The influence of Ecuadorian geographical location and climate on coffee grading system of Ecuadorian coffee
About Ecuador
Coffee was introduced to Ecuador in the 19th century. In the 1860s, the first coffee plantations were established on the coast of Manabi province. As one of the most biodiverse countries on Earth, Ecuador's unique ecosystem is ideal for this plant to flourish, and coffee quickly became one of Ecuador's top export commodities.
It was not until the late 1920s, when the cocoa industry was threatened by disease, that coffee became Ecuador's main business. Even then, coffee remained largely an afterthought for the national economy, with coffee production falling sharply during the price crisis of the 1990s. In the early 2000s, Ecuador's economy was primarily based on oil, with less agriculture than in many other coffee-growing countries.
Due to its geographical location, Ecuador's climate varies from region to region, with different temperature and rainfall patterns. Highland areas tend to be mild and cool, with growing production associated with higher northern latitudes, while coastal areas are warm and tropical, with fertile soils. In addition to coffee beans, the country is also known for producing cocoa, bananas, mangoes, citrus fruits, sugar, avocado (from which avocado oil is produced) and rice. Coffee beans are usually grown with other crops.
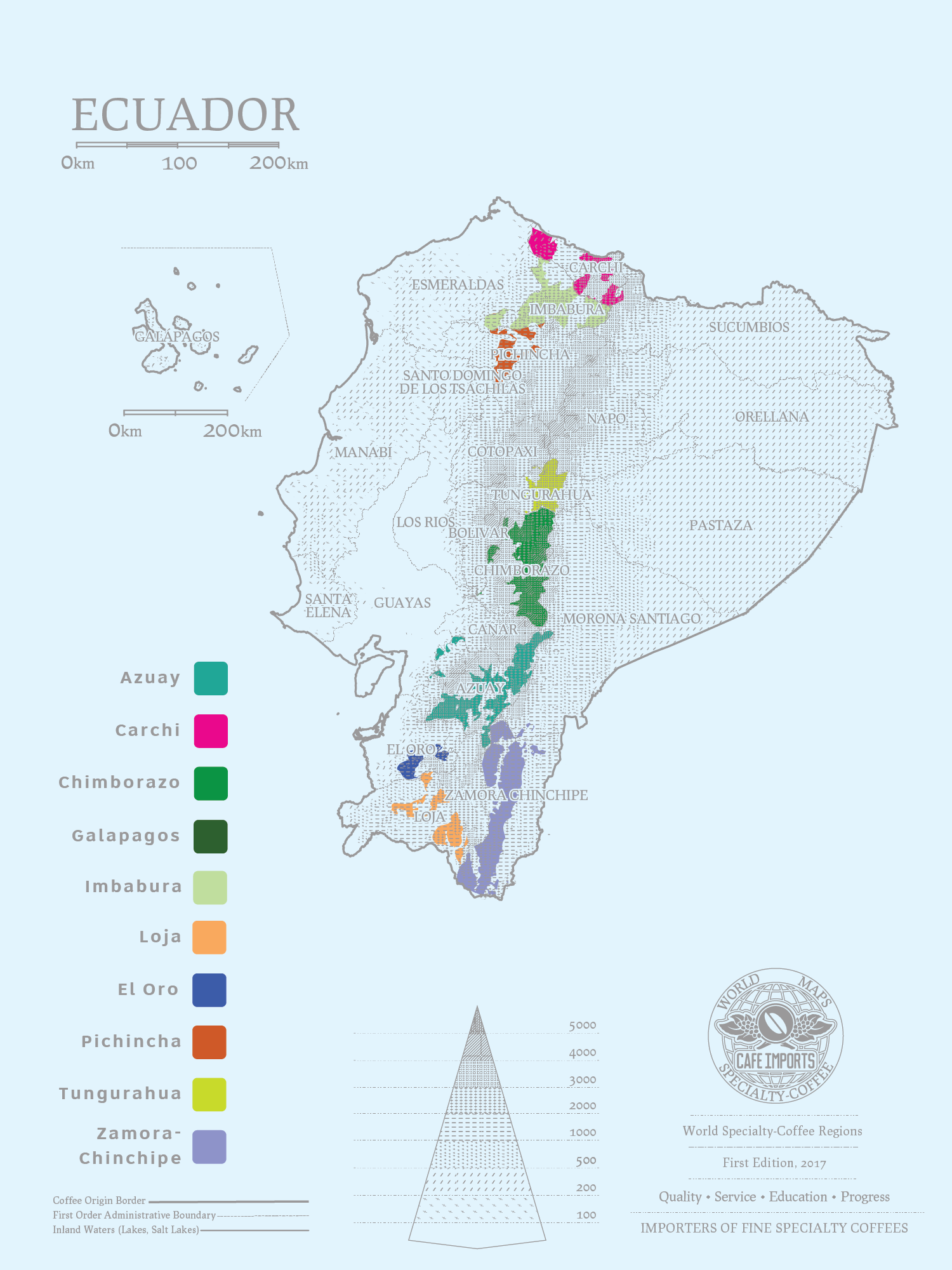
Ecuadorian coffee grading system
Graded cultivation in Ecuador Altitude Grading
Strictly High Bean (SHB): 1300 meters or more.
High Bean (HB): 1220-1300 m.

Important Notice :
前街咖啡 FrontStreet Coffee has moved to new addredd:
FrontStreet Coffee Address: 315,Donghua East Road,GuangZhou
Tel:020 38364473
- Prev
What are the flavor characteristics of Cuzco coffee beans in Peru? introduction to the method of variety treatment in Cuzco coffee producing area
In the southeast, Cusco is 9002000 meters above sea level, and the coffee-growing area is located at the top of the Andes. Most of the varieties of coffee here are Caturra,Bourbon and Typica. Most coffee is grown by small farmers, not by large estates.
- Next
Flavor characteristics of Manawi Coffee Bean
Manabi, the first Ecuadorian province to grow coffee, uses felling and burning to cut down local forests and then burn the remaining stumps and vegetation to grow coffee. Nearly 50% of Ecuador's Arabica coffee beans come from Manawi province, but because almost all of the coffee beans in this area are planted below 700 meters above sea level, there is no place to produce another flying place.
Related
- Beginners will see the "Coffee pull flower" guide!
- What is the difference between ice blog purified milk and ordinary milk coffee?
- Why is the Philippines the largest producer of crops in Liberia?
- For coffee extraction, should the fine powder be retained?
- How does extracted espresso fill pressed powder? How much strength does it take to press the powder?
- How to make jasmine cold extract coffee? Is the jasmine + latte good?
- Will this little toy really make the coffee taste better? How does Lily Drip affect coffee extraction?
- Will the action of slapping the filter cup also affect coffee extraction?
- What's the difference between powder-to-water ratio and powder-to-liquid ratio?
- What is the Ethiopian local species? What does it have to do with Heirloom native species?

