Flavor characteristics of Little Blue Mountain Coffee beans Story of Coffee beans in Kimmel Manor, Papua New Guinea

Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style)

Papua New Guinea Coffee
For years, coffee from Papua New Guinea has been overshadowed by coffee from neighboring Indonesia. However, its fruit is full of tonality, sweet coffee and ideal growing conditions have attracted the attention and interest of Qianjie coffee. With coffee production growing by 65% between 2015 and 2016, it's time for us to pay more attention to the Oceanian country. Papua New Guinea is one of the least developed countries in the world, with dense rainforests, rugged mountains and diverse indigenous peoples. In addition, the country has an equatorial rainy climate, dominated by tropical rain forests, and its biodiversity amazed Qianjie's partners. There are about 6500 species of native plants and 380 species of native birds, which can be said to be an important biological treasure house in the world.
Although Papua New Guinea is close to Indonesia, because the variety of coffee is different from that of Indonesia and the elevation is higher than that of Sumatra, coupled with the use of water washing treatment, Qianjie Coffee believes that the regional flavor of Papua New Guinea coffee is very different from that of Indonesia. Sweet and sour, flower and fruit aroma.
The island of New Guinea was colonized by the Netherlands, Germany, Britain, Japan, Australia and other countries from the 18th century to the 19th century. In 1961, the western half of the island became an Indonesian dependency, while the eastern half became independent from Australia in 1975, becoming the present-day PAPUA NEW GUINEA of Papua New Guinea.
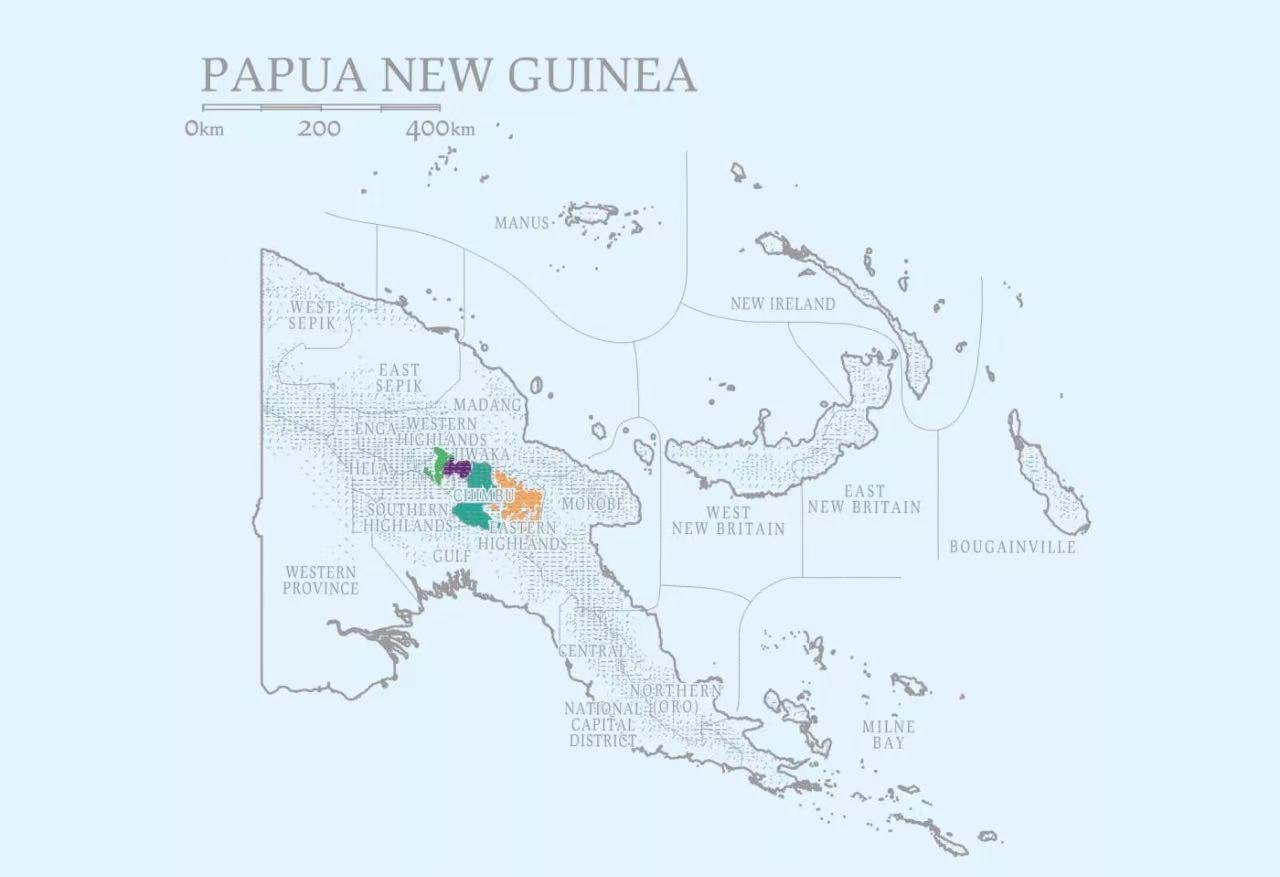
Papua New Guinea is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. Coffee is the only cash crop in the highlands of Papua New Guinea, accounting for 40% of the country. More than 2 million small farmers depend on coffee for a living. The coffee produced is mainly distributed in the mountains at an altitude of 1500 to 1900 meters, where the scenery is picturesque and there is abundant Rain Water and volcanic soil, which is very suitable for growing high-quality Arabica coffee beans.
According to the Standard Papua New Guinea Coffee Industry Corporation (Coffee Industry Corporation), Papua New Guinea has 16 producing provinces. However, more than 90% of production is in the eastern highlands, western highlands, Guihuaca, Morobe and Chinbu provinces. Most of the coffee is exported to Germany, the United States and Australia. Even though production in Papua New Guinea has increased by 65 per cent so far, the country's harvest is still small. According to ICO, it produced nearly 1.2 million bags of coffee (60kg/ bags) in 2016 (compared with nearly 11.5 million bags in Indonesia). More importantly, the industry was in a state of decline until 2016. But many Papua New Guineans are affected by the coffee industry: CIC estimates that it provides income for 400000 rural households.
Challenges facing Papua New Guinea
Coffee producers in Papua New Guinea face many challenges, but one of the biggest is logistics. Scott Bennett, managing director of Australian Bennetts importers, worked in Papua New Guinea in the 1990s. "it's not an easy country," he told Front Street Coffee. The roads between the mountains are poor, which makes transportation a little unstable. "
Although leaf rust is not a major problem today, there is still an environmental threat. CIC called on the Government of Papua New Guinea to provide financial support for the fight against this pest. Similarly, the International Centre for Agriculture and Biosciences is working to prevent and manage its presence, while Fairtrade Australia in New Zealand is providing domestic farmer training to coffee groups applying for Fairtrade certification.
Another challenge for producers is to ensure the consistency of crops so that they can access professional markets.

Grading standard of coffee beans in Papua New Guinea
PNG's raw coffee beans are graded in the same way as Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Zimbabwe and Puerto Rico, all of which are based on the size of coffee beans. Although the size of coffee beans is not the absolute standard of flavor quality, it is a very useful reference index for coffee beans in some producing areas, where mature beans with strong growth and full shape can best show beautiful flavor. Consistent factors such as maturity and hardness and moisture content make it easier for the baking process to achieve a homogeneous and perfect flavor, so many emerging producing areas will also classify this as a way of grading.
The coffee grade of Papua New Guinea is divided into a total of 12 grades, classified by defects:
Grade Grade
Legume size Screen Size
AA
> 18
A
seventeen
AB
> 16 (50%) > 17 (50%)
B
> 16
C
> 15
PB
11-14s
X
Mixed
E
> 19
PSC
> 15mm
Y1
Mixed
Y2
Mixed
T
Mixed
The meaning and rules of the name of raw coffee beans in Papua New Guinea:
PNG Plantation Y
Country + planting type + grading name
In Papua New Guinea, Plantation (plantations) and Large Estates (large estates) account for 25 per cent of the country's production; 10 per cent of small and medium-sized farms (Holdings or Blocks) with a size of 10-20 hectares; in PNG, there are 76 registered plantations and estates.
Take the most eye-catching boutique AA and An as an example:
The main results are as follows: (1) AA and Grade A coffee belong to the grade of boutique coffee, mainly from larger estates.
In the case of AA, the size of the bean is larger than 18 mesh, and the shape of the bean is oval. Number of shortcomings: a maximum of 10 defects per kilogram. The appearance of raw beans is green and slightly blue. The taste of raw beans should be clean and the taste of baking should be clean and smooth. The taste of the cup should be excellent (Fine Cup).
(2) the size of Class An is larger than that of 17 mesh, and the cup test must be at least GTF (Good to Fine), that is, good to excellent taste-the number of other defects and the condition of raw beans are the same as AA.

Papua New Guinea producing area
Eastern Highland Province
Most coffee in Papua New Guinea comes from the Highlands Province, which is undoubtedly the best coffee producer in Papua New Guinea.
■ altitude: 400-1900m
■ harvest period: April-September
■ varieties: bourbon, iron pickup, Arusha
West Highland Province
The West Highlands Province is another major coffee-producing region of Papua New Guinea, and how much coffee is grown around the regional capital Mount Hagen, named after an ancient dormant volcano. Most of the coffee from this area is processed in Goroka, so it is not easy to get a production and marketing resume for some coffee. Altitude and extremely fertile soil make the quality potential of coffee here boundless.
■ altitude: 1000-1800m
■ harvest period: April-September
■ varieties: bourbon, iron pickup, Arusha
Qinbu province
Chimbu has a short history of growing coffee trees, but it has rich soil, high altitude, mild climate all the year round, and good processing of raw beans: coffee farmers will manually select ripe coffee cherries and transport them to the Goroka processing plant for peeling and fermentation, washing and sun drying, which is now a popular honey treatment to ensure quality and give coffee beans a mellow taste. It's an excellent coffee bean. 90% of the population in the area is engaged in coffee-related industries, which is basically the only local cash crop.
■ altitude: 1300-1900m
■ harvest period: April-September
■ varieties: bourbon, iron pickup, Arusha
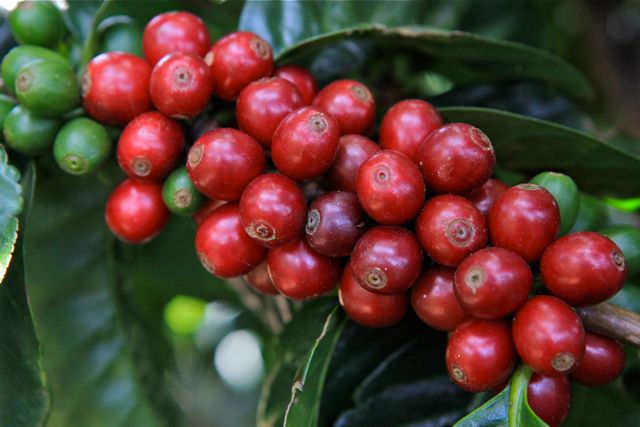

Chimeier Manor
In the 1920s, the British from Kenya set up large plantations to grow commercial coffee in Papua New Guinea. They introduced native Arabica species from Ethiopia and Kenya, as well as Blue Mountains and Typica from Jamaica. At that time, most of the coffee was produced by 18 large coffee farms, and times have changed. although there are still large coffee farms in operation, the output accounts for only 15% of the country's total output. At present, most of the coffee comes from individual small farmers who grow coffee in their own "coffee gardens". These farmers rely on farming for a living.
Chimeier is located in the Wiki Valley (Waghi Valley) of the western Asian plateau near the kimel River Valley and belongs to volcanic soil. Like many large farms or estates have their own washing plants, but in fact this is a manor owned by many independent coffee farmers of the surrounding Opais nationality. Because of the excellent growth environment and the stable quality control process of the treatment plant, the coffee produced has an active sense of brightness and retains a considerable degree of flavor uniqueness of Papua New Guinea coffee. The variety of coffee planted by Kimmel includes Typica, Arusha, Blue Mountai, Mundo Novo, Catimor and Caturra.... Most farmers will plant different varieties to avoid the risk of abnormal production of specific varieties, but also create an interesting performance of this coffee.
Founded in 1974 by Australian businessman Bobby Bobby Gibbs, the estate is named after the adjacent river (Kimel River) and now houses 432 employees, mainly from the Opais tribe. Although the owner is a foreigner, local farmers are responsible for coffee production and manor management. The manor also provides sound educational institutions and medical facilities. The coffee trees in the manor are cultivated in shade, which can not only adjust the temperature but also reduce excessive sunshine, and local farmers also adopt practices that do not burden the environment as far as possible, such as recycling of water conservancy resources and residual berries as fertilizer. There are a wide range of planting products in the manor, from the traditional Tibica and bourbon to the rare Blue Mountain species, making the coffee here more resistant to various diseases and insect pests and natural disasters, stabilizing the quality and bringing more elements to the coffee flavor.

Chimeier Manor has scored a cup over the years.
November 2014 Coffee Review 92
November 2013 Coffee Review 93
What is Little Blue Mountain Coffee?
In 1937, coffee cultivation in Papua New Guinea began with seeds imported from the famous Blue Mountain region of Jamaica. The saplings of Chimel Manor are the Arabica species of Tibica (Typical Arabica) transplanted from native seedlings in Jamaica, which can be called a descendant of the Blue Mountains, also known as "Little Blue Mountain Coffee". The flavor of Little Blue Mountain Coffee is similar to that of authentic Blue Mountain Coffee, but there are some differences. The acidity of Xiaolan Mountain Coffee is more obvious and fuller, not as sour and bitter as authentic Blue Mountain Coffee.
Test report of Coffee Cup in Kimmel Manor
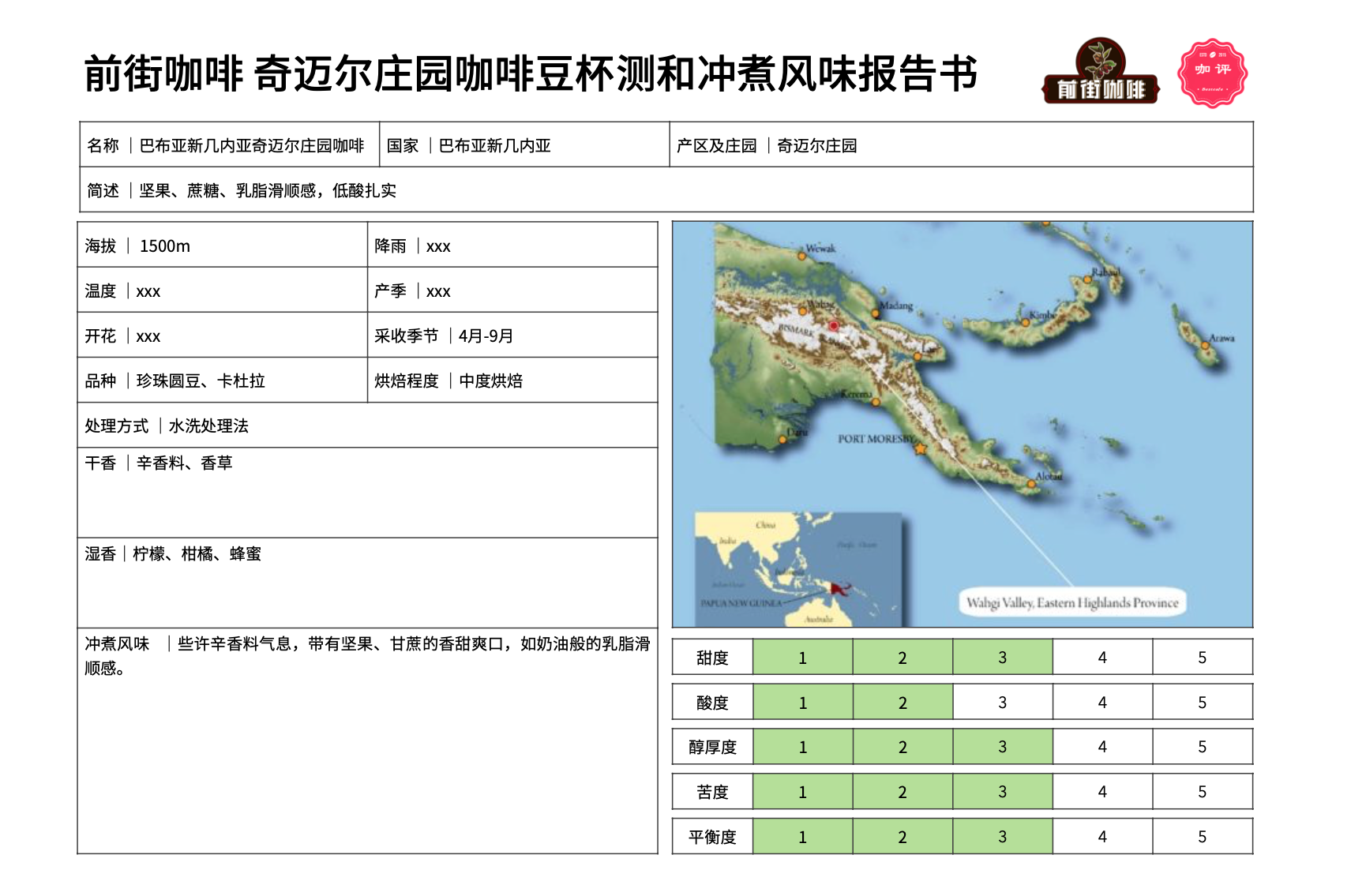
Flavor: the round beans of this Chimeier Manor have a spicy flavor on the palate, with sweet and refreshing notes of nuts and sugar cane after the entrance, such as creamy creamy smoothness. The round beans taste more solid and the overall performance is balanced and smooth. Rich flavor, pleasant aroma, no herbal flavor or soil flavor, its texture is as strong and mellow as a Van Gogh painting.
For more boutique coffee beans, please add private Qianjie coffee on Wechat. WeChat account: kaixinguoguo0925
Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev

What kind of coffee is Mantenin, an alpine panther in Indonesia? what is the advantage of coffee over other mantenins?
Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information Please follow the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) people who love boutique coffee have heard of Manning Coffee, and learn more about Golden Manning, Lin Dong Manning and Tiger Manning. There are so many varieties of Manning, is there any other variety of Manning? The answer is yes! The world of coffee is very
- Next

What is the treatment of Ethiopian boutique coffee beans Humbela Lion 88 coffee?
Professional coffee knowledge exchange more coffee bean information Please pay attention to the coffee workshop (Wechat official account cafe_style) why boutique coffee is loved by so many coffee fans, because different countries have different unique coffee flavor, with fruit, flower, herbal aroma and other aroma, round, smooth, bright and other acidity, resulting in the high status of boutique coffee. Especially
Related
- Detailed explanation of Jadeite planting Land in Panamanian Jadeite Manor introduction to the grading system of Jadeite competitive bidding, Red bid, Green bid and Rose Summer
- Story of Coffee planting in Brenka region of Costa Rica Stonehenge Manor anaerobic heavy honey treatment of flavor mouth
- What's on the barrel of Blue Mountain Coffee beans?
- Can American coffee also pull flowers? How to use hot American style to pull out a good-looking pattern?
- Can you make a cold extract with coffee beans? What is the right proportion for cold-extracted coffee formula?
- Indonesian PWN Gold Mandrine Coffee Origin Features Flavor How to Chong? Mandolin coffee is American.
- A brief introduction to the flavor characteristics of Brazilian yellow bourbon coffee beans
- What is the effect of different water quality on the flavor of cold-extracted coffee? What kind of water is best for brewing coffee?
- Why do you think of Rose Summer whenever you mention Panamanian coffee?
- Introduction to the characteristics of authentic blue mountain coffee bean producing areas? What is the CIB Coffee Authority in Jamaica?

