World Fine Coffee El Salvador Manor beans: El Salvador Coffee Cafe de El Salvador
country profiles
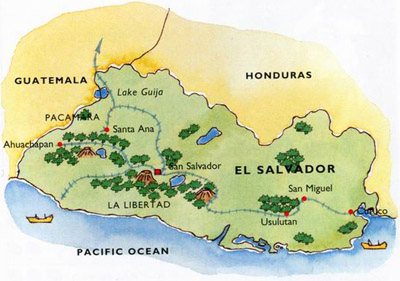
El Salvador, Spanish República de El Salvador, English the Republic of El Salvador
Located in Central America, it is adjacent to Guatemala and Honduras in the north and the Pacific coastline in the west and south.
The smallest country in Central America is also the most densely populated country in Central America. The land area is 21393 square kilometers, with a population of 6.25 million (data 2012) and a population density of 327 people/square kilometer.
The economy is dominated by agriculture, with a per capita GDP of $3722 in 2011. Agricultural products are mainly coffee and cotton.
The country is divided into 14 provinces, 7 of which produce coffee.
There are many volcanoes in the territory, with the name of "Volcano Country". The lowest altitude in the territory is 0 meters, and the highest is Santa Ana active volcano 2385 meters.
In 1524 it became a Spanish colony.
1821 Independence from Spain.
In 1824, it joined the Central American Federation, which included Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Mexico.
In 1841, it seceded from the Federation and became independent.
Photo: Flag and Emblem of El Salvador
A brief history of coffee production
Coffee was introduced to El Salvador from the Caribbean in 1742 (1740).
In the mid-19th century, El Salvador's original export pillar Indigo (Indigo, a dye) gradually declined after receiving the development of synthetic dyes in Europe, and coffee gradually became the main export product under the leadership of the government.
In 1856, the first 693 bags of coffee beans were shipped to Europe. Europe was El Salvador's leading coffee customer until World War II, when it was replaced by the United States.
In the 1970s, El Salvador produced a record 350,000 bags of coffee. As the civil war intensified, the coffee industry was in turmoil.
Coffee production in El Salvador was affected by domestic political instability, and the civil war was suspended after the parties signed a peace agreement in 1992. The coffee industry is beginning to recover.
Coffee production status
"Natural disasters" and "bad luck" are the words that describe the challenges facing El Salvador's coffee industry. Although it has escaped the shadow of war, El Salvador's coffee production still faces challenges from time to time, including: hurricane in 1998; earthquake in 2001; volcanic eruption in 2002; and leaf rust in 2012.
Despite these challenges, El Salvador has maintained a high coffee production, consistently ranking in the top 15 of ICO member countries for total coffee production between 2008 and 2012, according to ICO International Coffee Organization data. In 2013, affected by leaf rust disaster, 70% of farms in China were infected, and the yield dropped sharply by about 40%, ranking down to 16.
El Salvador 08-13 Total coffee production and ranking (unit: 000 bags, 60kg per bag)
Year 200820092010201120122013
Total output 14101065181411521360844
Ranked 121412141416
Note: Ranking is limited to ICO member states.
coffee varieties
The chaos caused by the civil war affected economic development, but ironically allowed the ancient coffee species to remain. The situation was too chaotic for Salvadoran coffee farmers to catch up with the trend of coffee variety renewal in Central and South America.
El Salvador produces 100% Arabica coffee, of which 68% is Bourbon (Coffea arabica var. Bourbon), 29% Pacas, the rest include Pacamara, Caturra, etc.
Pacas, first discovered in Salvador in 1949, is a natural hybrid of Bourbon and Catula.
Pacamara, an artificially selected variety of pacas and maragogipe (or maragogype), was first bred in 1958 (1954). Pacamara is a rare excellent variety under artificial breeding. Green is better than blue. It perfectly inherits the advantages of the mother plant. It has the excellent taste of pacas and the big size of malagogipe. Pacamara species are thought to be the result of the pursuit of larger Arabica species.
coffee planting
Most are grown by small farmers. Classification of Salvadoran farmers: ( 1 htct= 105 mu = 10000 square meters)
Small farmer, small producer, area less than 7.0 hect;
Medium farmer, medium producer, area between 7.0-70hect;
Large farmer, large producer, area greater than 70hect.
Farmers use traditional planting methods with almost 100% shade.
coffee harvest
Hand picked.
The harvest season lasts from October to March. The peak occurs between November and February.
coffee processing
Water washing treatment, sun drying.
Coffee Grading
According to altitude, the highest is SHG: ( 1 feet = 0.3048 meters)
SHG, strictly high grown, above 3950 feet (about 1200m);
HG, high grown, above 2950 feet (about 899m);
CS, central standard, above 1960 feet(about 597m).
coffee outlet
Raw beans are exported throughout the year and stored in warehouses in the form of shelled beans.
coffee producing areas
coffee is produced in 7 of the countrys 14 departments, with chalatenango and santa ana being the largest producers.
Geographically, it is mainly distributed in the north and south mountain systems, the north is the mountain system at the junction of land and Guatemala and Honduras, and the south is the mountain system composed of numerous volcanoes extending along the Pacific coastline.
El Salvador divides the region into six mountain ranges.
Chalatenango is famous for its outstanding performance in coe competitions this year. Chalatenango was unknown a few years ago, and some farmers in the area began planting Pacamara species in the 1990s. In 2006, a small farm in the area competed with pacamara against coe and finished second in that year's event with a killer flavor. In 2007, a number of farms in the region competed again as pacamara, winning first, third and fourth place, chalatenango and ta pacamara becoming famous. The region is located in the northern Altotepec Metagan mountain range, the purple top area in the image above.
Coffee flavor and quality
El Salvador is a producer of high-quality commercial Arabica beans and is known for its strict and effective quality control.
Since 2003, he has participated in COE competitions.
With excellent ancient coffee, successfully entered the fine coffee market.
Coffee flavor is related to the microclimate of the producing area. Generally speaking, Salvadoran coffee inherits the mild quality of Sino-American coffee, which is soft, slightly sour and has a good sweetness, suitable for blending.
Fine Salvadoran coffees can also be impressive, including certain pacamara varieties that exhibit active acidity, depth and depth, and a long finish.
coffee organization
UCAFES: Organization of coffee production cooperatives of el salvador, production accounts for 25% of the total;
UCRAPROBEX: Organization of Land Reform Coffee Producing & Processing Cooperatives, including landless smallholder farmers who produced 10% of the total;
ABECAFE: Association of mills and Coffee Exporters, including 99 processors and most exporters;
The Association of Coffee Producers of El Salvador represents all coffee producers.
These four coffee organizations, together with four national research institutes, constitute a coffee policy-making body-
Salvadoran Coffee Association Consejo Salvador doreno del cafe(salvador coffee council), an organization involved in coffee promotion, data collection and international cooperation.
Source:
Reflected blog
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

World Coffee Manor El Finca Loma La Gloria La Gloria. Introduction to the manor
Manor: Finca Loma La Gloria Raglory. Manor beans: red bourbon De Agustin de Augustine treatment: REPOSADOWASHEDSUNDRY dry fermentation washing natural drying cup test Cupping: red apple, chocolate, excellent round taste and aftertaste Chocolate, red apple, nice body andaftertaste, bold El Vola
- Next

Characteristics of Coffee Bean Flavor in three Coffee producing areas in the World
Under the influence of Chinese culture, Asian tea culture is booming, while coffee appears to be on its own by comparison.
Related
- Does Rose Summer choose Blue, Green or Red? Detailed explanation of Rose Summer Coffee plots and Classification in Panamanian Jade Manor
- What is the difference between the origin, producing area, processing plant, cooperative and manor of coffee beans?
- How fine does the espresso powder fit? how to grind the espresso?
- Sca coffee roasting degree color card coffee roasting degree 8 roasting color values what do you mean?
- The practice of lattes: how to make lattes at home
- Introduction to Indonesian Fine Coffee beans-- Java Coffee producing area of Indonesian Arabica Coffee
- How much will the flavor of light and medium roasted rose summer be expressed? What baking level is rose summer suitable for?
- Introduction to the characteristics of washing, sun-drying or wet-planing coffee commonly used in Mantenin, Indonesia
- Price characteristics of Arabica Coffee Bean Starbucks introduction to Manning Coffee Bean Taste producing area Variety Manor
- What is the authentic Yega flavor? What are the flavor characteristics of the really excellent Yejasuffi coffee beans?

