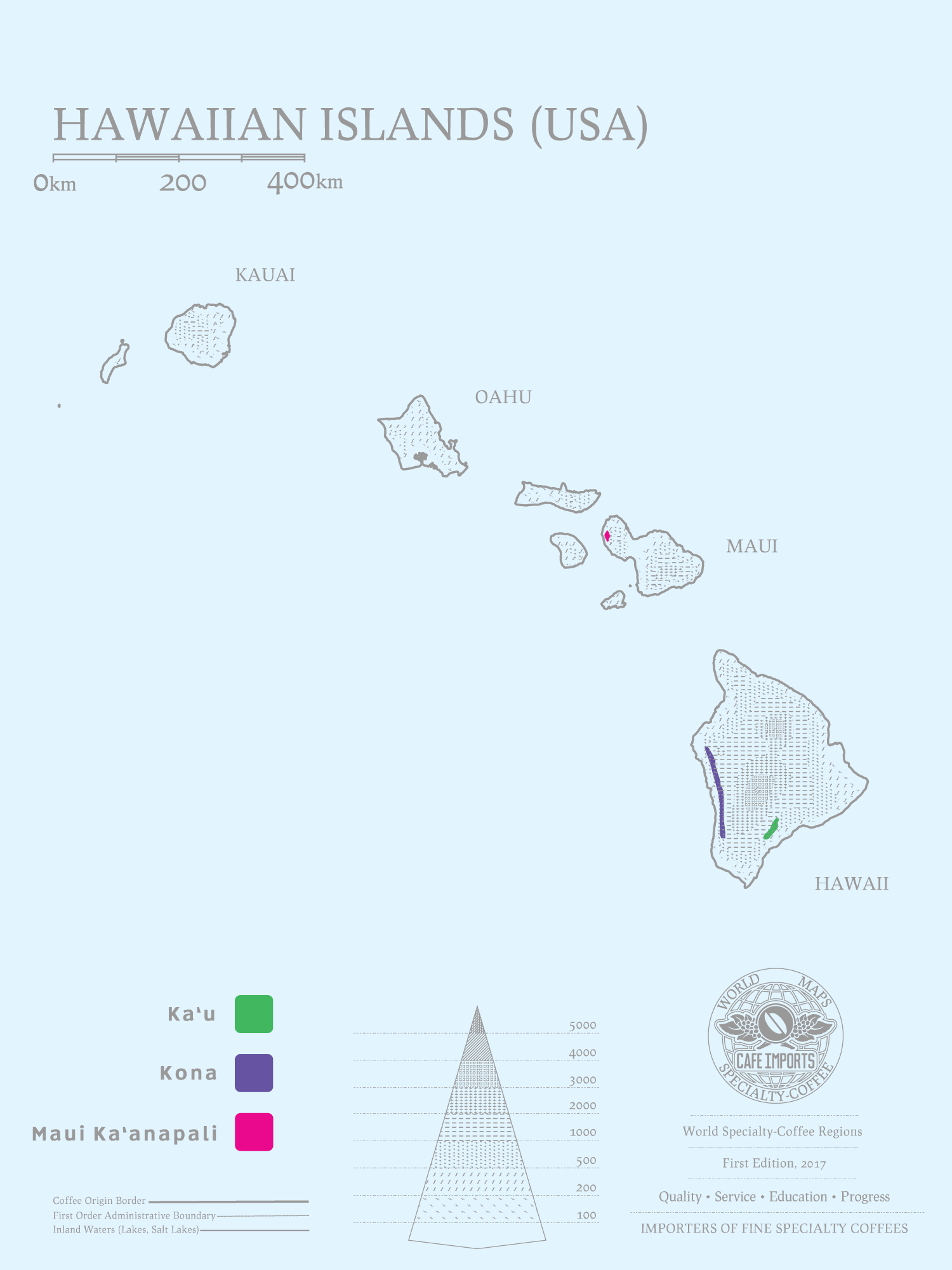
The Development background of Hawaiian Coffee introduces the grading system of Hawaiian Coffee
Hawaiian coffee
In 1813, the first plants were brought to Oahu, although sugar as an agricultural product for farmers far exceeded coffee. In the late 1820s, the bourbon variety of coffee was brought to the Big Island, and the first coffee-focused estates were established over the next decade.
However, the development of the coffee industry here is not smooth. For example, in 1858, coffee production on the island of Kauai was halted by Fusarium wilt. Then there was competition in the sugar industry, with landowners switching from coffee to sugar to increase income. These factors led to the abandonment of many plantations and subsequent division into smaller farms. The United States began to occupy the islands in 1898 and removed protective tariffs on coffee, further weakening the market. As a result, more farmers began to plant sugar cane. It wasn't until the 1980s that the coffee industry took a turn for the better because of falling sugar prices.
There are currently 12 coffee areas spread throughout the island, of which Kona is the most famous. However, due to low production and high production costs, with the increasing demand for boutique coffee in recent years, the price of Kona on the market is catching up with the Blue Mountain of Jamaica, and it is becoming more and more difficult to buy good Kona beans. Although the price of Hawaiian coffee is often high, traceability is high.
Hawaiian Coffee grading system
Extra Fancy: particle size is more than 19 mesh, only 8 complete defects are allowed per 300g.
Fancy: particle size is 18 mesh, only 12 complete defects are allowed per 300g.
No.1: particle size is 16 mesh, only 18 complete defects are allowed per 300g
Estate Select: there is no special specification for particle size, only 5% defect rate of total weight is allowed.
Prime: there is no special specification for particle size, only 5% defect rate of total weight is allowed.
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

Introduction to the producing area of Chinbu Coffee in Papua New Guinea the characteristics and flavor of Chinbu coffee
Chinbu province (Chimbu) is the third largest coffee producing area in the country, but its production is relatively lower than that of the other two highland producing areas. The name of the district comes from the local dialect, and the word Sipuuuu means thank you. Most of the local coffee comes from the coffee courtyard around small farmers, and 90% of the population in the area is engaged in the coffee-related industry, which for many people is their only cash crop. Qinbu grows Coffee
- Next
How about Jamaica coffee? Introduction and Grading System of Jamaica Coffee
Governor Sir Nicholas Rouse in 1728 received coffee plants from the governor of Martinique and immediately planted them in the St Andrews area. Production was limited in the first half of the century, but as coffee cultivation expanded from St Andrews to the Blue Mountains, it flourished in 686 plantations. By 1814, Jamaica's peak annual production exceeded 16,5
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

