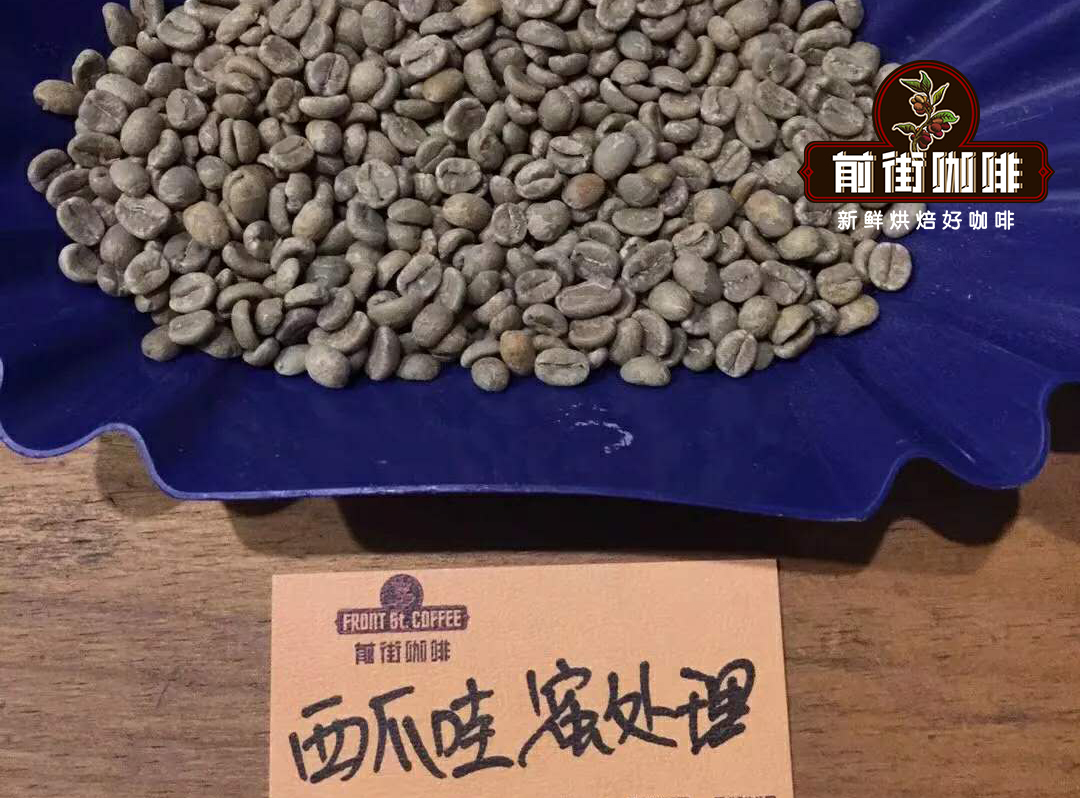
Qianjie Coffee Honey treats West Java Coffee beans
Producing area: Tiegula Mountain, West Java, Indonesia
Manor: Edini Manor
Altitude: 1400-1600 m
Variety: Jember
Treatment method: honey treatment

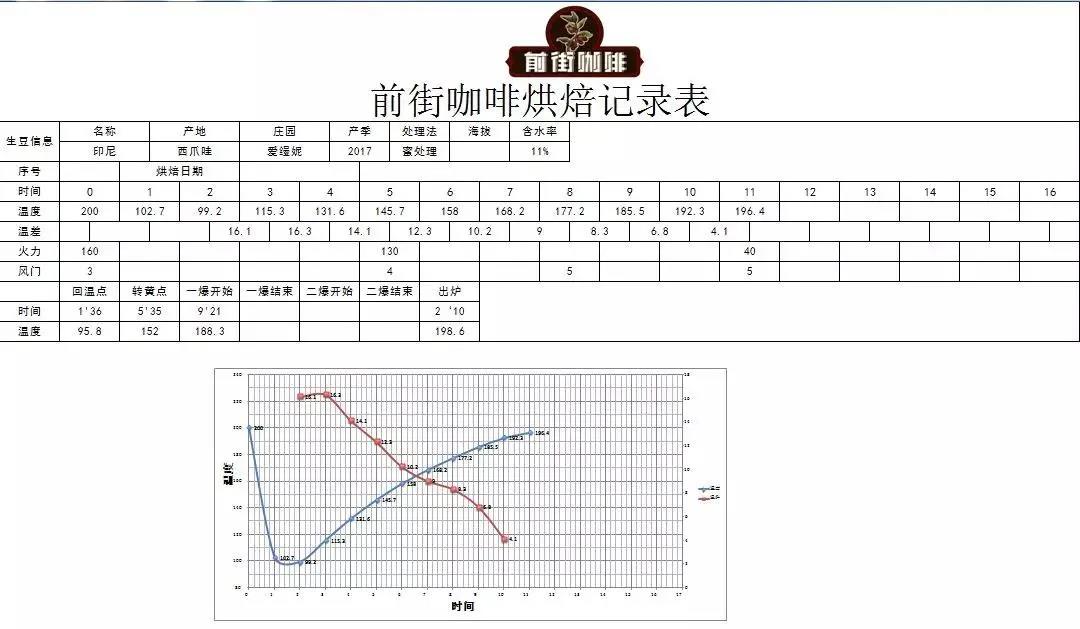
The coffee variety S795 is locally known as Jemner, its bean color is blue and green, and its original tree species natural variation comes from S288, which was originally an excellent hybrid cultivated in India in 1946. S288 was named S26 after the mixture of S288 (the first generation) and Typica, because the first generation of beans of S288 were crossed between Arabica and Liberian Liberica and always had the fishy smell of Liberika. Indian botanists then used the first generation of S288 and Typica hybrid Kent and the second generation of S288 to become the present S795. The S795 planted in West Java is introduced by the Provera Coffee Research Center (Jember Coffee Research Center) in East Java to Javanese farmers after introducing local varieties from India, so the local farmers in Java are also directly known as Jember. Honey treatment is a complex, time-consuming, difficult and easy processing method. The first step is to select high-quality fruit, and then peel off the pulp to leave the endocarp, where the endocarp is the core of honey treatment. The endocarp is rich in sugar and sour taste, which will slowly seep into the coffee beans during the drying process. The second step is drying, which is the most important condition for the production of high-quality coffee beans. Honey treatment keeps the coffee clean after washing, and although the brightness of the coffee decreases, it increases the sweetness and caramel taste. According to the different degree of honey treatment, honey-treated coffee can be divided into yellow honey treatment, red honey treatment and black honey treatment. Qianjie baking parameters Qianjie Baker noticed the high density of West Java raw beans, so the firepower adjustment should be very careful, and highlight the fruit flavor and sweetness, choose moderate baking, you can fully show the uniqueness of raw beans, after 1 minute, the initial firepower will be relatively large, until the early stage of dehydration to adjust the firepower, so that the taste and aroma of coffee become uniform.
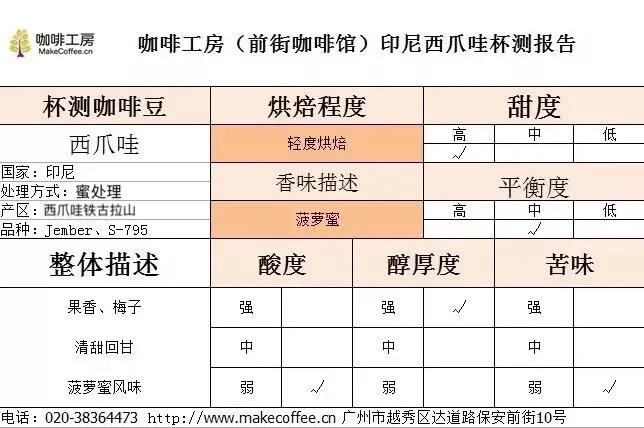
Qianjie Cup Test report Qianjie found that the main feature of this Java coffee is its complex sweetness and fruity aroma, which is more obvious than the African Yega Sheffield, which is also famous for its floral aroma. Its taste spectrum is inclined to the tropical fruits with heavy flavors such as mango and polo honey, which are complex and calm, while the unique honey treatment techniques bring a faint flavor of red wine.
Recommended water temperature for coffee brewing in front street: 90-91 ℃ Grinding degree: BG#6m (size of fine sugar / size of sieve bowl 20 to 80%) ratio of powder to water: 1:15 Powder content: 15 g
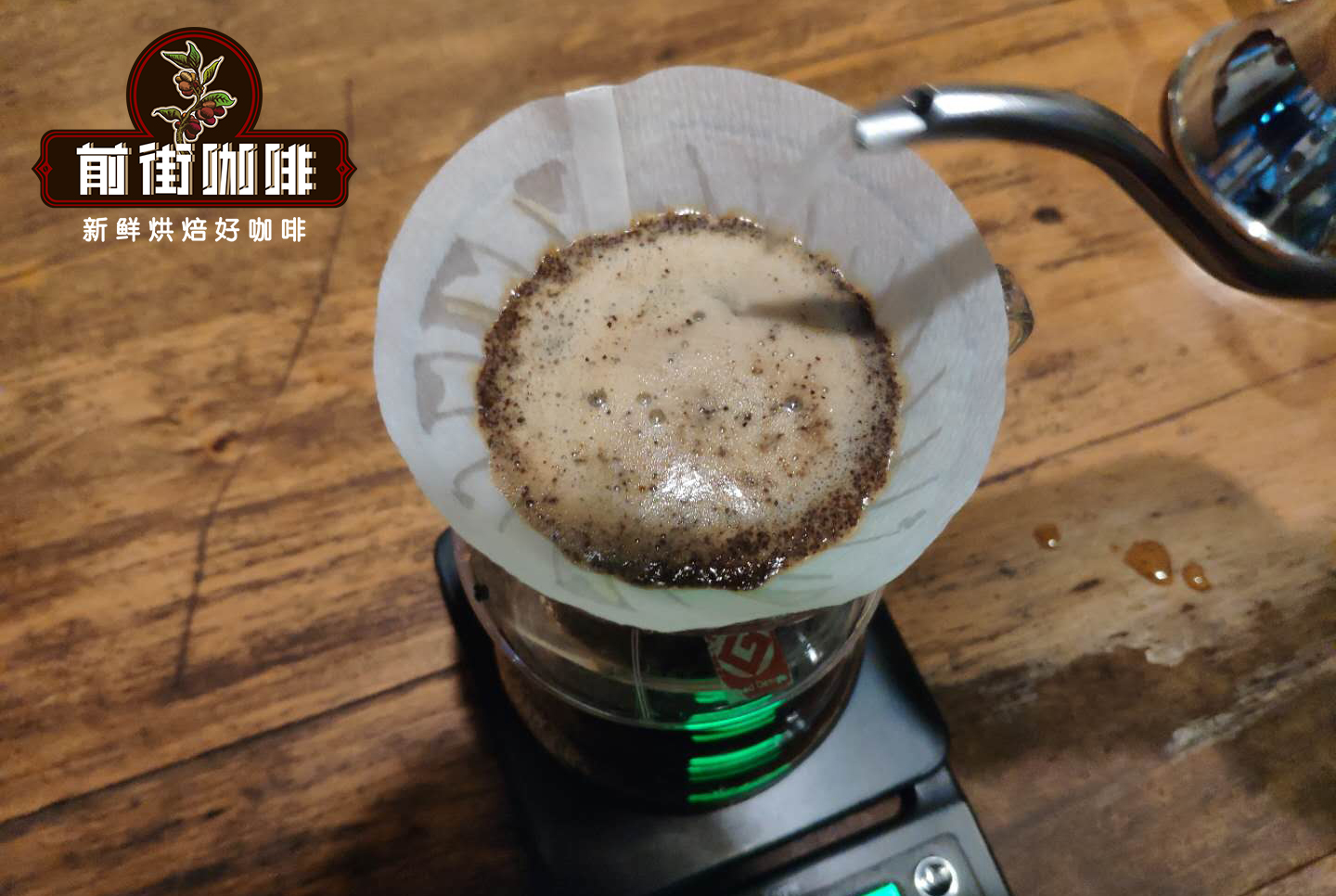

Qianjie cooking technique: the first section is filled with 30 grams of water for 30 seconds, followed by 95 grams (the electronic scale shows that about 125 grams), and the injection is completed in about 1 minute. When the water level drops to the powder layer 2 gram 3, inject the remaining 100 grams (about 225 grams shown by the electronic scale), about 1 minute and 40 seconds. Remove the filter cup and finish the extraction. Brewing flavor: very rich tropical fruit flavor, sweet taste of mango, jackfruit and other fruits, with red wine fermentation feeling.
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

Santa Ana Paradise Manor El Salvador Coffee Fine Coffee
Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) Salvadoran coffee has six major producing areas, generally distributed on the volcanic ash-covered mountain slopes or plateau areas at an altitude of 1200 meters above sea level. The harvest and harvest season is from November to April of the following year. Because coffee prefers a mild climate, most coffee trees in the country are planted in
- Next

High-quality Costa Rican coffee with ideal acidity, unique aroma and charming boutique coffee
Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) high-quality Costa Rican coffee is called extra hard beans, this kind of coffee can grow above 1500 meters above sea level. Altitude has always been a problem for coffee growers. The higher the altitude, the better the coffee beans, not only because higher elevations can increase the coffee beans.
Related
- Does Rose Summer choose Blue, Green or Red? Detailed explanation of Rose Summer Coffee plots and Classification in Panamanian Jade Manor
- What is the difference between the origin, producing area, processing plant, cooperative and manor of coffee beans?
- How fine does the espresso powder fit? how to grind the espresso?
- Sca coffee roasting degree color card coffee roasting degree 8 roasting color values what do you mean?
- The practice of lattes: how to make lattes at home
- Introduction to Indonesian Fine Coffee beans-- Java Coffee producing area of Indonesian Arabica Coffee
- How much will the flavor of light and medium roasted rose summer be expressed? What baking level is rose summer suitable for?
- Introduction to the characteristics of washing, sun-drying or wet-planing coffee commonly used in Mantenin, Indonesia
- Price characteristics of Arabica Coffee Bean Starbucks introduction to Manning Coffee Bean Taste producing area Variety Manor
- What is the authentic Yega flavor? What are the flavor characteristics of the really excellent Yejasuffi coffee beans?

