El Salvador Coffee Bean grading system SHG meaning El Salvador Coffee Story and characteristics

Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style)
Salvadoran coffee beans are light, aromatic, pure, mild acidity and excellent balance. Many friends who like Central and South American coffee varieties also like the high-quality coffee produced by El Salvador. If you follow the Qianjie official account or those who often come to Guangzhou stores, you should know that Qianjie has shared several Salvadoran coffee beans. Qianjie collects these coffee materials not just for sale, but to set up a database of information so that people can have a better understanding of coffee. In fact, Qianjie has gone through a lot of identification and accumulation of producing areas before it is put on the shelves. Many beans will not be on the shelves. Some coffee beans are actually of good quality, but the characteristics of the producing areas are not prominent. Or they are similar to the beans currently on the shelves in Qianjie, so they will not be on the shelves.

El Salvador Coffee Story
In 1742, coffee was introduced into El Salvador from the Caribbean.
In the middle of the 19th century, El Salvador's original export pillar Indigo (a kind of dye) industry gradually declined under the influence of European synthetic dyes, and coffee gradually became the main export product under the guidance of the government.
The land used to grow locust blue is controlled by a small number of large estate families, while coffee cultivation requires different land, which colluded with the government to force the poor to move out of their land and bring these areas into the category of new coffee plantations. At that time, there were no so-called compensation measures, and the poor only got seasonal job opportunities.
In 1856, the first 693 bags of coffee beans were shipped to Europe. By 1930, coffee accounted for more than 90% of El Salvador's exports. Europe was the most important coffee carrier in El Salvador until World War II, which was replaced by the United States after World War II.
In the 1970s, El Salvador produced a record 350000 bags of coffee. Even after two world wars and a global recession, El Salvador remains among the top coffee-producing countries.
Until after the civil war in the 1980s, the land reform reversed the previous land policy and broke the country's original manor system. Although the land has been redistributed among farmers, the government remains in control and no farmer is allowed to own more than 245 hectares of land. Today, land reform policies still work, with more than 90% of coffee production provided by small farmers with a land area of less than 20 hectares.
However, between 1997 and 2001, the price of Salvadoran coffee beans fell sharply, when coffee production in El Salvador fell by more than 34 per cent, according to ICO.
In addition to decades of political and price factors, leaf rust spread in El Salvador in 2013, and production in El Salvador fell by nearly 60% during the 2014 harvest season. This is because only 3 per cent of the coffee trees planted in El Salvador at that time were rustproof, most of which were weakly disease-resistant coffee trees such as bourbon and Pacas.
Although various private and government assistance programs in recent years have increased annual production by 7.5 per cent since 2014, it is still a far cry from the past 2.4 million bags.
In 2016, the Ministry of Agriculture of El Salvador launched a new plan to distribute 20 million antirust plants to small farmers to further revitalize the coffee industry in El Salvador.
At the end of 2017, the Government of El Salvador signed a political agreement proposing to invest US $100 million over the next eight years to renovate 70,000 hectares of rustproof land. However, the report points out: "the main problem is that most seedlings are not certified and do not have any funds to provide the necessary maintenance until the plants reach production age." At the same time, World Coffee Research has established its Central American headquarters in El Salvador, where it has carried out several research projects and operates a 7-hectare research farm near Santa Ana, El Salvador.

Planting conditions of coffee beans in El Salvador
Geographically, El Salvador is located between Honduras and Guatemala, with the Pacific Ocean to the south and the terrain dominated by mountains and plateaus. El Salvador is known as the "country of volcanoes". The volcanic zone is rich in minerals, creating high-quality and fertile soil, which is conducive to the cultivation of coffee trees. Coffee gardens in El Salvador are mostly planted in shade, with the harvest season from November to April.
There are currently 23000 coffee growers in El Salvador, nearly 90 per cent of whom own farms with an area of less than 17 hectares, with small and medium-sized farmers accounting for 80 per cent of the country's total output. In addition, some 15000 smallholder farmers have formed 119 cooperatives to provide economic and social support to member families.
Coffee cultivation in El Salvador is mostly small farmers. Classification of farmers in El Salvador:
Small farmers, small producer, area less than 7.0hect
Medium-sized peasant household, medium producer, area between 7. 0-70hect
Large farmers, large producer, the area is larger than 70hect.
Note: 1 hect hectare = 10000 square meters = 15 mu

Salvadoran coffee grading system
Salvadoran coffee is graded according to altitude. Generally, the higher the altitude, the better the coffee:
SHG (Strictly High Grown) extremely high altitude growth: ≥ 1200m
HG (High Grown) Highland growth: 900-1200m
CS (Central Standard) Central Standard: 500m-900m

Coffee bean producing area of El Salvador
El Salvador has nine major coffee producing areas, which are as follows:
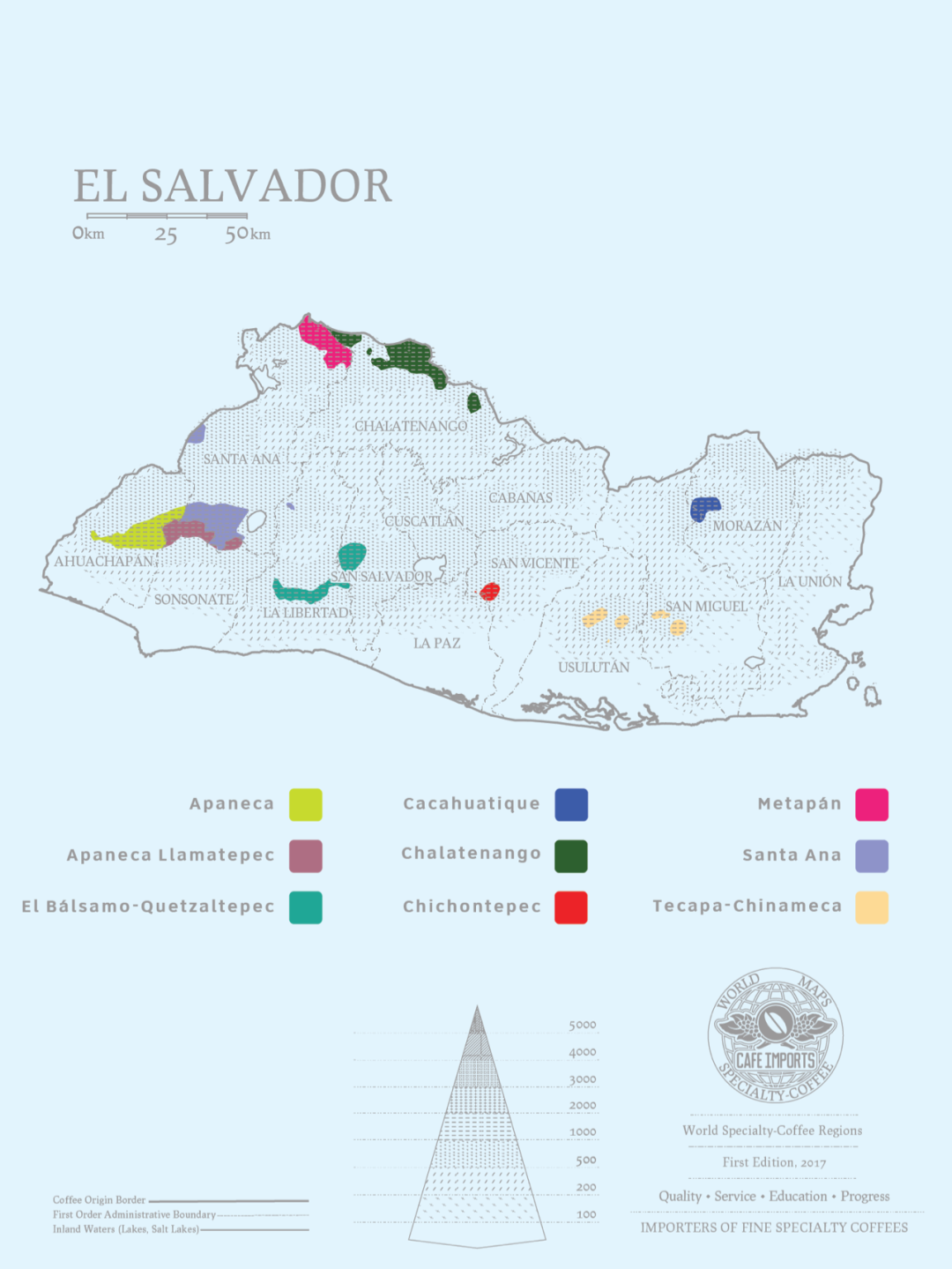
Apaneca is located in the west of El Salvador.
Coffee flavor: with excellent aroma
Apaneca Llamatepec is located in the mountains of western El Salvador.
Coffee flavor: coffee has the flavor of peach, cream and chocolate, with citrus acidity and delicate taste
Lemus Manor in El Salvador
Producing area: Apaneca-Ilamatepec, Apaneca Mountains
Manor: Lemus Manor Finca Lemus Bella Vista
Altitude: 1250 m
Varieties: bourbon, Kaduai
Treatment method: black honey treatment
Grade: SHB
Flavor: citrus, berries, grapes, cocoa, balance

El Balsamo-Quetzaltepec is located in the mountains of southwestern El Salvador.
Coffee flavor: with creamy flavor, excellent concentration and supple taste
Cacahuatique is located between San Miguel and Moraz á provinces.
Coffee flavor: with delicate fruit juice flavor and almond flavor
Chalatenango is located in the north of El Salvador
Coffee flavor: soft slightly sour, obvious sweetness, nut chocolate, smooth taste
Chichontepec is located in the center of El Salvador.
Coffee flavor: with chocolate sweetness and orange flavor
Metapan is located in the north of El Salvador
Coffee flavor: floral flavor, with chocolate, citrus and special sour caramel sweet neutralization, obvious fruit flavor
Santa Ana is located in the west of El Salvador.
Coffee flavor: aroma with mild acidity, good balance, smooth flavor of cream chocolate
El Salvador Santa Ana chocolate lover
Producing area: Santa Ana Santa Ana
Manor: chocolate Lover Manor El Guayabo
Altitude: 1450m
Variety: bourbon
Treatment: 50% washing + 50% honey treatment
Grade: SHB
Flavor: cocoa, caramel, cream, soft fruit acid, berry finish

Tecapa-Chinameca is located in the San Miguel city, the Lempa River and the Grande River.
Coffee flavor: coffee is rich in taste, with sweet flavors of chocolate and ripe fruits such as cantaloupe, apple and grape.
Salvadoran coffee varieties
The main varieties of coffee grown in El Salvador are Typica, Bourbon, Pacas and Pacamara.
Tippika is the oldest native variety in Ethiopia. The top leaf of the iron pickup is bronzed, the bean body is oval or thin, and the flavor is elegant, but the physique is weak, the disease resistance is poor and the fruit yield is low. High-quality coffee beans such as the Blue Mountains of Jamaica, Mantenin of Sumatra and Kona of Hawaii all belong to iron pickups.

Bourbon is an early variant of the iron pickup that was transplanted to Yemen, and the bean shape changed from thin and pointed to round. It was named bourbon in 1715 after France transplanted round beans from Yemeni mocha to the island of Bourbon on the east coast of Africa (renamed Reunion after the French Revolution). Bourbon beans spread to Brazil and Central and South America in 1727, and the British transplanted Yemeni mochas to St. Helena Island (where Napoleon was later imprisoned) in 1732. Bourbon is the winner of the American boutique coffee cup test.
Pacas is a bourbon variety found in El Salvador. In 1935, Salvadoran coffee farmer Pacas selected high-capacity varieties of San Ramon bourbon (San Ramon bourbon) to be planted on farms. In 1956, a friend found that the number of bourbon in his farm was higher than that of the same kind of coffee tree, so he asked a professor at the University of Florida to identify the bourbon gene mutation and named the new variety after the farm's evaluation, "Pacas." Pacas is very popular in Central America because of its high yield and good quality.
Pacamara was first cultivated by researchers in El Salvador in 1958. It perfectly inherits the advantages of the mother plant (Pacas and elephant beans). It not only has the excellent taste of Pacas, but also inherits the large size of bean Maragogipe. The bean body is at least 70% and 80% of that of beans, more than 17 orders, 100 percent, 18 eyes and 90 percent, and the average bean length is 1.03cm. The average width of beans is 0.71 cm (generally about 0.6-0.65), the thickness is 0.37 cm, and the bean is full and round. The biggest feature of this variety is that it is sour, lively and tricky, sometimes biscuit, sometimes fruity, thick and greasy. Pacamara is of the best quality from El Salvador and Guatemala.

How Salvadoran coffee beans are roasted
Take the coffee bean of Lemus Manor as an example. The front street determines the idea of shallow baking in order to highlight the soft acidity but not balanced taste of El Salvador.
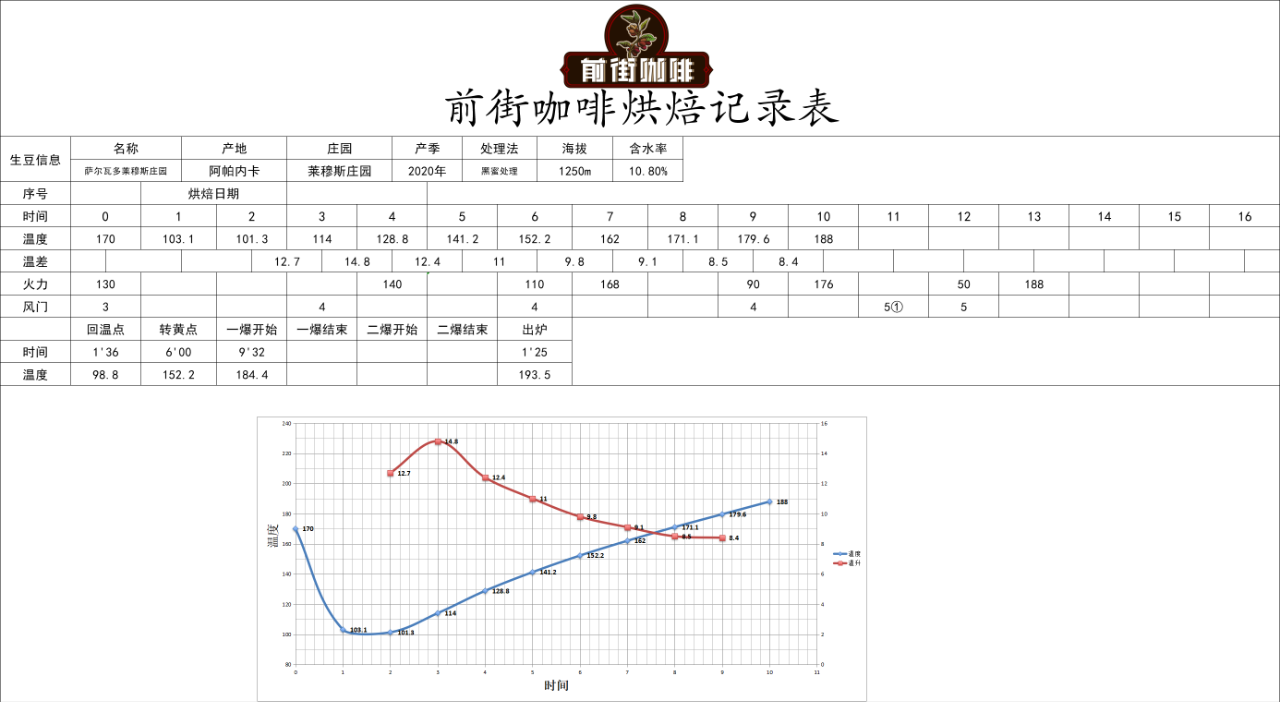
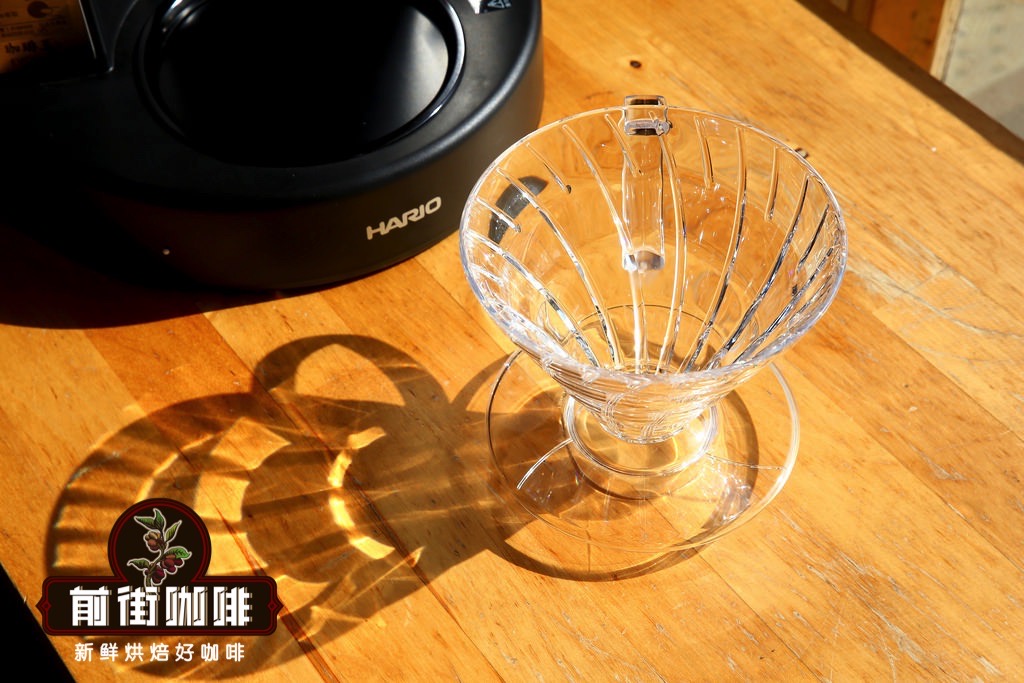
How to cook Salvadoran coffee beans in front of the street
Take the coffee bean of Lemus Manor as an example, the front street uses a V60 filter cup with higher water temperature and faster flow velocity to cook. The higher water temperature is used to extract the soft acidity of Salvadoran coffee beans, but to avoid excessive extraction caused by high temperature, faster filter cups, such as V60, are used. The V60 filter cup is in a 60 °cone shape, and the tapered angle allows the coffee powder to be distributed centrally, and when water is injected, the water can automatically converge to the center of the filter cup to ensure that the contact time between the water and the coffee powder is sufficient, so that the appropriate coffee liquid can be extracted. In addition, the ribs on the inside of the body of the V60 filter cup extend clockwise from the bottom to the top, so that there is enough space between the filter paper and the filter cup, so that the flow of water is good. Coupled with the large holes in the bottom, the flow velocity is relatively faster than that of many filter cups.

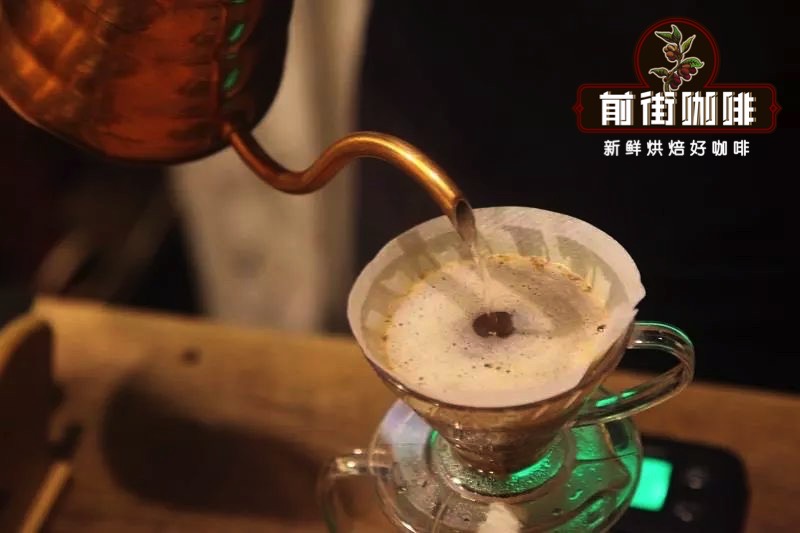
The specific cooking parameters of Qianjie are: V60 filter cup, water temperature 90 ℃, water powder ratio 1:15, powder quantity 15g, grinding degree (China No. 20 standard sieve pass rate 80%)
The front street uses segmented extraction, the amount of steaming water is twice that of coffee powder, that is, 30 grams of water is steamed for 30 seconds, the small flow is injected around to 125 grams, and the water level is about to be exposed when the powder bed is about to be exposed, continue to inject water to 225 grams to stop, the whole extraction time is 2 minutes.

For more boutique coffee beans, please add private Qianjie coffee on Wechat. WeChat account: kaixinguoguo0925
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

El Salvador Coffee Bean Taste Mirabella Manor El Salvador Coffee Flavor
Professional barista communication Please pay attention to coffee workshop (Weixin Official Accounts cafe_style) Product introduction Miralvalle 2011 COE#8 2012 COE#8 ; 2013 COE#12 2011 in Salvador COE See Mr. Menendez was delighted to receive the COE award for 8th place of the year with 88.89 points. Miravalle 2012
- Next

The characteristics of Colombian coffee beans what does Colombian fair trade coffee mean?
Professional barista communication please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) I believe everyone has heard of fair trade coffee, right? In fact, at first I was not quite sure what is fair trade coffee, but then I got a general idea that coffee farmers in Central and South America used to have the same exploitation as depicted in the movie Blood Diamond.
Related
- Detailed explanation of Jadeite planting Land in Panamanian Jadeite Manor introduction to the grading system of Jadeite competitive bidding, Red bid, Green bid and Rose Summer
- Story of Coffee planting in Brenka region of Costa Rica Stonehenge Manor anaerobic heavy honey treatment of flavor mouth
- What's on the barrel of Blue Mountain Coffee beans?
- Can American coffee also pull flowers? How to use hot American style to pull out a good-looking pattern?
- Can you make a cold extract with coffee beans? What is the right proportion for cold-extracted coffee formula?
- Indonesian PWN Gold Mandrine Coffee Origin Features Flavor How to Chong? Mandolin coffee is American.
- A brief introduction to the flavor characteristics of Brazilian yellow bourbon coffee beans
- What is the effect of different water quality on the flavor of cold-extracted coffee? What kind of water is best for brewing coffee?
- Why do you think of Rose Summer whenever you mention Panamanian coffee?
- Introduction to the characteristics of authentic blue mountain coffee bean producing areas? What is the CIB Coffee Authority in Jamaica?

